Onboard diagnostics (OBD) provide real-time data directly from the vehicle's internal systems, allowing for immediate detection and troubleshooting of mechanical issues. Remote diagnostics enable technicians to access vehicle data from a distance, offering proactive maintenance and the ability to monitor vehicle health without physical inspections. Combining both methods enhances vehicle pet care by ensuring timely repairs and continuous performance monitoring.
Table of Comparison
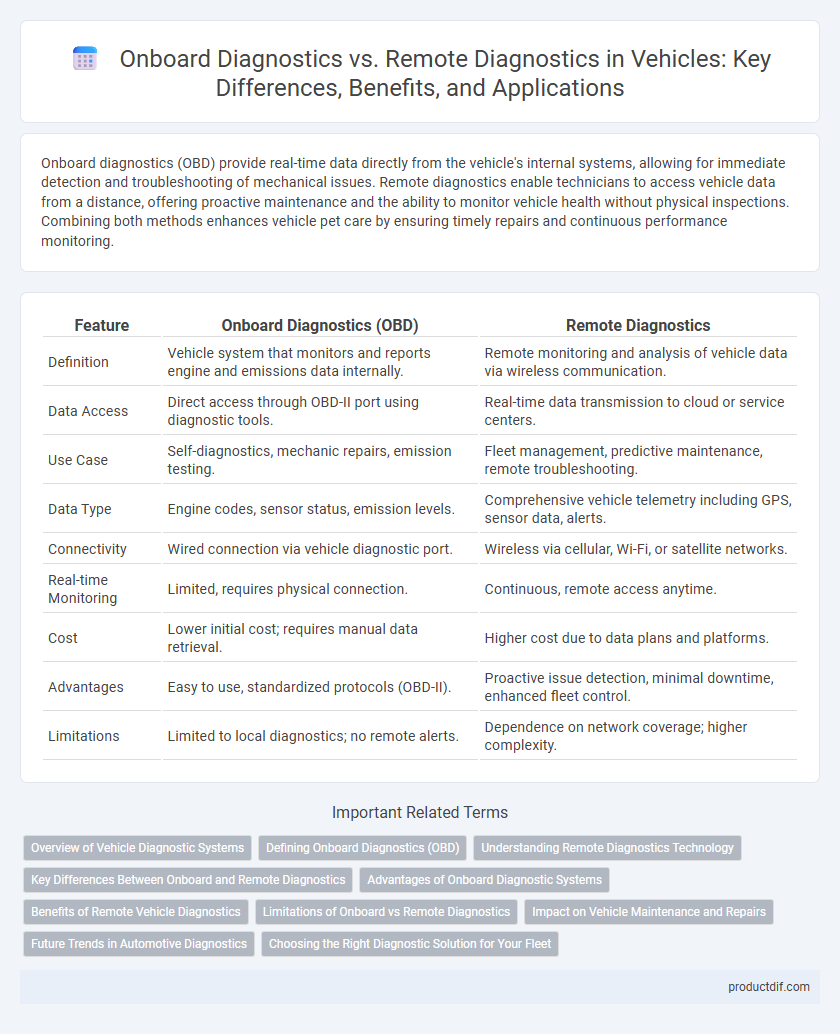
| Feature | Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) | Remote Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicle system that monitors and reports engine and emissions data internally. | Remote monitoring and analysis of vehicle data via wireless communication. |
| Data Access | Direct access through OBD-II port using diagnostic tools. | Real-time data transmission to cloud or service centers. |
| Use Case | Self-diagnostics, mechanic repairs, emission testing. | Fleet management, predictive maintenance, remote troubleshooting. |
| Data Type | Engine codes, sensor status, emission levels. | Comprehensive vehicle telemetry including GPS, sensor data, alerts. |
| Connectivity | Wired connection via vehicle diagnostic port. | Wireless via cellular, Wi-Fi, or satellite networks. |
| Real-time Monitoring | Limited, requires physical connection. | Continuous, remote access anytime. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; requires manual data retrieval. | Higher cost due to data plans and platforms. |
| Advantages | Easy to use, standardized protocols (OBD-II). | Proactive issue detection, minimal downtime, enhanced fleet control. |
| Limitations | Limited to local diagnostics; no remote alerts. | Dependence on network coverage; higher complexity. |
Overview of Vehicle Diagnostic Systems
Onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems enable real-time monitoring and reporting of a vehicle's performance through embedded sensors and diagnostic trouble codes accessible via a standardized port. Remote diagnostics utilize telematics and wireless communication to transmit vehicle data to service centers for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting without the need for physical inspections. Both systems enhance vehicle fault detection, but remote diagnostics offer the advantage of continuous monitoring and faster response to potential issues.
