Twin-turbo systems use two turbochargers to increase engine power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, improving high-end performance and reducing turbo lag compared to single turbos. Superchargers provide immediate throttle response as they are mechanically driven by the engine, making them ideal for low-end torque and consistent power delivery. Choosing between twin-turbo and supercharged setups depends on the desired power curve, with twin-turbos favoring higher RPM efficiency and superchargers excelling in instant acceleration.
Table of Comparison
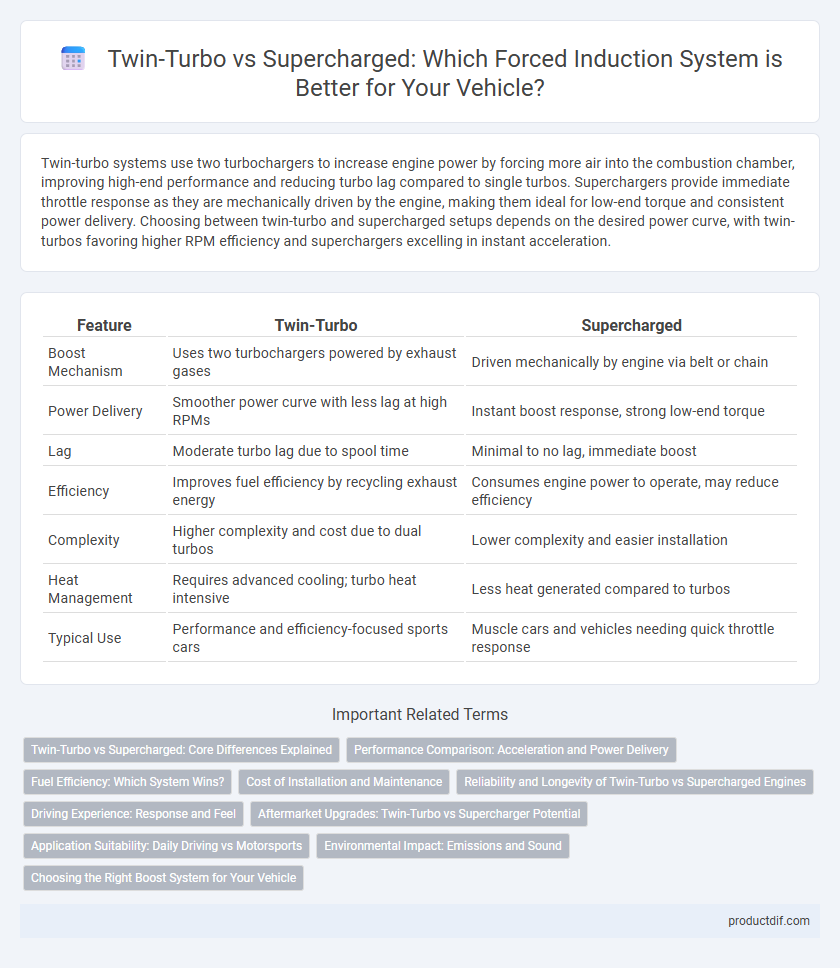
| Feature | Twin-Turbo | Supercharged |
|---|---|---|
| Boost Mechanism | Uses two turbochargers powered by exhaust gases | Driven mechanically by engine via belt or chain |
| Power Delivery | Smoother power curve with less lag at high RPMs | Instant boost response, strong low-end torque |
| Lag | Moderate turbo lag due to spool time | Minimal to no lag, immediate boost |
| Efficiency | Improves fuel efficiency by recycling exhaust energy | Consumes engine power to operate, may reduce efficiency |
| Complexity | Higher complexity and cost due to dual turbos | Lower complexity and easier installation |
| Heat Management | Requires advanced cooling; turbo heat intensive | Less heat generated compared to turbos |
| Typical Use | Performance and efficiency-focused sports cars | Muscle cars and vehicles needing quick throttle response |
Twin-Turbo vs Supercharged: Core Differences Explained
Twin-turbo systems use two turbochargers to reduce turbo lag and improve power delivery across a wider RPM range, while superchargers provide immediate boost since they are belt-driven and directly linked to engine speed. Twin-turbos are generally more efficient and deliver higher peak power, optimizing performance for sports and high-performance vehicles. Superchargers offer consistent low-end torque and simpler installation but can decrease fuel efficiency due to their mechanical load on the engine.
