Reactive dyeing creates vibrant, long-lasting colors by chemically bonding dyes to natural fibers, ensuring excellent colorfastness and softness. Pigment dyeing applies color particles on the fabric surface, offering bold shades but often resulting in a stiffer feel and less durability. Choosing between reactive and pigment dyeing depends on the desired texture, color intensity, and fabric type for the apparel product.
Table of Comparison
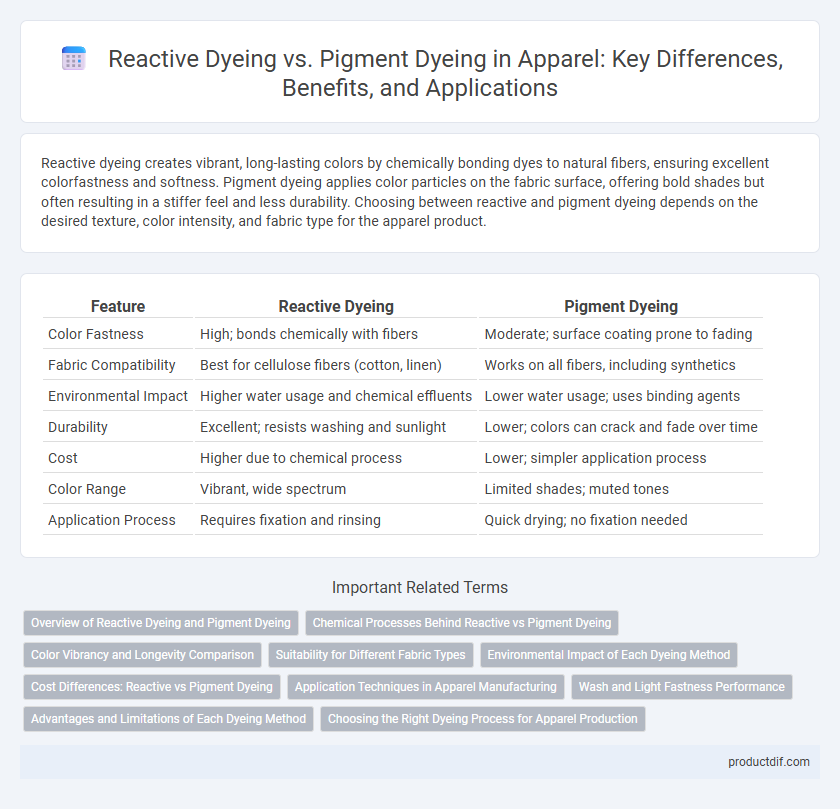
| Feature | Reactive Dyeing | Pigment Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Color Fastness | High; bonds chemically with fibers | Moderate; surface coating prone to fading |
| Fabric Compatibility | Best for cellulose fibers (cotton, linen) | Works on all fibers, including synthetics |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water usage and chemical effluents | Lower water usage; uses binding agents |
| Durability | Excellent; resists washing and sunlight | Lower; colors can crack and fade over time |
| Cost | Higher due to chemical process | Lower; simpler application process |
| Color Range | Vibrant, wide spectrum | Limited shades; muted tones |
| Application Process | Requires fixation and rinsing | Quick drying; no fixation needed |
Overview of Reactive Dyeing and Pigment Dyeing
Reactive dyeing involves chemically bonding dyes to cotton fibers, creating vibrant, long-lasting colors with excellent wash fastness and color retention. Pigment dyeing uses insoluble color pigments applied as a coating on fabric surfaces, resulting in a soft, vintage look but with lower colorfastness and potential fading over time. Reactive dyes are ideal for cellulose fibers requiring durable color, whereas pigment dyes suit varied fabrics for achieving washed or distressed aesthetics.
