Drum brakes feature a set of brake shoes inside a rotating drum, offering reliable stopping power and better performance in muddy or wet conditions due to their enclosed design. Disc brakes use a caliper to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or rotor, providing superior heat dissipation and more consistent braking performance, especially under heavy use. Disc brakes are generally preferred for their quicker response, easier maintenance, and enhanced durability in modern vehicles and pet carriers equipped with wheels.
Table of Comparison
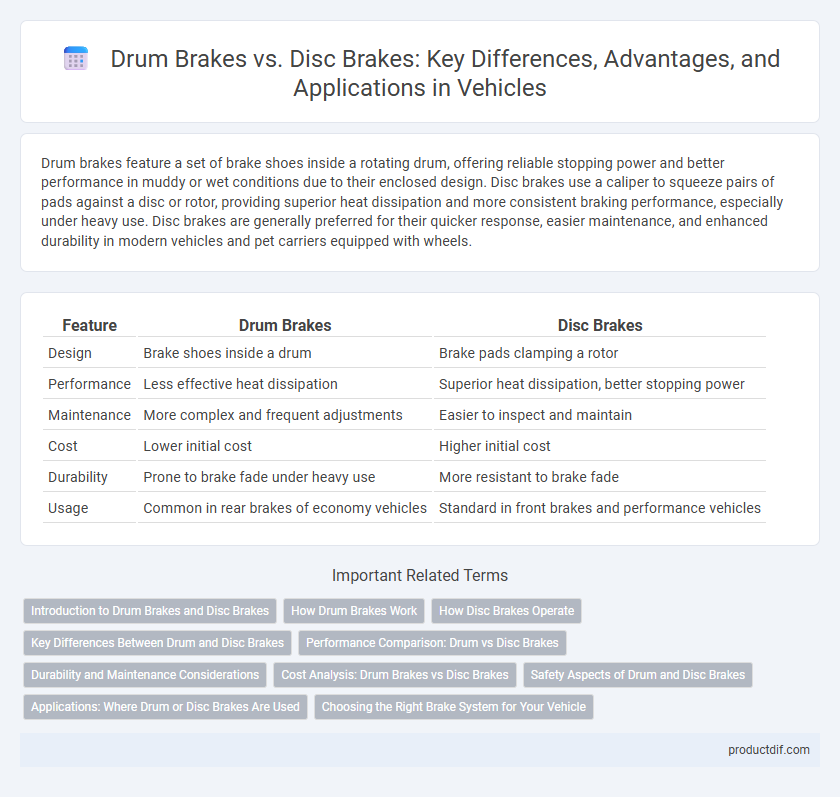
| Feature | Drum Brakes | Disc Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Brake shoes inside a drum | Brake pads clamping a rotor |
| Performance | Less effective heat dissipation | Superior heat dissipation, better stopping power |
| Maintenance | More complex and frequent adjustments | Easier to inspect and maintain |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Prone to brake fade under heavy use | More resistant to brake fade |
| Usage | Common in rear brakes of economy vehicles | Standard in front brakes and performance vehicles |
Introduction to Drum Brakes and Disc Brakes
Drum brakes feature a set of brake shoes that press outward against a rotating drum attached to the wheel, creating friction to slow the vehicle. Disc brakes use calipers to squeeze brake pads against a spinning disc rotor, providing faster heat dissipation and improved stopping power. Both systems serve essential roles in automotive braking performance, with disc brakes increasingly favored for their superior efficiency and durability.
How Drum Brakes Work
Drum brakes operate by pressing brake shoes against the inner surface of a rotating drum attached to the wheel, generating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. When the brake pedal is applied, hydraulic pressure pushes the brake shoes outward, causing them to clamp onto the drum. This mechanism is effective for providing strong braking force and is commonly used in rear-wheel braking systems due to its durability and cost efficiency.
How Disc Brakes Operate
Disc brakes operate by using calipers to squeeze brake pads against a spinning metal disc, creating friction that slows the vehicle. Hydraulic pressure from the brake fluid amplifies the force applied by the driver, ensuring efficient and responsive stopping power. This system offers consistent performance in wet conditions and dissipates heat better than drum brakes, reducing brake fade.
Key Differences Between Drum and Disc Brakes
Drum brakes employ a set of brake shoes that press outward against a rotating drum to create friction, while disc brakes use calipers to squeeze brake pads against a spinning disc for stopping power. Drum brakes typically offer better performance in parking and are more cost-effective, whereas disc brakes provide superior heat dissipation and consistent braking performance, especially under heavy use. The fundamental difference lies in design efficiency and heat management, with disc brakes favored in modern vehicles for enhanced safety and reliability.
Performance Comparison: Drum vs Disc Brakes
Disc brakes offer superior performance compared to drum brakes due to better heat dissipation, which reduces brake fade during prolonged or heavy braking. The open design of disc brakes allows faster cooling and consistent stopping power, especially in wet conditions, enhancing overall vehicle safety and control. Drum brakes, although cost-effective and durable in low-speed applications, typically provide less responsive braking and are more prone to overheating under high-stress driving scenarios.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Drum brakes generally offer greater durability due to their enclosed design, protecting components from dirt and debris, which reduces wear over time compared to disc brakes. Maintenance for drum brakes is typically less frequent but more complex, requiring specialized tools to access internal components, whereas disc brakes are easier to inspect and replace with straightforward pad replacement. Vehicles subjected to heavy-duty usage often favor drum brakes for longevity, while disc brakes are preferred in performance applications for quicker maintenance and consistent braking performance.
Cost Analysis: Drum Brakes vs Disc Brakes
Drum brakes generally cost less to manufacture and replace, making them a budget-friendly option for many vehicle owners. Disc brakes, while more expensive upfront, offer better performance and longer lifespan, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves considering initial expense, durability, and repair frequency for both brake types.
Safety Aspects of Drum and Disc Brakes
Disc brakes provide superior heat dissipation and consistent stopping power, reducing the risk of brake fade during intense or prolonged use, which enhances overall vehicle safety. Drum brakes, while often more protected from environmental elements, are prone to overheating and less effective in wet conditions, increasing the likelihood of reduced braking performance. Advanced safety features in disc brake systems, such as better responsiveness and easier maintenance, contribute to their widespread adoption in modern vehicles.
Applications: Where Drum or Disc Brakes Are Used
Drum brakes are commonly used in older and economy vehicles due to their lower manufacturing costs and effective performance in rear wheel braking systems. Disc brakes are favored in modern cars, motorcycles, and high-performance vehicles for their superior heat dissipation, improved stopping power, and reliable performance in wet conditions. Heavy-duty trucks often utilize a combination, with disc brakes on front wheels for better control and drum brakes on rear wheels for durability under load.
Choosing the Right Brake System for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right brake system depends on your vehicle's driving conditions, weight, and maintenance preferences. Drum brakes offer cost-effective, reliable stopping power ideal for smaller, lighter vehicles or rear wheel setups, while disc brakes provide superior heat dissipation, better performance under heavy loads, and enhanced stopping efficiency for high-performance and larger vehicles. Prioritize disc brakes for improved safety and braking consistency in demanding environments, and consider drum brakes for budget-friendly, low-maintenance options.
Drum Brakes vs Disc Brakes Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com