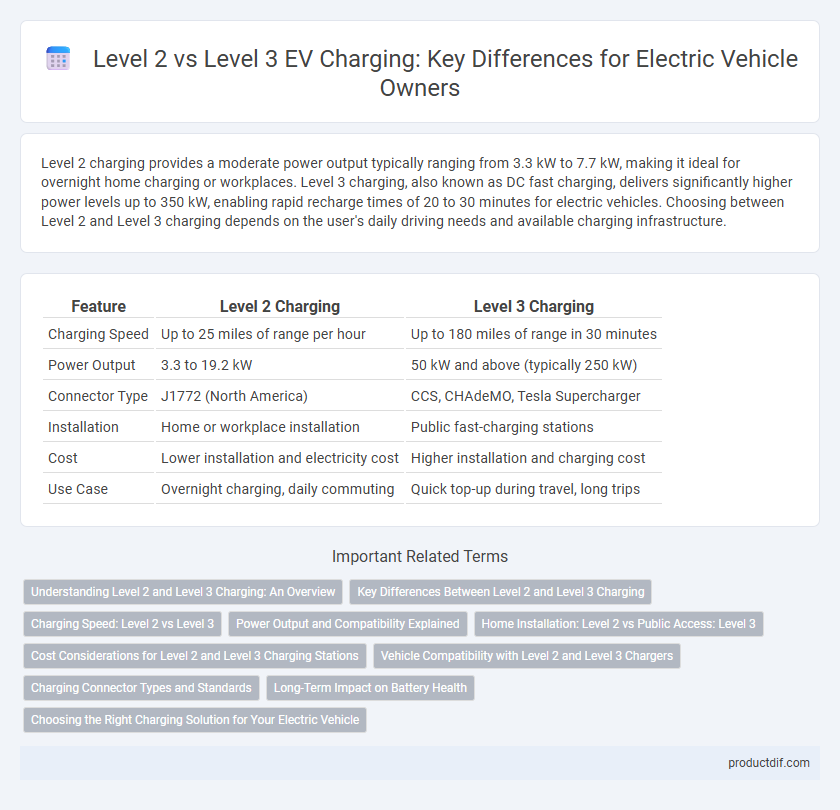
Level 2 charging provides a moderate power output typically ranging from 3.3 kW to 7.7 kW, making it ideal for overnight home charging or workplaces. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, delivers significantly higher power levels up to 350 kW, enabling rapid recharge times of 20 to 30 minutes for electric vehicles. Choosing between Level 2 and Level 3 charging depends on the user's daily driving needs and available charging infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Level 2 Charging | Level 3 Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Up to 25 miles of range per hour | Up to 180 miles of range in 30 minutes |
| Power Output | 3.3 to 19.2 kW | 50 kW and above (typically 250 kW) |
| Connector Type | J1772 (North America) | CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger |
| Installation | Home or workplace installation | Public fast-charging stations |
| Cost | Lower installation and electricity cost | Higher installation and charging cost |
| Use Case | Overnight charging, daily commuting | Quick top-up during travel, long trips |
Understanding Level 2 and Level 3 Charging: An Overview
Level 2 charging delivers AC power at 240 volts, typically providing 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, making it ideal for home and workplace use with moderate charging times. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, supplies high-voltage direct current, offering 60 to 100 miles of range in just 20 minutes, which significantly reduces charging time for electric vehicles on long trips. Understanding the differences in power output, charging speed, and infrastructure helps drivers choose the appropriate charging method based on their daily needs and travel patterns.
Key Differences Between Level 2 and Level 3 Charging
Level 2 charging provides 240 volts and typically delivers 10 to 25 miles of range per hour, making it ideal for overnight home charging. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, offers 400 volts or higher and can add up to 200 miles of range in about 30 minutes, designed for quick public charging stops. The key differences lie in voltage, charging speed, and infrastructure availability, with Level 3 chargers requiring more power and specialized equipment.
