Lidar uses laser pulses to create high-resolution 3D maps of a vehicle's surroundings, offering precise object detection and detailed spatial information. Radar relies on radio waves to detect objects and measure their distance and speed, performing reliably in adverse weather conditions like fog, rain, and dust. Combining lidar's accuracy with radar's robustness enhances vehicle safety systems and autonomous driving capabilities.
Table of Comparison
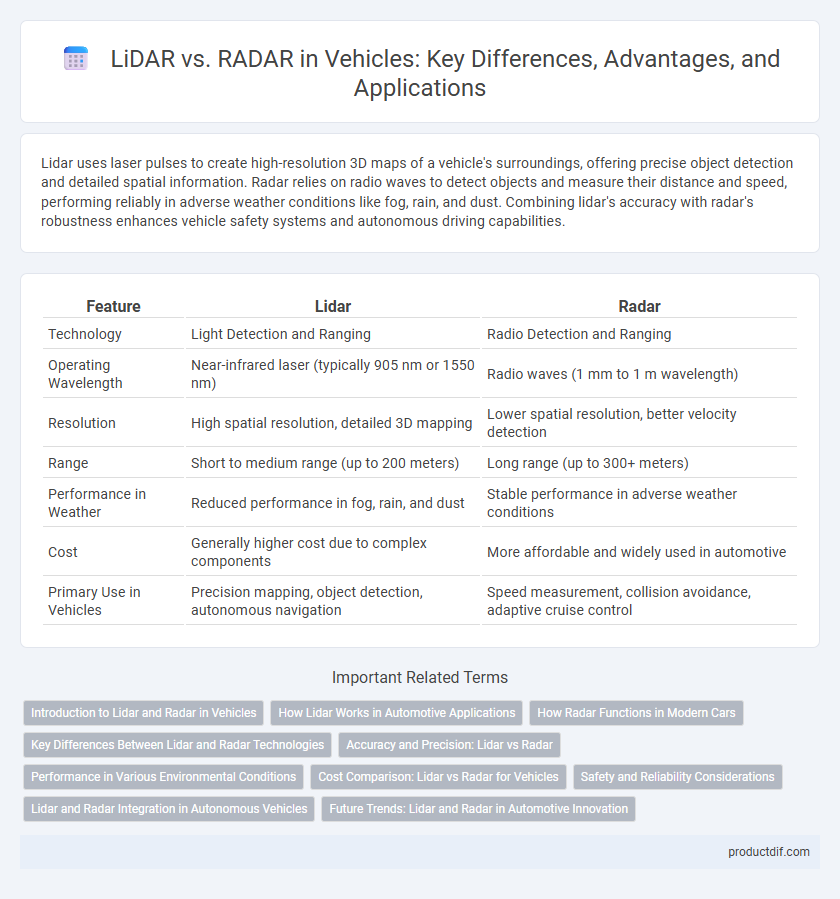
| Feature | Lidar | Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Light Detection and Ranging | Radio Detection and Ranging |
| Operating Wavelength | Near-infrared laser (typically 905 nm or 1550 nm) | Radio waves (1 mm to 1 m wavelength) |
| Resolution | High spatial resolution, detailed 3D mapping | Lower spatial resolution, better velocity detection |
| Range | Short to medium range (up to 200 meters) | Long range (up to 300+ meters) |
| Performance in Weather | Reduced performance in fog, rain, and dust | Stable performance in adverse weather conditions |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to complex components | More affordable and widely used in automotive |
| Primary Use in Vehicles | Precision mapping, object detection, autonomous navigation | Speed measurement, collision avoidance, adaptive cruise control |
Introduction to Lidar and Radar in Vehicles
Lidar and radar are essential sensing technologies used in vehicles for environment detection and autonomous driving. Lidar uses laser light pulses to create high-resolution 3D maps, offering precise distance measurements and object recognition. Radar employs radio waves to detect object speed and distance, functioning effectively in various weather conditions and improving vehicle safety systems.