Defining Onboard Diagnostics (OBD)
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) is an integrated vehicle system that monitors engine performance and emissions through a standardized computer interface. It collects real-time data from sensors and components, allowing for immediate detection and reporting of malfunctions or faults via diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). OBD systems enable mechanics to quickly identify issues, ensuring timely maintenance and compliance with environmental regulations.
Understanding Remote Diagnostics Technology
Remote diagnostics technology leverages wireless communication and cloud computing to monitor vehicle health in real-time, allowing technicians to access diagnostic data without physical vehicle access. Unlike onboard diagnostics (OBD), which require direct connection to the vehicle's onboard computer via OBD-II ports, remote diagnostics utilize telematics systems to transmit sensor data, fault codes, and performance metrics instantly to service centers. This technology enables proactive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances fleet management efficiency by providing comprehensive vehicle insights remotely.
Key Differences Between Onboard and Remote Diagnostics
Onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems provide real-time vehicle health data directly from the vehicle's embedded sensors and control modules, enabling immediate fault detection and error code retrieval. Remote diagnostics leverage telematics and wireless communication to transmit diagnostic information to off-site technicians, facilitating proactive maintenance and reducing downtime through continuous monitoring. Key differences include data accessibility, with onboard diagnostics requiring physical access for data reading, while remote diagnostics offer real-time remote access and centralized fleet management capabilities.
Advantages of Onboard Diagnostic Systems
Onboard diagnostic systems enable real-time monitoring of a vehicle's critical components, allowing immediate detection of malfunctions to prevent costly repairs. These systems provide precise diagnostic codes directly accessible via the vehicle's interface, facilitating quicker troubleshooting by technicians. Onboard diagnostics enhance vehicle safety and emissions control by continuously tracking engine performance and emissions-related components without relying on external connectivity.
Benefits of Remote Vehicle Diagnostics
Remote vehicle diagnostics offer real-time monitoring and quicker fault detection compared to onboard diagnostics, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing repair times. This technology supports continuous data transmission, allowing fleet managers to optimize vehicle performance and lower operational costs effectively. Enhanced access to diagnostic information remotely improves safety by addressing issues before they escalate into critical failures.
Limitations of Onboard vs Remote Diagnostics
Onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems are limited by their reliance on vehicle-installed sensors and processing power, restricting real-time analysis to data obtainable within the vehicle's network. Remote diagnostics leverage cloud-based platforms and telematics, enabling more comprehensive monitoring and predictive analytics by aggregating data from multiple vehicles over time. OBD cannot easily access system updates or external environmental data, which remote diagnostics utilize to provide proactive maintenance alerts and detailed fault identification.
Impact on Vehicle Maintenance and Repairs
Onboard diagnostics enable immediate detection of vehicle issues through integrated sensors and error codes, allowing technicians to quickly identify and fix problems during routine maintenance. Remote diagnostics leverage telematics and cloud-based systems to monitor vehicle health in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unexpected breakdowns. Combining both approaches enhances repair accuracy, decreases downtime, and lowers overall maintenance costs by facilitating proactive intervention.
Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics
Onboard diagnostics systems (OBD) remain crucial for real-time vehicle monitoring, enabling precise fault detection and compliance with emission standards. Remote diagnostics leverage telematics and IoT connectivity to provide continuous, off-site vehicle health analysis, predictive maintenance, and software updates, enhancing fleet management efficiency. Future trends emphasize integration of AI-driven analytics and 5G communication, resulting in faster, more accurate diagnostics and proactive repair scheduling.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Solution for Your Fleet
Onboard diagnostics provide real-time, vehicle-specific data directly from the vehicle's onboard computer, enabling immediate identification of issues essential for quick repairs. Remote diagnostics leverage telematics and cloud technology to monitor multiple fleet vehicles simultaneously, offering proactive maintenance and reducing downtime through data-driven insights. Choosing the right diagnostic solution depends on fleet size, operational complexity, and the balance between instant, localized troubleshooting and comprehensive, scalable monitoring capabilities.
Onboard diagnostics vs Remote diagnostics Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com