Chemical Processes Behind Reactive vs Pigment Dyeing
Reactive dyeing involves a chemical reaction between the dye molecules and the fiber, forming a covalent bond that ensures colorfastness and durability, particularly in cellulose fibers like cotton. Pigment dyeing, on the other hand, uses insoluble color particles that adhere to the fabric's surface through a binding agent without chemically bonding, often resulting in less colorfastness but vibrant, textured finishes. The distinct chemical mechanisms dictate the end-use performance and application techniques in textile manufacturing.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity Comparison
Reactive dyeing offers superior color vibrancy and longevity by chemically bonding with fabric fibers, resulting in deep, rich hues that resist fading after multiple washes. Pigment dyeing, while providing a wide range of color options, sits on the fabric surface and tends to fade more quickly under sunlight and washing, leading to less durable coloration. For apparel seeking long-lasting, vivid color, reactive dyes provide a more sustainable and high-quality solution compared to pigment dyes.
Suitability for Different Fabric Types
Reactive dyeing offers excellent color fastness and is especially suitable for natural fibers like cotton and silk, as it forms strong covalent bonds with the fabric. Pigment dyeing is more versatile, applicable to a wider range of fabrics including synthetics like polyester, but typically sits on the fabric surface, resulting in less durability. Choosing between reactive and pigment dyeing depends on the fiber composition and desired longevity of color in apparel.
Environmental Impact of Each Dyeing Method
Reactive dyeing utilizes water-soluble dyes that chemically bond with fibers, resulting in vibrant colors but often requiring large volumes of water and producing substantial wastewater with residual chemicals. Pigment dyeing applies color particles that adhere to the fabric surface without chemical bonding, consuming less water and generating minimal effluents, yet it may lead to reduced colorfastness and increased use of synthetic binders. Environmental impact assessments highlight that pigment dyeing generally offers lower water pollution and energy consumption compared to reactive dyeing, though trade-offs in fabric quality and durability should be considered.
Cost Differences: Reactive vs Pigment Dyeing
Reactive dyeing typically incurs higher costs due to the need for longer processing times, complex chemical use, and water-intensive washing steps to fix colors on fibers, especially cotton. Pigment dyeing offers a more cost-effective alternative by applying color on fabric surfaces with minimal water and energy consumption, reducing overall production expenses. Brands often select pigment dyeing for budget-sensitive collections because of its lower operational costs despite potential compromises in colorfastness compared to reactive dyeing.
Application Techniques in Apparel Manufacturing
Reactive dyeing uses a chemical reaction to bond dye molecules with natural fibers like cotton, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors ideal for high-quality apparel manufacturing. Pigment dyeing applies colorants that adhere to the fabric surface via binders, suitable for synthetic fibers and offering a more versatile, cost-effective method often used in denim and casual wear production. Both techniques require specific application equipment: reactive dyeing involves precise temperature and pH control in padding or exhaust processes, while pigment dyeing typically uses spraying or immersion followed by curing to fix the pigment.
Wash and Light Fastness Performance
Reactive dyeing delivers superior wash fastness by chemically bonding dyes with fiber molecules, ensuring vibrant colors that resist fading through multiple laundry cycles. Pigment dyeing relies on a surface coating that offers moderate light fastness but typically exhibits lower wash fastness due to dye particles being prone to abrasion and washing off. Textile manufacturers prioritize reactive dyeing for apparel demanding long-lasting color retention, while pigment dyeing suits items where soft hand feel and a vintage look outweigh durability concerns.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Dyeing Method
Reactive dyeing offers vibrant, long-lasting colors with excellent colorfastness and is ideal for cotton and cellulose fibers, but it requires precise control of water chemistry and consumes more water and energy. Pigment dyeing provides versatility across various fabric types and quick processing with less environmental impact, yet results in colors that are less durable, prone to fading and washing out over time. The choice between these methods depends on desired fabric characteristics, production costs, and sustainability goals in apparel manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Process for Apparel Production
Choosing the right dyeing process for apparel production depends on factors like fabric type, desired colorfastness, and production scale. Reactive dyeing excels with natural fibers such as cotton, offering vibrant colors and excellent wash durability, while pigment dyeing is versatile across fabric blends and delivers unique faded, vintage effects but with less color penetration. Evaluating cost efficiency, environmental impact, and end-use performance ensures optimal selection between reactive and pigment dyeing methods.
Reactive Dyeing vs Pigment Dyeing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com