Leasing a vehicle offers lower monthly payments and the opportunity to drive newer models more frequently, ideal for those seeking flexibility without long-term commitment. Buying a vehicle provides full ownership, allowing customization and no mileage restrictions, making it a cost-effective choice over time. The decision between lease and buy depends on personal finances, driving habits, and long-term vehicle needs.
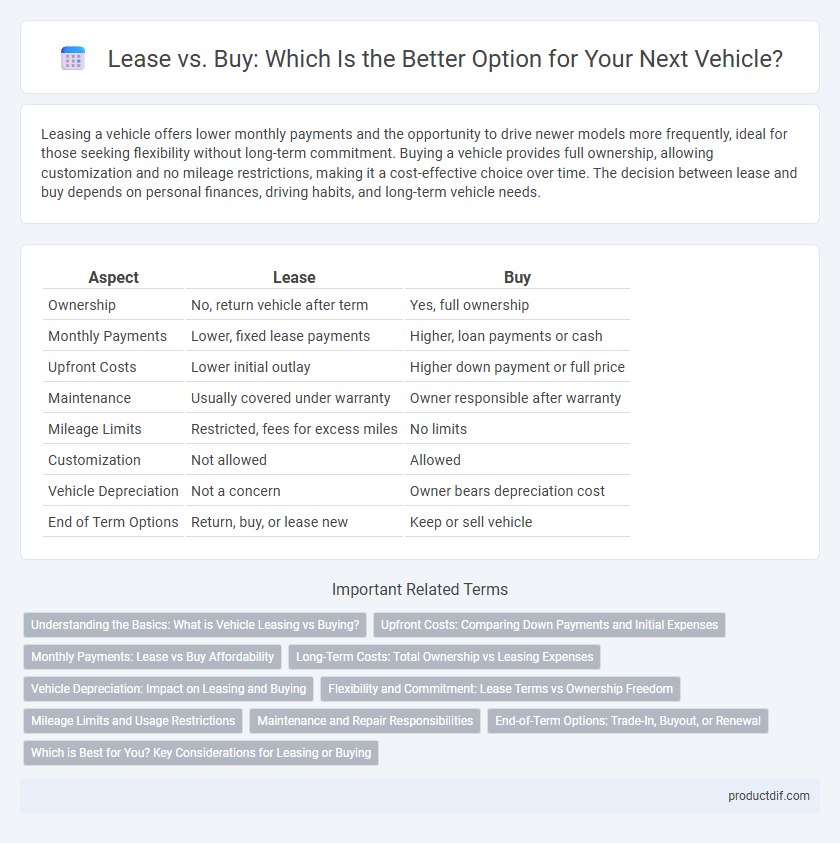
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lease | Buy |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | No, return vehicle after term | Yes, full ownership |
| Monthly Payments | Lower, fixed lease payments | Higher, loan payments or cash |
| Upfront Costs | Lower initial outlay | Higher down payment or full price |
| Maintenance | Usually covered under warranty | Owner responsible after warranty |
| Mileage Limits | Restricted, fees for excess miles | No limits |
| Customization | Not allowed | Allowed |
| Vehicle Depreciation | Not a concern | Owner bears depreciation cost |
| End of Term Options | Return, buy, or lease new | Keep or sell vehicle |
Understanding the Basics: What is Vehicle Leasing vs Buying?
Vehicle leasing involves paying monthly fees to use a car for a set period, typically 2 to 4 years, without ownership, while buying means financing or paying upfront to own the vehicle outright. Leasing generally offers lower monthly payments and access to newer models but comes with mileage limits and no equity build-up. Buying provides long-term ownership benefits, no mileage restrictions, and potential resale value, making it a better option for those intending to keep the car long-term.
Upfront Costs: Comparing Down Payments and Initial Expenses
Leasing a vehicle typically requires lower upfront costs, with down payments averaging between $1,000 and $3,000, compared to buying which often demands $3,000 to $7,000 due to higher down payments and taxes. Initial expenses for leasing also include acquisition fees and first-month payments, while purchasing involves title, registration, and possible dealer fees that can increase the total initial outlay. Understanding these upfront cost differences helps consumers optimize cash flow when deciding between leasing and buying a car.
Monthly Payments: Lease vs Buy Affordability
Monthly payments for leasing a vehicle are typically lower than loan payments for buying, making leases more affordable upfront. Lease payments cover depreciation and fees without building equity, while loan payments contribute to ownership but are higher due to interest and principal. Evaluating monthly budgets against total cost of ownership reveals that leasing offers short-term affordability, whereas buying may prove cost-effective long-term.
Long-Term Costs: Total Ownership vs Leasing Expenses
Calculating long-term costs reveals that buying a vehicle typically incurs higher upfront expenses but lower overall expenditure compared to leasing, which involves consistent monthly payments with potential mileage and wear-and-tear fees. Total ownership costs include depreciation, maintenance, insurance, and financing interest, while leasing often covers warranty-maintained services but restricts customization and accrues fees beyond set limits. Analyzing these factors helps determine whether the financial and lifestyle benefits of ownership outweigh the flexibility and lower initial costs of leasing for a specific vehicle model.
Vehicle Depreciation: Impact on Leasing and Buying
Vehicle depreciation significantly influences the financial outcomes of leasing versus buying, as leased cars typically lose value faster than buyers directly bear. Leasing mitigates depreciation risk since monthly payments cover predicted value loss, while buyers shoulder full depreciation cost, impacting resale value. Understanding depreciation rates helps consumers decide between lower lease payments or long-term ownership equity.
Flexibility and Commitment: Lease Terms vs Ownership Freedom
Leasing a vehicle offers greater flexibility with shorter term commitments, allowing drivers to upgrade to newer models every few years without long-term obligations. Buying provides ownership freedom, enabling unlimited mileage and customization without concerns about lease restrictions or penalties. The choice between lease and buy hinges on balancing adaptability against the desire for full control and long-term investment in the vehicle.
Mileage Limits and Usage Restrictions
Lease agreements often include strict mileage limits, typically ranging from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year, with significant fees imposed for exceeding these thresholds. Buying a vehicle provides unlimited mileage without penalties, making it more suitable for high-mileage drivers or businesses with extensive transportation needs. Usage restrictions in leases may also prohibit modifications and restrict usage to personal driving, while owning allows full control over vehicle customization and operation.
Maintenance and Repair Responsibilities
When leasing a vehicle, maintenance and repair responsibilities often fall under the leasing company's warranty coverage, minimizing out-of-pocket costs for routine services and unexpected repairs. Buyers are responsible for all maintenance and repair expenses, which can increase total ownership costs over time, especially as the vehicle ages. Understanding warranty terms and anticipated maintenance schedules is crucial for making cost-effective decisions between leasing and buying.
End-of-Term Options: Trade-In, Buyout, or Renewal
At the end of a vehicle lease, drivers typically choose between trade-in, buyout, or renewal options. Trade-in allows returning the leased car and applying its equity toward a new lease or purchase, while buyout involves purchasing the vehicle outright for the residual value set in the lease contract. Renewal extends the lease term under similar conditions, often with updated mileage limits and fees, providing flexibility based on the driver's long-term plans.
Which is Best for You? Key Considerations for Leasing or Buying
Evaluating lease vs buy options depends largely on your financial goals, driving habits, and long-term vehicle needs. Leasing offers lower monthly payments and the ability to drive a new vehicle every few years, ideal for those valuing flexibility and minimal maintenance costs. Buying builds equity and provides unlimited mileage, making it the better choice for drivers seeking ownership, long-term savings, and customization freedom.
Lease vs Buy Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com