Charging Speed: Level 2 vs Level 3
Level 2 charging delivers an average power output of 3.3 to 7.7 kW, typically providing about 10 to 30 miles of range per hour of charging, suitable for overnight or extended parking periods. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, offers rapid power levels ranging from 50 kW up to 350 kW, enabling an 80% charge in as little as 20 to 40 minutes, ideal for quick top-ups on long trips. The significant difference in charging speed makes Level 3 chargers essential for reducing downtime and supporting long-distance electric vehicle travel.
Power Output and Compatibility Explained
Level 2 charging delivers power output typically ranging from 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW, suitable for residential and workplace use with compatibility across most electric vehicles (EVs). Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, offers significantly higher power output from 50 kW to 350 kW, enabling much faster charging times primarily for compatible EVs with rapid charging capabilities. Compatibility depends on the vehicle's onboard charger and connector type, with Level 3 chargers requiring specialized ports like CCS or CHAdeMO.
Home Installation: Level 2 vs Public Access: Level 3
Level 2 charging stations, commonly installed at home, provide a balance between charge speed and electrical requirements, typically delivering 240 volts and adding about 25 miles of range per hour. Level 3 charging, or DC fast charging, found mainly in public locations, operates at much higher power levels up to 350 kW, allowing electric vehicles to gain 80% battery capacity in 20-30 minutes. Home installation of Level 3 chargers is often impractical due to high costs, complex electrical infrastructure needs, and limited residential grid capacity.
Cost Considerations for Level 2 and Level 3 Charging Stations
Level 2 charging stations typically cost between $500 and $2,000 for installation, making them a more affordable option for home and small business use compared to Level 3 chargers, which often require investments exceeding $30,000 due to advanced technology and higher power output. Operating expenses for Level 3 chargers are also higher, as they demand substantial electrical infrastructure upgrades and increased energy consumption, impacting the total cost of ownership. While Level 3 charging stations offer rapid charging speeds up to 350 kW, their elevated installation and maintenance costs necessitate thorough cost-benefit analysis for commercial deployment.
Vehicle Compatibility with Level 2 and Level 3 Chargers
Level 2 charging is compatible with most electric vehicles (EVs) as it uses a standardized J1772 connector, offering charging speeds typically between 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW suitable for overnight home or workplace charging. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, requires vehicles equipped with high-voltage battery systems and proprietary connectors like CCS, CHAdeMO, or Tesla Supercharger, enabling rapid charging up to 350 kW mostly at public charging stations. Compatibility depends on the EV model's onboard charging system and battery architecture, making Level 3 chargers ideal for quick top-ups during long-distance travel.
Charging Connector Types and Standards
Level 2 vehicle charging primarily uses the SAE J1772 connector standard in North America, providing 240 volts AC for home or public charging stations with power outputs ranging from 3.3 to 19.2 kW. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, employs various connector standards such as CCS (Combined Charging System) for most electric vehicles, CHAdeMO commonly used by Japanese manufacturers, and Tesla's proprietary Supercharger connector, delivering direct current at power levels between 50 kW up to 350 kW or more. The distinct connector types and communication protocols define compatibility and charging speed, making Level 3 chargers essential for rapid energy replenishment on long journeys.
Long-Term Impact on Battery Health
Level 2 charging delivers moderate power typically around 3.3 to 7.7 kW and is gentler on electric vehicle batteries, promoting longer overall battery lifespan due to reduced heat generation and slower charging rates. Level 3 charging, or DC fast charging, provides significantly higher power often exceeding 50 kW, which accelerates charging times but may increase battery degradation over time because of the higher thermal and electrical stress. Long-term use of Level 2 charging is often recommended by manufacturers to preserve battery capacity and maintain optimal performance, while frequent reliance on Level 3 charging can lead to faster capacity loss and reduced battery durability.
Choosing the Right Charging Solution for Your Electric Vehicle
Level 2 charging delivers 240 volts with a power output of 3.3 to 19.2 kW, ideal for overnight home charging and providing 20 to 80 miles of range per hour. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, offers 50 kW to over 350 kW, enabling an 80% charge in 20 to 40 minutes and suited for long-distance travel or commercial use. Selecting the right solution depends on daily driving patterns, vehicle compatibility, and charging infrastructure availability.
Level 2 Charging vs Level 3 Charging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com