Swappable batteries offer the advantage of quick replacement, minimizing downtime and extending vehicle usability, especially in electric vehicles. Fixed batteries provide a more compact design and structural rigidity, often resulting in better energy density and overall vehicle stability. Choosing between swappable and fixed battery systems depends on factors like convenience, cost, and vehicle application.
Table of Comparison
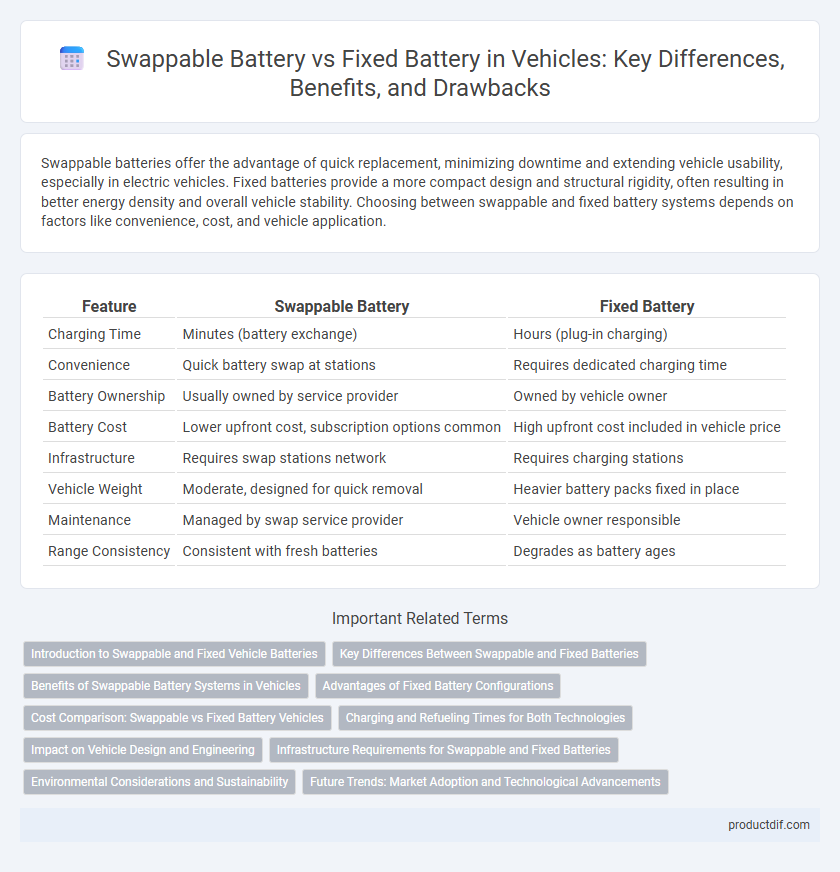
| Feature | Swappable Battery | Fixed Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | Minutes (battery exchange) | Hours (plug-in charging) |
| Convenience | Quick battery swap at stations | Requires dedicated charging time |
| Battery Ownership | Usually owned by service provider | Owned by vehicle owner |
| Battery Cost | Lower upfront cost, subscription options common | High upfront cost included in vehicle price |
| Infrastructure | Requires swap stations network | Requires charging stations |
| Vehicle Weight | Moderate, designed for quick removal | Heavier battery packs fixed in place |
| Maintenance | Managed by swap service provider | Vehicle owner responsible |
| Range Consistency | Consistent with fresh batteries | Degrades as battery ages |
Introduction to Swappable and Fixed Vehicle Batteries
Swappable vehicle batteries enable quick replacement of depleted packs with fully charged ones, significantly reducing downtime during trips. Fixed batteries are integrated into the vehicle's chassis, offering a more compact design and typically longer lifespan due to fewer handling risks. Innovations in swappable battery systems aim to standardize battery sizes and connections, improving convenience and promoting faster adoption of electric vehicles.