Performance Comparison: Acceleration and Power Delivery
Twin-turbo systems provide superior acceleration through sequential turbochargers that minimize lag and maximize power across a wide RPM range, delivering a more responsive throttle feel. Superchargers offer immediate power delivery due to their mechanically driven design, ensuring consistent boost at low engine speeds but often sacrificing top-end power efficiency. Twin-turbos excel in high-performance applications requiring dynamic power curves, while superchargers are favored for instant torque and smooth power transitions.
Fuel Efficiency: Which System Wins?
Twin-turbo systems typically offer better fuel efficiency by using two smaller turbochargers that spool faster and reduce turbo lag, optimizing air intake and combustion. Supercharged engines provide immediate power delivery but rely on belt-driven compressors that consume engine power, leading to lower fuel economy. Vehicles equipped with twin-turbo setups often achieve improved miles per gallon (MPG) compared to their supercharged counterparts, making them a preferred choice for performance-oriented yet fuel-efficient driving.
Cost of Installation and Maintenance
Twin-turbo systems generally have higher installation costs due to complex plumbing and electronic controls, often exceeding $3,000, while superchargers are simpler to install with costs typically ranging from $1,500 to $2,500. Maintenance expenses for twin-turbos can be more frequent and costly because of the increased wear on turbochargers and intercoolers, whereas superchargers usually require less maintenance, primarily involving belt replacements and occasional oil changes. Both systems impact long-term operating costs, but superchargers tend to be more budget-friendly for installation and upkeep in most vehicle applications.
Reliability and Longevity of Twin-Turbo vs Supercharged Engines
Twin-turbocharged engines generally offer better reliability and longevity compared to supercharged engines due to lower mechanical stress and improved heat management, as turbochargers use exhaust gases rather than direct engine power. Superchargers place additional load on the engine crankshaft, potentially increasing wear and reducing overall engine lifespan. Maintenance practices and build quality impact durability, but twin-turbos typically achieve longer service intervals and fewer mechanical failures under similar driving conditions.
Driving Experience: Response and Feel
Twin-turbo systems deliver rapid, sequential boost that minimizes turbo lag, providing smooth acceleration and enhanced throttle response for a dynamic driving experience. Supercharged engines offer immediate power delivery due to their direct belt-driven connection, resulting in a consistently strong and linear feel throughout the rev range. Drivers often prefer twin-turbos for high-speed performance and efficiency, while superchargers excel in low-end torque and instant throttle feedback.
Aftermarket Upgrades: Twin-Turbo vs Supercharger Potential
Twin-turbo systems offer greater potential for high horsepower gains and improved efficiency through sequential boost control, making them ideal for performance-focused aftermarket upgrades. Superchargers provide immediate, consistent power delivery with less lag, enhancing throttle response and drivability in street applications. Choosing between them depends on the desired balance of peak power, response time, and installation complexity in aftermarket vehicle enhancements.
Application Suitability: Daily Driving vs Motorsports
Twin-turbo systems provide optimized power delivery and improved fuel efficiency, making them ideal for daily driving by balancing performance and economy. Superchargers offer immediate throttle response and consistent boost across the RPM range, which benefits motorsports requiring rapid acceleration and sustained power. Vehicle enthusiasts should consider twin-turbo setups for smoother street performance, while superchargers excel in track environments demanding instant power.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sound
Twin-turbo systems generally produce lower emissions compared to superchargers due to their more efficient air intake and reduced parasitic loss on the engine. Superchargers, driven mechanically by the engine, often increase fuel consumption and result in higher CO2 emissions. Sound levels from twin-turbo setups are typically quieter and more refined, while superchargers emit a louder, more pronounced whine that can contribute to noise pollution.
Choosing the Right Boost System for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right boost system depends on your vehicle's performance goals and driving style. Twin-turbo setups offer improved high-end power and better turbo lag management, ideal for sports cars and high-performance applications. Superchargers provide instant throttle response and consistent power delivery, making them suitable for daily driving and applications requiring low-end torque.
Twin-Turbo vs Supercharged Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com