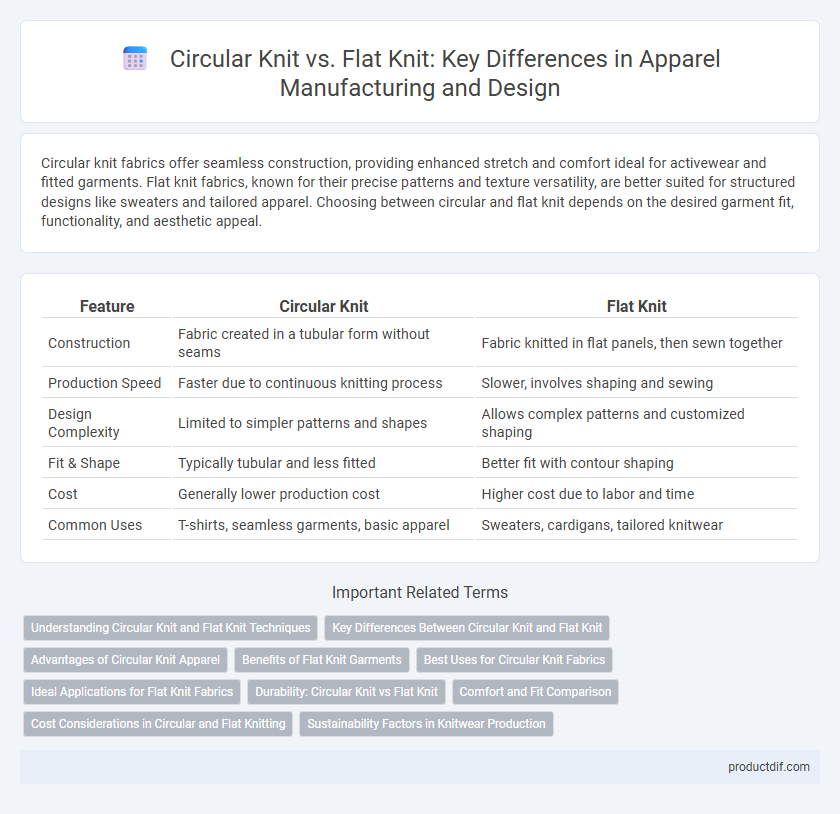
Circular knit fabrics offer seamless construction, providing enhanced stretch and comfort ideal for activewear and fitted garments. Flat knit fabrics, known for their precise patterns and texture versatility, are better suited for structured designs like sweaters and tailored apparel. Choosing between circular and flat knit depends on the desired garment fit, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Circular Knit | Flat Knit |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Fabric created in a tubular form without seams | Fabric knitted in flat panels, then sewn together |
| Production Speed | Faster due to continuous knitting process | Slower, involves shaping and sewing |
| Design Complexity | Limited to simpler patterns and shapes | Allows complex patterns and customized shaping |
| Fit & Shape | Typically tubular and less fitted | Better fit with contour shaping |
| Cost | Generally lower production cost | Higher cost due to labor and time |
| Common Uses | T-shirts, seamless garments, basic apparel | Sweaters, cardigans, tailored knitwear |
Understanding Circular Knit and Flat Knit Techniques
Circular knit fabric is produced using a seamless, tubular knitting process that creates continuous loops, making it ideal for garments like t-shirts and hosiery due to its stretch and comfort. Flat knit fabric is constructed on flat knitting machines, forming individual panels with minimal stretch, providing structured shapes often used in sweaters and tailored apparel. Understanding the distinct machine operations and resulting fabric characteristics helps manufacturers select the appropriate knit technique for specific apparel designs and performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Circular Knit and Flat Knit
Circular knit fabric is produced using a seamless, tubular knitting process ideal for creating stretchy, form-fitting garments like t-shirts and activewear. Flat knit fabric is created on flatbed machines producing panels with seams, commonly used for structured garments such as sweaters and cardigans. The key differences in production method result in variations in fabric stretch, seam presence, and garment shape versatility.
Advantages of Circular Knit Apparel
Circular knit apparel offers superior stretch and flexibility, making it ideal for activewear and form-fitting garments. The seamless construction minimizes irritation and enhances comfort during prolonged wear. Production efficiency is increased with circular knitting machines, resulting in faster turnaround times and reduced fabric waste.
Benefits of Flat Knit Garments
Flat knit garments offer superior fit and structure compared to circular knit, making them ideal for tailored apparel and detailed designs. The flat knitting technique allows for precise shaping and seamless integration of patterns, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal. Fabric produced via flat knitting also tends to be more durable and less prone to distortion, ensuring longer-lasting wear in high-quality apparel.
Best Uses for Circular Knit Fabrics
Circular knit fabrics excel in producing seamless garments such as t-shirts, underwear, and activewear due to their elasticity and smooth texture. These fabrics provide enhanced comfort and fit for body-hugging apparel, making them ideal for sportswear and loungewear applications. Their efficient production process allows for faster manufacturing of tubular shapes without side seams, reducing material waste and improving durability.
Ideal Applications for Flat Knit Fabrics
Flat knit fabrics are ideal for structured garments such as sweaters, cardigans, and tailored outerwear due to their ability to create intricate patterns and maintain shape without curling at the edges. Their construction allows for varied textures and thicknesses, making them suitable for high-quality, detailed designs in fashion and sportswear. Flat knit fabric's stability and versatility cater to applications requiring precision and durability, especially in custom-fit and performance apparel.
Durability: Circular Knit vs Flat Knit
Circular knit fabrics exhibit superior durability due to their continuous loop construction, which reduces seam stress and enhances elasticity. Flat knit fabrics, while offering detailed patterns and structure, often have seams that can weaken over time under mechanical strain. The choice between circular and flat knit impacts the garment's longevity, with circular knits generally providing greater resistance to wear and tear in active apparel.
Comfort and Fit Comparison
Circular knit fabrics offer superior stretch and seamless construction, enhancing overall comfort and allowing garments to move naturally with the body. Flat knit fabrics provide more structure and precision in fit, making them ideal for tailored apparel that requires defined shapes and reduced elasticity. The choice between circular and flat knit directly impacts garment comfort and fit, with circular knits favoring flexibility and flat knits emphasizing contour and support.
Cost Considerations in Circular and Flat Knitting
Circular knit fabrics often offer lower production costs due to faster manufacturing speeds and minimal fabric waste, making them ideal for high-volume apparel items. Flat knitting incurs higher costs because of slower machine operation and increased labor intensity, but it provides greater design versatility and reduces fabric waste for complex patterns. Cost efficiency between circular and flat knitting depends on the balance of production volume, design complexity, and fabric utilization in apparel manufacturing.
Sustainability Factors in Knitwear Production
Circular knit fabrics generate less waste due to their seamless tubular construction, significantly reducing material offcuts compared to flat knit techniques that produce separate panels requiring stitching. Energy consumption in circular knitting machines tends to be lower, promoting eco-friendly manufacturing processes, whereas flat knitting often involves higher resource use during assembly. Both methods offer distinct sustainability advantages, but circular knitting's efficient fabric utilization and minimized waste contribute directly to greener knitwear production.
Circular Knit vs Flat Knit Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com