Two-wheelers offer greater maneuverability and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for urban commuting and quick trips. Three-wheelers provide enhanced stability and increased cargo capacity, which benefits heavier loads and passenger transport. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs for balance, storage, and road conditions.
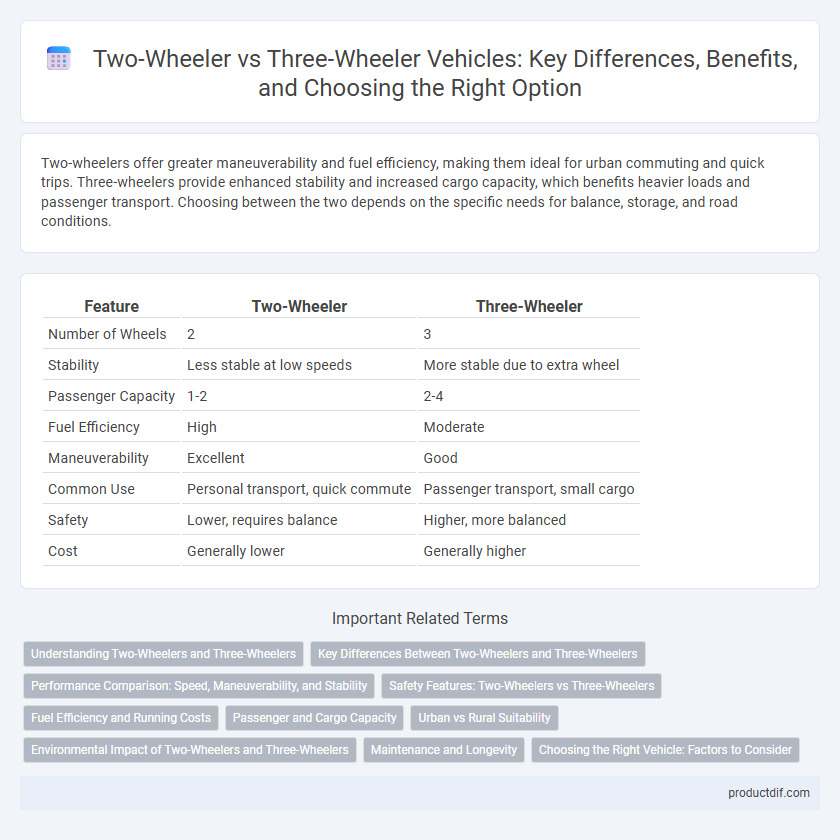
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Two-Wheeler | Three-Wheeler |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wheels | 2 | 3 |
| Stability | Less stable at low speeds | More stable due to extra wheel |
| Passenger Capacity | 1-2 | 2-4 |
| Fuel Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Maneuverability | Excellent | Good |
| Common Use | Personal transport, quick commute | Passenger transport, small cargo |
| Safety | Lower, requires balance | Higher, more balanced |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Understanding Two-Wheelers and Three-Wheelers
Two-wheelers, such as motorcycles and scooters, offer superior maneuverability and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for urban commuting and congested traffic conditions. Three-wheelers, often used as auto-rickshaws or cargo carriers, provide enhanced stability and higher load capacity, catering to passenger transport and small-scale goods delivery. Understanding these core functional differences helps in selecting the appropriate vehicle based on transportation needs and usage patterns.
Key Differences Between Two-Wheelers and Three-Wheelers
Two-wheelers offer greater maneuverability and fuel efficiency due to their lighter weight and streamlined design, making them ideal for congested urban areas. Three-wheelers provide enhanced stability and increased cargo capacity with their additional wheel, supporting better balance and load distribution. Maintenance costs for two-wheelers tend to be lower, but three-wheelers deliver superior safety and passenger comfort, especially on uneven terrain.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Maneuverability, and Stability
Two-wheelers generally offer higher speed and superior maneuverability due to their lightweight design and agile handling, making them ideal for urban commuting and quick lane changes. Three-wheelers provide enhanced stability and load-carrying capacity with a wider base, which reduces the risk of tipping over, especially at lower speeds and on uneven terrain. Performance-wise, two-wheelers excel in acceleration and cornering agility, while three-wheelers prioritize stability and comfort for passengers or cargo.
Safety Features: Two-Wheelers vs Three-Wheelers
Two-wheelers typically offer limited safety features, relying mostly on helmets and rider skills, which increases vulnerability to accidents. In contrast, three-wheelers provide enhanced stability and often come equipped with seat belts, metal frames, and enclosed cabins, reducing the risk of injury. Advanced safety systems like anti-lock braking and electronic stability control are more commonly integrated into three-wheelers, making them safer for urban and commercial use.
Fuel Efficiency and Running Costs
Two-wheelers typically offer superior fuel efficiency, averaging around 40-60 km/liter, compared to three-wheelers which generally achieve 20-30 km/liter due to their larger engine capacity and heavier weight. Running costs for two-wheelers are lower, with cheaper maintenance, spare parts, and insurance premiums, making them more economical for daily commuting. In contrast, three-wheelers incur higher fuel consumption and maintenance expenses but provide greater passenger or cargo capacity, influencing their overall cost-effectiveness.
Passenger and Cargo Capacity
Two-wheelers typically accommodate one to two passengers, offering limited cargo space suitable for small bags or personal items. Three-wheelers provide higher passenger capacity, often seating three to six people, and feature a larger cargo area for carrying substantial goods. The added stability of three-wheelers enhances safety when transporting heavier loads compared to two-wheelers.
Urban vs Rural Suitability
Two-wheelers offer superior maneuverability and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for congested urban environments where tight traffic and limited parking space are common. Three-wheelers provide greater stability and load capacity, better suited for rural areas with uneven roads and the need to transport goods or passengers over longer distances. Urban settings prioritize speed and agility, while rural settings demand durability and versatility, influencing the suitability of two-wheelers versus three-wheelers accordingly.
Environmental Impact of Two-Wheelers and Three-Wheelers
Two-wheelers generally produce lower carbon emissions per kilometer than three-wheelers due to their smaller engines and lighter weight, making them more environmentally efficient for short-distance travel. Three-wheelers, often used for public transport or freight, tend to have higher fuel consumption and emissions, especially those powered by older diesel engines. Electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and urban air pollution, promoting sustainable mobility solutions in dense cities.
Maintenance and Longevity
Two-wheelers generally require less maintenance due to fewer mechanical components and simpler engine systems, leading to lower overall upkeep costs. Three-wheelers, while providing enhanced stability and payload capacity, often demand more frequent servicing of their additional wheel assemblies and more complex drive mechanisms. Longevity for two-wheelers is typically extended by easier access to spare parts and straightforward repair processes compared to three-wheelers, which may face accelerated wear on their tricycle structure under heavy loads.
Choosing the Right Vehicle: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a two-wheeler and a three-wheeler, consider factors such as stability, fuel efficiency, and intended use. Two-wheelers offer greater agility and fuel economy, ideal for urban commuting and quick maneuvering through traffic. Three-wheelers provide enhanced balance and cargo capacity, making them suitable for heavier loads and uneven road conditions.
Two-Wheeler vs Three-Wheeler Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com