Digital fashion offers innovative ways to personalize and visualize clothing through virtual try-ons and customizable designs, reducing waste and production costs compared to physical garments. Physical garments provide tangible quality, texture, and durability that digital fashion currently cannot replicate, appealing to consumers seeking authentic sensory experiences. Combining digital fashion with traditional apparel enables brands to expand creative boundaries while addressing sustainability challenges in the industry.
Table of Comparison
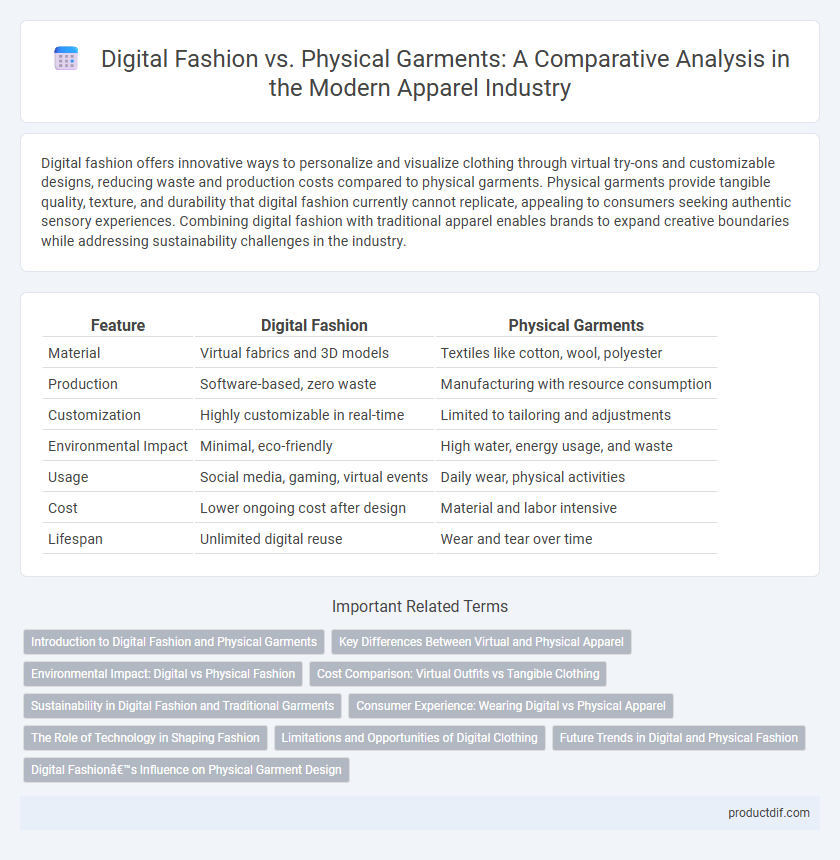
| Feature | Digital Fashion | Physical Garments |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Virtual fabrics and 3D models | Textiles like cotton, wool, polyester |
| Production | Software-based, zero waste | Manufacturing with resource consumption |
| Customization | Highly customizable in real-time | Limited to tailoring and adjustments |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal, eco-friendly | High water, energy usage, and waste |
| Usage | Social media, gaming, virtual events | Daily wear, physical activities |
| Cost | Lower ongoing cost after design | Material and labor intensive |
| Lifespan | Unlimited digital reuse | Wear and tear over time |
Introduction to Digital Fashion and Physical Garments
Digital fashion leverages 3D design technology to create virtual garments that can be worn in online environments or augmented reality platforms. Physical garments involve traditional textile manufacturing processes where fabrics are cut, sewn, and assembled into tangible clothing items. Emerging technologies in digital fashion are reshaping consumer experiences by enabling customization and instant wardrobe changes without environmental impact.
Key Differences Between Virtual and Physical Apparel
Digital fashion offers limitless design possibilities and instant customization, while physical garments require material sourcing, manufacturing, and logistics. Virtual apparel exists solely in digital environments, enabling sustainable consumption by eliminating waste, unlike physical clothing that impacts the environment through production and disposal. The tactile experience and fit accuracy remain exclusive to physical garments, whereas digital fashion thrives in augmented reality and social media integration.
Environmental Impact: Digital vs Physical Fashion
Digital fashion significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for physical materials, water consumption, and waste associated with garment production. Physical garments contribute to pollution through raw material extraction, chemical processing, and textile waste, with the fashion industry accounting for roughly 10% of global carbon emissions. Virtual clothing offers a sustainable alternative by minimizing resource use and lowering the carbon footprint inherent in traditional apparel manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Virtual Outfits vs Tangible Clothing
Virtual outfits in digital fashion offer significantly lower production and distribution costs compared to physical garments due to the elimination of materials, labor, and shipping expenses. Digital clothing requires minimal resources, often just design software and creative input, enabling brands to scale rapidly with reduced financial risk. Physical garments incur ongoing costs for raw materials, manufacturing, inventory management, and retail overhead, making digital fashion a cost-effective alternative in the evolving apparel industry.
Sustainability in Digital Fashion and Traditional Garments
Digital fashion reduces environmental impact by eliminating fabric waste, lowering water consumption, and minimizing carbon emissions compared to traditional garment production. Physical garments involve significant resource use in materials, manufacturing, and transportation, contributing to pollution and landfill accumulation. Embracing digital fashion supports sustainable practices by promoting virtual try-ons, reducing overproduction, and extending lifecycle value through augmented reality applications.
Consumer Experience: Wearing Digital vs Physical Apparel
Wearing digital apparel offers immersive customization and instant style changes through augmented reality, enhancing consumer creativity without physical constraints. Physical garments provide tactile comfort, fabric texture, and a sensory connection that digital fashion cannot replicate, fostering emotional attachment and real-world utility. The evolving consumer experience increasingly blends digital innovation with physical wear, reshaping how apparel is valued and experienced.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Fashion
Digital fashion leverages advanced technologies such as 3D design software, augmented reality, and blockchain to create virtual garments that enhance customization and sustainability, reducing waste associated with traditional production. Physical garments continue to evolve through innovations like smart textiles, wearable tech, and automated manufacturing, improving functionality, durability, and user experience. Technology accelerates the fusion of digital and physical fashion, transforming consumer engagement, supply chains, and industry standards worldwide.
Limitations and Opportunities of Digital Clothing
Digital clothing eliminates physical production costs and environmental waste, offering limitless design possibilities and instant customization. However, it faces challenges in consumer adoption due to lack of tangibility, durability concerns in virtual environments, and limited integration with existing fashion retail models. Opportunities lie in leveraging augmented reality, enhancing virtual try-ons, and creating exclusive digital wardrobes that complement physical apparel collections.
Future Trends in Digital and Physical Fashion
Digital fashion leverages augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to enable personalized, on-demand clothing experiences, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. Physical garments are increasingly integrating smart textiles and wearable technology to enhance functionality and consumer engagement. Future trends indicate a convergence of digital and physical fashion, with hybrid products that combine virtual customization and physical production.
Digital Fashion’s Influence on Physical Garment Design
Digital fashion leverages advanced 3D modeling and virtual try-on technologies, enabling designers to experiment with intricate patterns and innovative textures that inspire new physical garment concepts. This integration accelerates prototyping processes, reducing material waste and cost while enhancing creativity in physical apparel collections. Brands increasingly incorporate digital design insights to create more customized, sustainable, and trend-responsive physical garments.
Digital Fashion vs Physical Garments Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com