How Lidar Works in Automotive Applications
Lidar operates by emitting laser pulses that bounce off surrounding objects and return to the sensor, allowing precise measurement of distances based on the time of flight. This technology generates high-resolution 3D maps of the vehicle's environment, enabling accurate detection and classification of obstacles, road features, and pedestrians. Automotive Lidar systems enhance autonomous driving capabilities by providing detailed spatial data that radar systems, which rely on radio waves, cannot achieve with the same precision.
How Radar Functions in Modern Cars
Radar in modern cars operates by emitting radio waves that bounce off objects and return to the sensor, enabling precise detection of the vehicle's surroundings. This technology excels at measuring the speed and distance of moving objects, using Doppler shifts to provide real-time data essential for adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance systems. Unlike Lidar, radar performs reliably in adverse weather conditions, making it a critical sensor for autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems.
Key Differences Between Lidar and Radar Technologies
Lidar uses laser light to measure distances with high precision and creates detailed 3D maps, making it ideal for object recognition and environment scanning in vehicles. Radar employs radio waves to detect objects and measure speed, offering superior performance in poor weather and longer range detection. Lidar provides higher resolution but is more sensitive to weather conditions, while radar is more robust in harsh environments but offers lower resolution data.
Accuracy and Precision: Lidar vs Radar
Lidar offers superior accuracy and precision in vehicle detection by using laser pulses to create detailed 3D maps of the environment, enabling centimeter-level resolution. Radar provides robust detection under diverse weather conditions but typically yields lower spatial resolution, resulting in less precise object identification. High-precision Lidar systems enhance autonomous driving safety by delivering accurate distance and shape measurements, while radar excels in long-range detection despite reduced accuracy.
Performance in Various Environmental Conditions
Lidar offers high-resolution, detailed 3D mapping ideal for clear weather but struggles with fog, rain, and snow due to light scattering. Radar performs reliably in adverse weather like fog, rain, and dust by using radio waves that penetrate these conditions, though it provides lower spatial resolution compared to Lidar. Combining Lidar and Radar sensors enhances vehicle perception by balancing precise object detection with robust performance under diverse environmental challenges.
Cost Comparison: Lidar vs Radar for Vehicles
Lidar systems for vehicles generally come at a higher cost compared to radar, with lidar sensors priced between $1,000 to $4,000 per unit, while radar units typically range from $50 to $500. The significant price difference stems from lidar's complex laser technology and higher resolution capabilities necessary for detailed object detection and mapping. Despite its higher cost, lidar provides superior accuracy for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), whereas radar remains favored for cost-effective, long-range detection and all-weather performance.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Lidar provides high-resolution 3D mapping, enhancing vehicle safety by accurately detecting obstacles and pedestrians in various driving conditions. Radar offers superior reliability in adverse weather such as fog, rain, and snow, maintaining consistent object detection where Lidar performance may degrade. Combining both technologies optimizes overall safety and reliability, leveraging Lidar's precision with Radar's robustness for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles.
Lidar and Radar Integration in Autonomous Vehicles
Lidar and radar integration in autonomous vehicles enhances object detection accuracy by leveraging lidar's high-resolution 3D mapping and radar's reliable performance in adverse weather conditions. Combining lidar's precise spatial data with radar's long-range velocity measurement improves environment perception, enabling safer navigation and obstacle avoidance. This sensor fusion technology is critical for advancing real-time decision-making and increasing the robustness of autonomous driving systems.
Future Trends: Lidar and Radar in Automotive Innovation
Emerging automotive technologies are increasingly integrating lidar and radar systems to enhance vehicle autonomy and safety. Lidar offers high-resolution 3D mapping essential for precise object detection, while radar provides robust performance in adverse weather and longer detection ranges. Future trends emphasize sensor fusion, combining lidar and radar data to overcome individual limitations and accelerate the development of fully autonomous vehicles.
Lidar vs Radar Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com