Active safety systems in vehicles focus on preventing accidents through technologies like anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and adaptive cruise control, which enhance driver control and awareness. Passive safety features, such as airbags, seatbelts, and crumple zones, are designed to minimize injury during a collision by absorbing impact forces and protecting occupants. Both systems work together to improve overall vehicle safety, with active safety aiming to avoid crashes and passive safety mitigating harm when accidents occur.
Table of Comparison
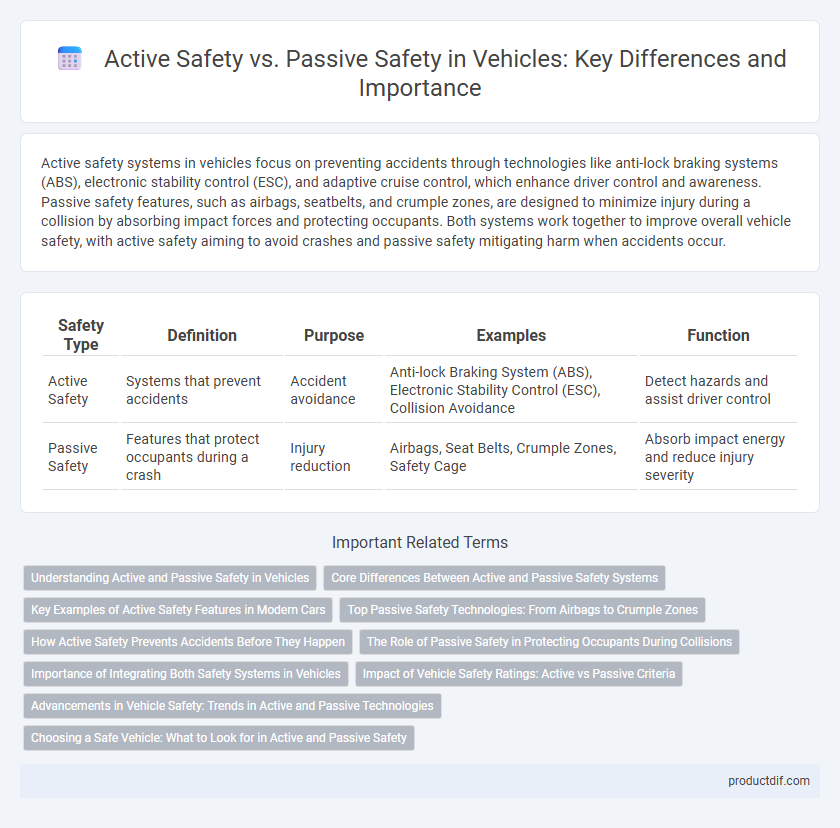
| Safety Type | Definition | Purpose | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Safety | Systems that prevent accidents | Accident avoidance | Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), Electronic Stability Control (ESC), Collision Avoidance | Detect hazards and assist driver control |
| Passive Safety | Features that protect occupants during a crash | Injury reduction | Airbags, Seat Belts, Crumple Zones, Safety Cage | Absorb impact energy and reduce injury severity |
Understanding Active and Passive Safety in Vehicles
Active safety systems in vehicles include technologies such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and adaptive cruise control that work to prevent accidents before they occur. Passive safety features, like airbags, seat belts, and crumple zones, are designed to minimize injury during a collision. Understanding the interplay between active safety mechanisms that avoid crashes and passive safety components that protect occupants enhances overall vehicle safety performance.
Core Differences Between Active and Passive Safety Systems
Active safety systems in vehicles proactively prevent accidents by employing technologies such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control. Passive safety systems focus on minimizing injury during collisions through features like airbags, seat belts, crumple zones, and reinforced cabin structures. The core difference lies in active safety aiming to avoid crashes before they happen, while passive safety mitigates harm after an impact.
Key Examples of Active Safety Features in Modern Cars
Modern vehicles prioritize active safety features such as automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control to prevent accidents before they occur. These systems use advanced sensors, cameras, and radar technology to monitor the vehicle's surroundings and intervene when necessary, enhancing driver awareness and response time. Active safety complements passive safety elements like airbags and crumple zones by reducing the likelihood of collisions through real-time assistance.
Top Passive Safety Technologies: From Airbags to Crumple Zones
Top passive safety technologies in vehicles include airbags, crumple zones, seatbelt pre-tensioners, and reinforced passenger cabins, all designed to minimize injury during collisions. Airbags deploy instantly to cushion occupants, while crumple zones absorb and dissipate impact energy, reducing force transmitted to passengers. Advances in passive safety engineering have significantly improved crash survivability by integrating these systems with vehicle structural integrity.
How Active Safety Prevents Accidents Before They Happen
Active safety systems in vehicles utilize advanced technologies such as automatic emergency braking, lane departure warnings, and adaptive cruise control to detect potential hazards and intervene before collisions occur. These proactive measures enhance driver awareness and vehicle control, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidents. By continuously monitoring the driving environment, active safety features prevent dangerous situations, ensuring safer travel conditions.
The Role of Passive Safety in Protecting Occupants During Collisions
Passive safety systems play a crucial role in minimizing injury during vehicle collisions by absorbing and dissipating impact forces. Components such as airbags, seat belts, crumple zones, and reinforced cabin structures are engineered to protect occupants by reducing the risk of severe trauma. Unlike active safety technologies that prevent accidents, passive safety measures provide essential protection when a crash is unavoidable.
Importance of Integrating Both Safety Systems in Vehicles
Integrating both active safety and passive safety systems in vehicles significantly enhances overall protection by preventing accidents and minimizing injury severity when collisions occur. Active safety technologies such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control work proactively to reduce crash risks, while passive safety features like airbags, seatbelts, and crumple zones provide essential protection during impact. The synergy between these systems is critical for achieving higher safety ratings and reducing fatalities on the road.
Impact of Vehicle Safety Ratings: Active vs Passive Criteria
Vehicle safety ratings heavily influence consumer decisions by evaluating both active and passive safety features, where active safety includes advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist that help prevent accidents. Passive safety focuses on structural integrity and occupant protection through airbags, crumple zones, and seatbelt technologies designed to mitigate injury during a collision. Higher ratings in active safety criteria often correlate with fewer accidents, while superior passive safety ratings ensure reduced fatalities and injuries when crashes occur, making a balanced integration essential for comprehensive vehicle protection.
Advancements in Vehicle Safety: Trends in Active and Passive Technologies
Advancements in vehicle safety increasingly emphasize active safety systems such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control, which proactively prevent collisions through real-time hazard detection and response. Passive safety technologies, including reinforced vehicle structures, airbags, and advanced seatbelt designs, continue to evolve by improving crash energy absorption and occupant protection during collisions. Integration of sensor fusion and AI-driven decision-making enhances the synergy between active and passive safety, driving significant reductions in vehicle accident severity and injury rates.
Choosing a Safe Vehicle: What to Look for in Active and Passive Safety
Evaluating a vehicle's active safety features, such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control, helps prevent accidents by enhancing driver control and awareness. Passive safety components include airbags, crumple zones, and reinforced cabin structures designed to protect occupants during a collision. Prioritize vehicles with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and high crash test ratings from organizations like IIHS and NHTSA to ensure comprehensive protection in various driving scenarios.
Active Safety vs Passive Safety Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com