Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) deliver faster gear shifts and improved acceleration by using two separate clutches for odd and even gears, enhancing driving performance and efficiency. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) provide seamless acceleration without gear steps, optimizing fuel economy and smoothness, especially in urban driving conditions. Choosing between DCT and CVT depends on the preference for sporty responsiveness versus comfort and efficiency in a vehicle pet's driving experience.
Table of Comparison
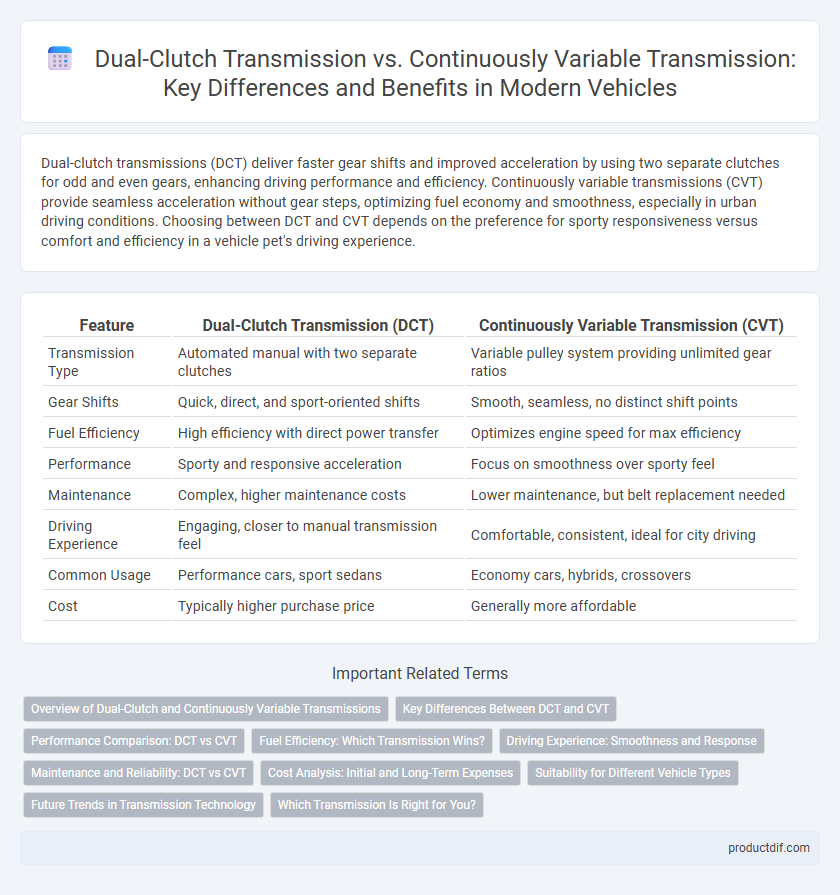
| Feature | Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) | Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Type | Automated manual with two separate clutches | Variable pulley system providing unlimited gear ratios |
| Gear Shifts | Quick, direct, and sport-oriented shifts | Smooth, seamless, no distinct shift points |
| Fuel Efficiency | High efficiency with direct power transfer | Optimizes engine speed for max efficiency |
| Performance | Sporty and responsive acceleration | Focus on smoothness over sporty feel |
| Maintenance | Complex, higher maintenance costs | Lower maintenance, but belt replacement needed |
| Driving Experience | Engaging, closer to manual transmission feel | Comfortable, consistent, ideal for city driving |
| Common Usage | Performance cars, sport sedans | Economy cars, hybrids, crossovers |
| Cost | Typically higher purchase price | Generally more affordable |
Overview of Dual-Clutch and Continuously Variable Transmissions
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) use two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling faster and more efficient gear shifts compared to traditional automatics. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) employ a system of pulleys and belts to provide an infinite range of gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration. Both transmission types aim to enhance vehicle performance, with DCT offering sportier driving dynamics and CVT focusing on seamless power delivery.
