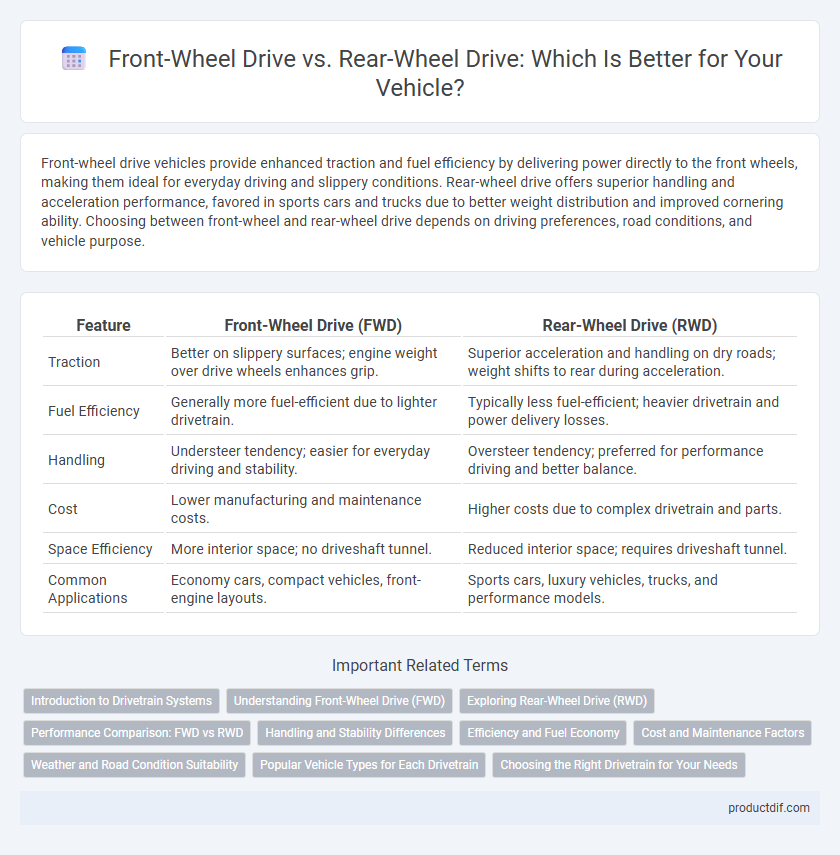
Front-wheel drive vehicles provide enhanced traction and fuel efficiency by delivering power directly to the front wheels, making them ideal for everyday driving and slippery conditions. Rear-wheel drive offers superior handling and acceleration performance, favored in sports cars and trucks due to better weight distribution and improved cornering ability. Choosing between front-wheel and rear-wheel drive depends on driving preferences, road conditions, and vehicle purpose.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) | Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) |
|---|---|---|
| Traction | Better on slippery surfaces; engine weight over drive wheels enhances grip. | Superior acceleration and handling on dry roads; weight shifts to rear during acceleration. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally more fuel-efficient due to lighter drivetrain. | Typically less fuel-efficient; heavier drivetrain and power delivery losses. |
| Handling | Understeer tendency; easier for everyday driving and stability. | Oversteer tendency; preferred for performance driving and better balance. |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing and maintenance costs. | Higher costs due to complex drivetrain and parts. |
| Space Efficiency | More interior space; no driveshaft tunnel. | Reduced interior space; requires driveshaft tunnel. |
| Common Applications | Economy cars, compact vehicles, front-engine layouts. | Sports cars, luxury vehicles, trucks, and performance models. |
Introduction to Drivetrain Systems
Front-wheel drive (FWD) systems deliver power to the front wheels, improving traction and fuel efficiency, especially in compact cars and urban driving conditions. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) systems send power to the rear wheels, offering better handling and acceleration performance, commonly favored in sports cars and trucks. Understanding drivetrain layouts is essential for optimizing vehicle dynamics, safety, and purpose-specific performance.
Understanding Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) vehicles deliver engine power to the front wheels, enhancing traction and stability, especially in wet or slippery conditions. This drivetrain layout typically offers improved fuel efficiency and more efficient use of interior space due to the compact design of the engine and transmission placement. FWD is commonly found in compact and mid-sized cars, providing predictable handling and easier control for everyday driving.
Exploring Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles distribute engine power to the rear wheels, enhancing acceleration and handling by improving weight distribution and traction during high-performance driving. RWD systems are preferred in sports cars and trucks for their superior balance, durability, and ability to handle high torque loads. This drivetrain layout offers improved steering response since the front wheels are dedicated solely to steering, reducing understeer compared to front-wheel drive configurations.
Performance Comparison: FWD vs RWD
Front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles typically offer better fuel efficiency and improved traction in slippery conditions due to the engine's weight over the driving wheels, enhancing stability during acceleration. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) configurations deliver superior handling and balanced weight distribution, allowing for more precise cornering and higher performance in sporty and high-powered vehicles. The choice between FWD and RWD impacts acceleration dynamics, with RWD providing better power delivery under aggressive driving while FWD excels in everyday driving scenarios and inclement weather.
Handling and Stability Differences
Front-wheel drive vehicles typically offer better traction and stability on slippery or wet roads due to the engine's weight over the driving wheels, enhancing grip during acceleration. Rear-wheel drive cars provide superior handling dynamics by distributing weight more evenly and allowing for better balance during cornering, resulting in a more responsive steering feel. The choice between front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive significantly impacts vehicle stability, with front-wheel drive favoring straight-line traction and rear-wheel drive excelling in dynamic handling and performance driving.
Efficiency and Fuel Economy
Front-wheel drive vehicles typically offer better fuel economy due to lighter drivetrain components and reduced mechanical losses compared to rear-wheel drive systems. The compact layout of front-wheel drive improves weight distribution, enhancing traction and efficiency in urban and highway driving. Rear-wheel drive, while often providing better handling dynamics, generally incurs higher fuel consumption due to increased drivetrain complexity and weight.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles typically offer lower maintenance costs due to fewer drivetrain components and easier access to parts, which reduces labor expenses. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) systems involve more complex mechanics, such as a driveshaft and differential, increasing both initial repair costs and ongoing upkeep. Insurance premiums can also be lower for FWD cars because of their enhanced stability and lower risk of accidents, contributing to overall cost efficiency.
Weather and Road Condition Suitability
Front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles provide superior traction on wet, snowy, or icy roads due to the engine's weight over the drive wheels, enhancing stability in slippery conditions. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) excels in dry conditions, offering better handling and acceleration on paved surfaces but can be prone to oversteer and reduced traction on slick roads. All-wheel drive (AWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) systems typically outperform both in adverse weather by delivering power to all wheels, improving control on uneven or low-traction surfaces.
Popular Vehicle Types for Each Drivetrain
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is commonly found in compact cars, small SUVs, and fuel-efficient sedans due to its cost-effectiveness and better traction in slippery conditions. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) dominates in sports cars, luxury sedans, and pickup trucks, offering superior handling, acceleration, and weight distribution. Popular models with FWD include the Honda Civic and Toyota Corolla, while RWD is prevalent in vehicles like the BMW 3 Series and Ford Mustang.
Choosing the Right Drivetrain for Your Needs
Front-wheel drive vehicles offer superior traction on slippery roads and improved fuel efficiency, making them ideal for daily commuting and urban driving. Rear-wheel drive systems provide better handling, acceleration, and balance, preferred in performance cars and towing applications. Selecting the right drivetrain depends on your driving conditions, such as weather, terrain, and the specific demands of your vehicle use.
Front-Wheel Drive vs Rear-Wheel Drive Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com