All-wheel drive (AWD) provides superior traction and stability by powering all four wheels, making it ideal for off-road conditions and slippery surfaces. Front-wheel drive (FWD) powers only the front wheels, offering better fuel efficiency and lower maintenance costs, suitable for everyday city driving. Choosing between AWD and FWD depends on driving needs, weather conditions, and terrain preferences.
Table of Comparison
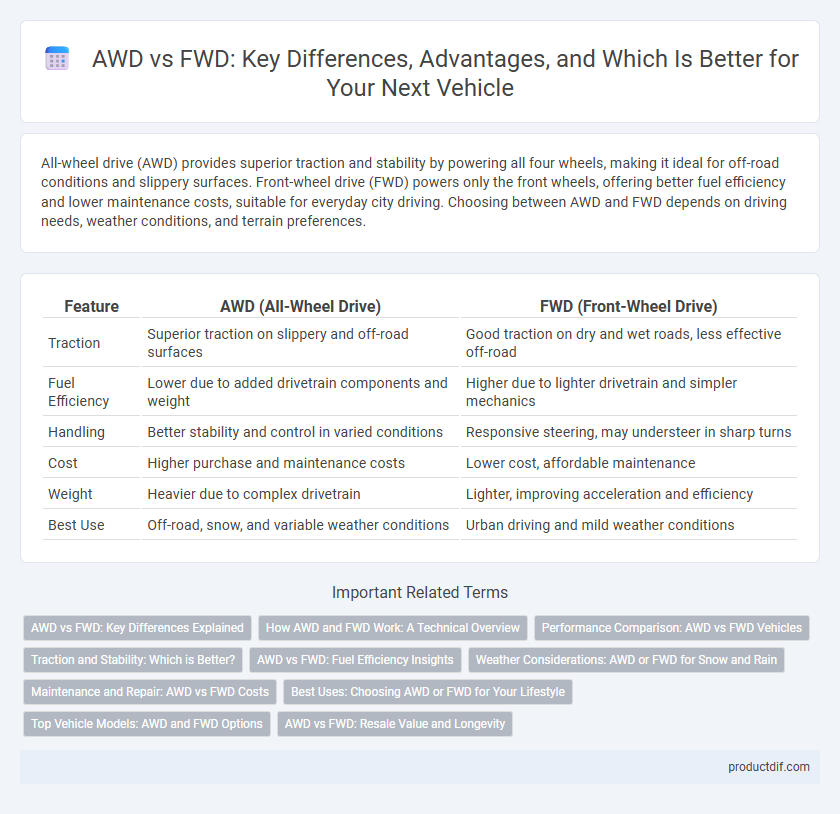
| Feature | AWD (All-Wheel Drive) | FWD (Front-Wheel Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Traction | Superior traction on slippery and off-road surfaces | Good traction on dry and wet roads, less effective off-road |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower due to added drivetrain components and weight | Higher due to lighter drivetrain and simpler mechanics |
| Handling | Better stability and control in varied conditions | Responsive steering, may understeer in sharp turns |
| Cost | Higher purchase and maintenance costs | Lower cost, affordable maintenance |
| Weight | Heavier due to complex drivetrain | Lighter, improving acceleration and efficiency |
| Best Use | Off-road, snow, and variable weather conditions | Urban driving and mild weather conditions |
AWD vs FWD: Key Differences Explained
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) systems deliver power to all four wheels simultaneously, enhancing traction and stability on diverse road conditions such as snow, mud, and wet surfaces. Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) powers only the front wheels, offering better fuel efficiency and lower drivetrain weight but less optimal traction in slippery conditions. AWD provides superior handling and safety in off-road or adverse weather scenarios, while FWD is more cost-effective and efficient for everyday urban and highway driving.
How AWD and FWD Work: A Technical Overview
AWD (All-Wheel Drive) systems distribute power to all four wheels simultaneously or automatically as needed, enhancing traction and stability by adjusting torque based on driving conditions. FWD (Front-Wheel Drive) systems send power exclusively to the front wheels, improving fuel efficiency and reducing drivetrain complexity but offering less grip on slippery surfaces. AWD utilizes components like a center differential or electronic clutch to manage torque split between front and rear axles, whereas FWD relies on a transaxle that combines transmission and differential functions in one unit.
Performance Comparison: AWD vs FWD Vehicles
AWD vehicles deliver superior traction by distributing power to all four wheels, enhancing acceleration and stability on slippery or uneven surfaces compared to FWD models. FWD systems typically offer better fuel efficiency and lower production costs, making them ideal for urban driving and light weather conditions. Performance-wise, AWD excels in off-road and high-performance scenarios, while FWD provides adequate handling and control for everyday driving needs.
Traction and Stability: Which is Better?
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) systems provide superior traction by distributing power to all four wheels, enhancing grip on slippery or uneven surfaces for improved stability. Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) offers adequate traction in most conditions but tends to lose stability on wet or snow-covered roads due to powering only the front wheels. For consistent traction and better control in varied driving environments, AWD is generally considered the better option for stability and performance.
AWD vs FWD: Fuel Efficiency Insights
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) systems generally consume more fuel than Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) due to the added weight and mechanical complexity of powering all four wheels. FWD vehicles typically offer better fuel efficiency by reducing drivetrain losses and having lighter components, which improves miles per gallon (MPG) especially in city and highway driving. Studies show that AWD can decrease fuel economy by 5-10% compared to FWD, making FWD preferable for drivers prioritizing fuel savings.
Weather Considerations: AWD or FWD for Snow and Rain
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) systems provide superior traction and stability in snow and rain by distributing power to all four wheels, reducing the likelihood of slipping on icy or wet surfaces. Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) vehicles offer adequate performance in mild weather conditions, as the weight of the engine over the front wheels improves grip, but they can struggle in deeper snow or heavy rain. Choosing AWD enhances safety and control in challenging weather, making it the preferred option for regions with frequent snowfall or persistent wet roads.
Maintenance and Repair: AWD vs FWD Costs
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles typically incur higher maintenance and repair costs compared to Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) models due to the complexity of their drivetrain systems, which include additional components like a center differential and multiple driveshafts. FWD vehicles have simpler mechanical layouts, resulting in less frequent repairs and lower labor costs, making them more cost-effective to maintain over time. The increased wear and tear on AWD parts such as transfer cases and differentials contribute to more expensive servicing requirements, especially in harsh driving conditions.
Best Uses: Choosing AWD or FWD for Your Lifestyle
AWD systems excel in providing superior traction and control on slippery or uneven terrain, making them ideal for drivers frequently facing snow, rain, or off-road conditions. FWD vehicles offer better fuel efficiency and lower maintenance costs, perfect for urban commuters and those primarily driving on paved roads. Selecting AWD or FWD hinges on assessing your daily driving environment and performance needs, ensuring optimal safety and efficiency.
Top Vehicle Models: AWD and FWD Options
Top vehicle models like the Subaru Outback and Toyota RAV4 offer AWD options, providing superior traction and stability for off-road and adverse weather conditions. Popular FWD models such as the Honda Civic and Toyota Camry deliver better fuel efficiency and lower production costs, making them ideal for urban and highway driving. Choosing between AWD and FWD depends on driving needs, with AWD favored for rugged terrains and FWD suited for everyday commuting.
AWD vs FWD: Resale Value and Longevity
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles typically retain higher resale value compared to Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) cars due to enhanced traction and performance in diverse driving conditions. AWD systems generally contribute to increased longevity through better handling and stability, reducing wear on tires and brakes. However, maintenance costs for AWD models can be higher, slightly affecting long-term ownership expenses.
AWD vs FWD Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com