Key Differences Between DCT and CVT
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) provide faster gear shifts and improved fuel efficiency through two separate clutches managing odd and even gears, enhancing performance and driving dynamics. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) offer seamless acceleration without fixed gear ratios by using a belt and pulley system, optimizing engine efficiency under varying driving conditions. Key differences include DCT's mechanical complexity and sporty feel versus CVT's smooth operation and better adaptability to varying speeds.
Performance Comparison: DCT vs CVT
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) offer faster and more precise gear shifts, providing superior acceleration and a sportier driving experience compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT), which prioritize smoothness and fuel efficiency through seamless gear ratio changes. DCT systems typically deliver higher torque capacity and better power transfer, making them ideal for performance-oriented vehicles, while CVTs excel in optimizing engine speed for fuel economy during steady driving conditions. Overall, DCTs enhance driving dynamics with minimal power loss, whereas CVTs focus on consistent performance and lower emissions.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Transmission Wins?
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) deliver superior fuel efficiency by combining the efficiency of manual gear shifting with automated control, reducing power loss during gear changes. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) optimize engine performance by maintaining constant RPM, enhancing fuel economy in city driving conditions. DCTs generally outperform CVTs in fuel efficiency for highway and dynamic driving due to quicker gear changes and reduced internal friction.
Driving Experience: Smoothness and Response
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) deliver rapid gear shifts with minimal power loss, enhancing acceleration and providing a sporty, responsive driving feel. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) offer seamless, stepless acceleration that maximizes smoothness by eliminating traditional gear changes, resulting in a consistently refined ride. While DCTs cater to drivers seeking sharp responsiveness and performance, CVTs prioritize fluidity and fuel efficiency for everyday comfort.
Maintenance and Reliability: DCT vs CVT
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) typically require less frequent maintenance due to their robust clutch components and sealed hydraulic systems, offering higher reliability for performance-oriented vehicles. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) demand more regular fluid changes and careful monitoring of belt or chain wear to prevent slipping and overheating, which can compromise longevity. Overall, DCTs deliver greater durability and consistent shifting performance, while CVTs prioritize smooth operation but may incur higher maintenance costs over time.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) typically have higher initial costs due to their complex design and advanced technology compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT), which are generally more affordable upfront. Over the long term, DCTs may incur higher maintenance and repair expenses because of their intricate clutch mechanisms, while CVTs, although cheaper to maintain, can face higher replacement costs due to belt or pulley wear. Evaluating total ownership costs requires considering vehicle usage, driving habits, and manufacturer reliability ratings for both transmission types.
Suitability for Different Vehicle Types
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) provide rapid gear shifts and high efficiency, making them ideal for performance vehicles and sporty sedans seeking precise control and responsive acceleration. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) offer seamless acceleration and superior fuel economy, better suited for compact cars, hybrids, and urban commuters prioritizing smooth driving and efficiency. SUVs and trucks benefit more from DCT when requiring quicker power delivery, while CVT is typically preferred in smaller, lighter vehicles for optimized fuel consumption.
Future Trends in Transmission Technology
Dual-clutch transmission (DCT) and continuously variable transmission (CVT) technologies are evolving with a focus on improving fuel efficiency, performance, and driver experience in electric and hybrid vehicles. Future trends include integration of advanced software for adaptive gear shifting in DCTs and enhanced CVTs with wider ratio ranges and reduced friction to maximize power delivery and energy savings. Innovations in materials and real-time data analytics are expected to further optimize transmission systems for autonomous and connected vehicles.
Which Transmission Is Right for You?
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) offer rapid gear shifts and sportier performance ideal for drivers seeking precise control and quick acceleration. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) provide smooth, seamless acceleration with improved fuel efficiency, making them better suited for daily commuting and fuel-conscious drivers. Choosing between DCT and CVT depends on your driving style and priorities, with DCT favored for dynamic driving and CVT for comfort and economy.
Dual-clutch transmission vs Continuously variable transmission Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com