Key Differences Between Swappable and Fixed Batteries
Swappable batteries enable quick replacement at designated stations, reducing downtime and extending the vehicle's operational range, while fixed batteries require longer charging periods and remain integrated within the vehicle. Swappable systems promote modularity and scalability, allowing standardized battery packs across different models and brands, whereas fixed batteries offer higher structural rigidity and optimized energy density tailored to specific vehicles. Maintenance and lifecycle management differ significantly; swappable batteries are maintained independently, facilitating battery reuse and recycling, while fixed batteries necessitate in-vehicle servicing and eventual disposal.
Benefits of Swappable Battery Systems in Vehicles
Swappable battery systems in vehicles offer rapid energy replenishment, drastically reducing downtime compared to fixed battery charging. These systems enhance vehicle lifecycle sustainability by allowing battery upgrades without replacing the entire vehicle, lowering long-term costs. Improved flexibility supports diverse use cases such as commercial fleets and electric taxis by enabling continuous operation through quick battery exchanges.
Advantages of Fixed Battery Configurations
Fixed battery configurations in vehicles provide superior structural integrity and weight distribution, enhancing overall safety and handling performance. They offer prolonged lifespan and reliability due to sealed designs that minimize exposure to environmental factors and reduce maintenance needs. Fixed batteries also optimize energy density and integration, enabling longer driving ranges and streamlined vehicle architecture.
Cost Comparison: Swappable vs Fixed Battery Vehicles
Swappable battery vehicles generally have higher initial infrastructure costs due to the need for battery swapping stations, but they can reduce long-term expenses by minimizing downtime and extending battery life through shared usage. Fixed battery vehicles often incur lower upfront costs but face higher maintenance and replacement expenses as the battery ages and degrades. Overall, the total cost of ownership depends on factors such as mileage, battery lifetime, and energy prices, with swappable battery systems offering potential savings in fleet and high-usage scenarios.
Charging and Refueling Times for Both Technologies
Swappable batteries enable rapid vehicle turnaround with replacement times often under five minutes, significantly reducing downtime compared to fixed batteries that require charging durations ranging from 30 minutes with fast chargers to several hours on standard chargers. Fixed batteries provide convenience through widespread charging infrastructure but struggle with long refueling times that impact overall vehicle usage and efficiency. Swappable battery systems also support standardized charging processes, enhancing operational reliability in commercial and urban transport sectors.
Impact on Vehicle Design and Engineering
Swappable batteries enable modular vehicle architectures by allowing quick removal and replacement, reducing downtime and enhancing user convenience while necessitating standardized battery shapes and secure locking mechanisms in design. Fixed batteries allow for optimized integration within the chassis, improving structural rigidity, safety, and overall weight distribution but require sophisticated thermal management systems and can increase vehicle weight. Engineering trade-offs revolve around balancing ease of maintenance with vehicle performance, safety standards, and manufacturing complexity.
Infrastructure Requirements for Swappable and Fixed Batteries
Swappable batteries require a robust network of exchange stations equipped with standardized connectors and automated systems to enable quick battery swapping, reducing vehicle downtime significantly. Fixed batteries demand widespread charging infrastructure with high-capacity chargers capable of handling prolonged use and various charging speeds, ensuring accessible and reliable recharging options. The scalability and location of swappable stations involve higher upfront investment but facilitate faster turnaround times compared to the more flexible and dispersed charging points for fixed batteries.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Swappable battery systems reduce electronic waste by extending the lifecycle of batteries through reuse across multiple vehicles, minimizing the need for new battery production. Fixed batteries often lead to higher resource consumption and disposal challenges due to shorter lifespan and complex recycling processes. Implementing swappable battery technology supports environmental sustainability by promoting circular economy practices and lowering the carbon footprint of electric vehicles.
Future Trends: Market Adoption and Technological Advancements
Swappable battery systems are gaining momentum in urban mobility markets due to faster recharge times and reduced downtime compared to fixed batteries, driving higher consumer adoption in electric scooters and bikes. Technological advancements in modular battery design and smart battery management systems enhance the efficiency and safety of swappable batteries, making them more viable for large-scale deployment. Future market trends indicate increasing investments in standardized swappable battery infrastructure, supporting seamless interoperability across vehicle brands and facilitating mass adoption in shared and commercial electric vehicle fleets.
Swappable Battery vs Fixed Battery Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com