Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, offering improved fuel efficiency and increased power by optimizing the air-fuel mixture. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, promoting better mixing with air and reducing carbon buildup on intake valves. Vehicles equipped with combined direct and port injection systems benefit from enhanced performance, lower emissions, and improved fuel economy under various driving conditions.
Table of Comparison
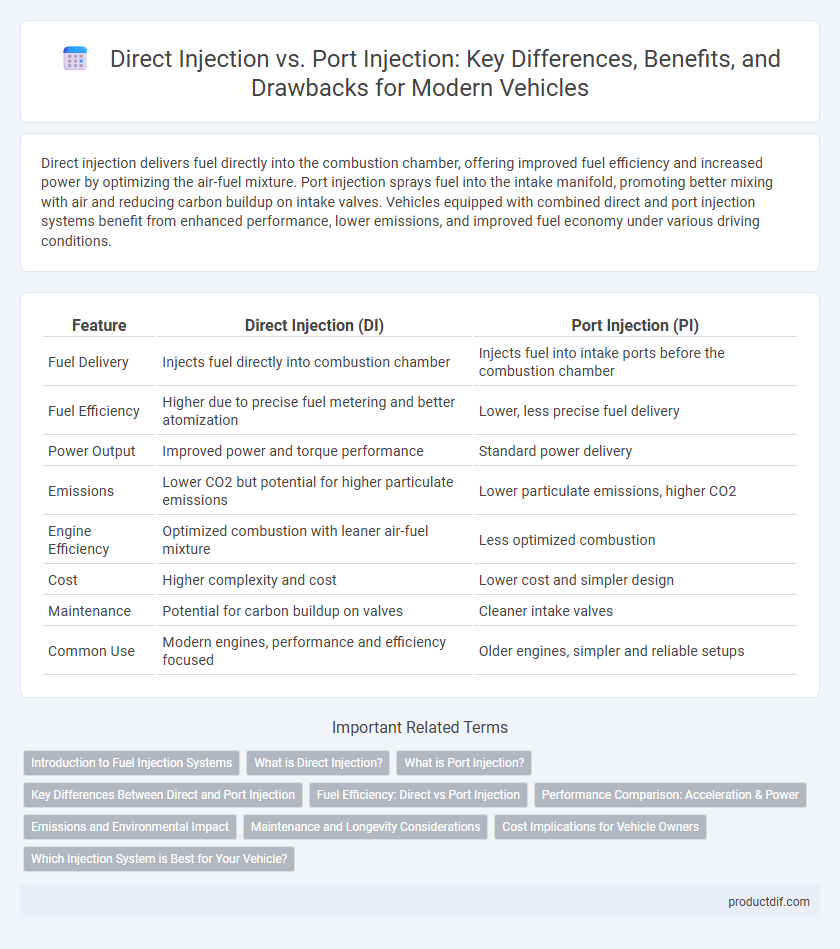
| Feature | Direct Injection (DI) | Port Injection (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Injects fuel directly into combustion chamber | Injects fuel into intake ports before the combustion chamber |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher due to precise fuel metering and better atomization | Lower, less precise fuel delivery |
| Power Output | Improved power and torque performance | Standard power delivery |
| Emissions | Lower CO2 but potential for higher particulate emissions | Lower particulate emissions, higher CO2 |
| Engine Efficiency | Optimized combustion with leaner air-fuel mixture | Less optimized combustion |
| Cost | Higher complexity and cost | Lower cost and simpler design |
| Maintenance | Potential for carbon buildup on valves | Cleaner intake valves |
| Common Use | Modern engines, performance and efficiency focused | Older engines, simpler and reliable setups |
Introduction to Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injection systems play a crucial role in optimizing engine performance and efficiency by controlling the precise delivery of fuel into the combustion chamber. Direct injection sprays fuel directly into the cylinder, improving fuel atomization and combustion control, while port injection delivers fuel into the intake manifold, enhancing air-fuel mixing before entering the cylinder. Both systems aim to maximize power output and reduce emissions, with direct injection offering better fuel efficiency and port injection providing smoother engine operation.
What is Direct Injection?
Direct Injection is a fuel delivery system where fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber of each cylinder, allowing for precise control of the air-fuel mixture. This method improves engine efficiency, increases power output, and reduces emissions compared to traditional Port Injection, which injects fuel into the intake manifold before the combustion chamber. Modern gasoline engines increasingly adopt Direct Injection technology to optimize performance and fuel economy.
What is Port Injection?
Port injection is a fuel delivery system where fuel is injected directly into the intake ports just before the intake valve in an internal combustion engine. This method allows precise fuel metering, improved air-fuel mixing, and reduced emissions compared to carbureted engines. Port injection systems are commonly used in gasoline engines to enhance throttle response and fuel efficiency.
Key Differences Between Direct and Port Injection
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing combustion efficiency and power output, while port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, promoting better fuel-air mixing before combustion. Direct injection offers improved fuel atomization and allows higher compression ratios, increasing engine performance and reducing emissions, whereas port injection systems are simpler and often provide more consistent fuel delivery at lower engine loads. The choice between direct and port injection impacts engine responsiveness, fuel economy, and maintenance complexity, with many modern vehicles employing combined systems to optimize benefits.
Fuel Efficiency: Direct vs Port Injection
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, improving fuel atomization and combustion efficiency, which typically enhances fuel economy compared to port injection. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, promoting better air-fuel mixing before entering the cylinder but often results in slightly lower fuel efficiency. Studies show direct injection engines can achieve up to 10-15% better fuel efficiency under certain driving conditions due to more precise fuel delivery and reduced pumping losses.
Performance Comparison: Acceleration & Power
Direct injection systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enabling more precise fuel metering and improved combustion efficiency, which results in higher horsepower and torque. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, promoting better air-fuel mixing at lower engine speeds, enhancing throttle response and smoother acceleration. Vehicles with direct injection typically achieve faster acceleration and increased power output due to optimized combustion and reduced fuel wastage.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Direct Injection engines improve fuel atomization, resulting in more efficient combustion and reduced CO2 emissions compared to Port Injection systems. However, Direct Injection tends to produce higher particulate matter and NOx emissions, requiring advanced after-treatment technologies like particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction for compliance with environmental standards. Port Injection engines generally emit fewer particulates due to better fuel-air mixing, making them advantageous in urban areas with stringent air quality regulations.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Direct injection engines often require more frequent maintenance due to carbon buildup on intake valves, which can affect performance and longevity if left unchecked. Port injection systems tend to have fewer issues with carbon deposits, resulting in potentially lower maintenance costs and improved engine lifespan. Regular fuel system cleaning and using high-quality fuels can enhance the durability of both injection types.
Cost Implications for Vehicle Owners
Direct injection systems typically cost more to maintain due to higher fuel system complexity and potential for carbon buildup, leading to increased cleaning expenses. Port injection engines generally have lower maintenance costs and longer intervals between servicing because they inject fuel before the intake valve, reducing buildup risks. Vehicle owners should weigh initial savings against potential future repair costs when choosing between direct injection and port injection technologies.
Which Injection System is Best for Your Vehicle?
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel efficiency and power output by improving atomization and combustion precision. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, promoting better mixing with air and reducing carbon buildup on intake valves, which benefits engine longevity. Selecting the best injection system depends on your vehicle's performance needs, fuel economy goals, and maintenance preferences, with direct injection favored for high-performance applications and port injection preferred for durability and cleaner intake systems.
Direct Injection vs Port Injection Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com