Fast charging significantly reduces charging time by delivering high power directly to the vehicle's battery, making it ideal for quick top-ups during long trips. Level 2 charging provides a moderate power output suitable for overnight or workplace charging, promoting battery health and energy efficiency. Choosing between fast charging and Level 2 charging depends on balancing convenience, battery longevity, and electricity costs.
Table of Comparison
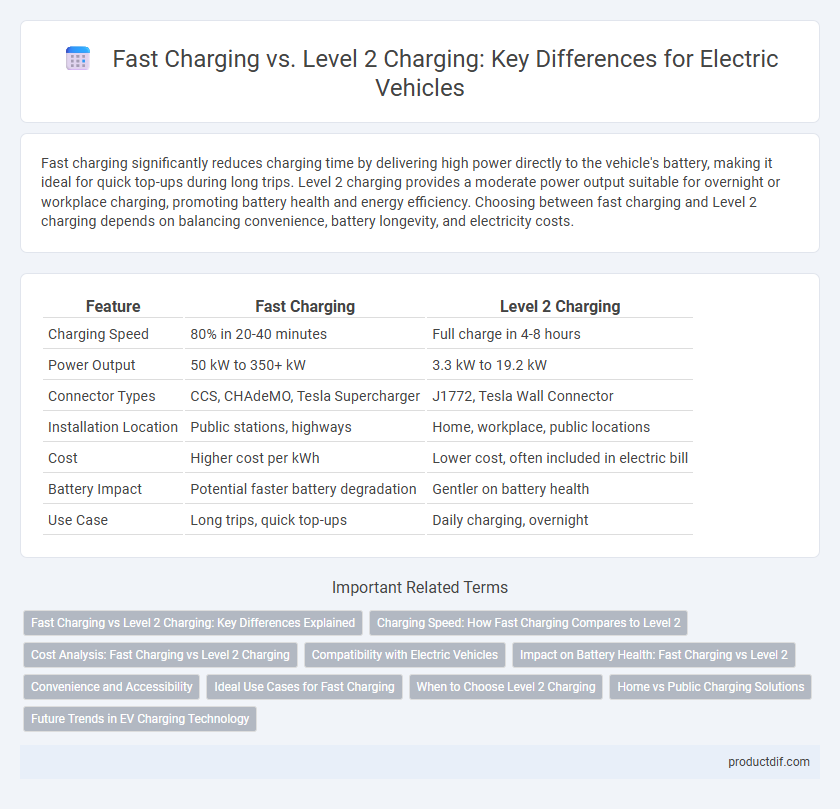
| Feature | Fast Charging | Level 2 Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | 80% in 20-40 minutes | Full charge in 4-8 hours |
| Power Output | 50 kW to 350+ kW | 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW |
| Connector Types | CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger | J1772, Tesla Wall Connector |
| Installation Location | Public stations, highways | Home, workplace, public locations |
| Cost | Higher cost per kWh | Lower cost, often included in electric bill |
| Battery Impact | Potential faster battery degradation | Gentler on battery health |
| Use Case | Long trips, quick top-ups | Daily charging, overnight |
Fast Charging vs Level 2 Charging: Key Differences Explained
Fast charging delivers high power output ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, enabling electric vehicles to recharge up to 80% in 20-40 minutes, whereas Level 2 charging typically provides 6.6-19.2 kW, requiring 4-8 hours for a full charge. Fast chargers use direct current (DC) and bypass the vehicle's onboard charger, making them ideal for quick top-ups during travel, while Level 2 chargers use alternating current (AC) and rely on the onboard charger, suited for home or workplace charging. The infrastructure cost of fast chargers is significantly higher due to advanced technology and grid requirements, compared to the relatively affordable and widespread Level 2 chargers.
Charging Speed: How Fast Charging Compares to Level 2
Fast charging delivers high power outputs typically ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, enabling electric vehicles (EVs) to recharge up to 80% battery capacity in approximately 20 to 40 minutes. In contrast, Level 2 charging operates at 3.3 to 19.2 kW, requiring 4 to 10 hours for a full charge depending on the EV battery size. The significant difference in charging speed makes fast charging ideal for long-distance travel, while Level 2 chargers suit overnight or home use.
Cost Analysis: Fast Charging vs Level 2 Charging
Fast charging stations typically cost between $10,000 to $40,000 for installation, while Level 2 chargers range from $500 to $2,000, making Level 2 charging more budget-friendly upfront. Operational costs for fast charging are higher due to increased electricity demand charges, whereas Level 2 charging benefits from lower energy rates and minimal demand fees. Long-term expenses depend on usage patterns, with fast charging preferred for quick turnaround despite greater costs, and Level 2 offering economical daily home or workplace charging.
Compatibility with Electric Vehicles
Fast charging compatibility with electric vehicles depends on the vehicle's onboard charger and battery management system, typically supporting CCS or CHAdeMO connectors for rapid energy delivery. Level 2 charging offers wider compatibility with most EVs via the standardized J1772 connector, enabling slower but steady charging suitable for overnight use. Understanding the charger type and plug standards is essential for ensuring efficient and safe energy replenishment tailored to specific electric vehicle models.
Impact on Battery Health: Fast Charging vs Level 2
Fast charging delivers higher voltage and current, significantly reducing charging time but potentially accelerating battery degradation due to increased heat and stress on lithium-ion cells. Level 2 charging operates at a lower power level, providing a gentler charge that helps maintain battery capacity and prolongs overall battery lifespan by minimizing thermal impact. Studies reveal that frequent use of fast chargers may decrease battery health by up to 20% over several years compared to consistent Level 2 charging.
Convenience and Accessibility
Fast charging delivers up to 80% battery in 20-40 minutes, making it ideal for quick stops during long trips, while Level 2 charging provides a full charge in 4-8 hours, better suited for overnight or workplace use. Fast chargers are typically found at highways and public locations, offering high convenience for drivers on the go, whereas Level 2 chargers are more accessible at homes and parking facilities, facilitating regular daily charging. Balancing fast charging's speed with Level 2's broader accessibility supports varied driving patterns and enhances overall electric vehicle usability.
Ideal Use Cases for Fast Charging
Fast charging stations, providing up to 350 kW of power, are ideal for drivers needing rapid battery replenishment during long-distance travel or tight schedules. These chargers reduce charging time to 20-30 minutes, making them suitable for highway rest stops and urban quick top-ups. In contrast, Level 2 chargers, delivering around 7-22 kW, better serve overnight home charging or workplaces where vehicles remain parked for several hours.
When to Choose Level 2 Charging
Level 2 charging is ideal for daily electric vehicle (EV) use where charging time aligns with home or workplace parking durations, typically providing 10 to 60 miles of range per hour. This method offers a balanced solution for overnight or extended stops without the need for rapid energy replenishment, preserving battery longevity compared to fast charging. Choosing Level 2 chargers is cost-effective for routine charging needs, supporting consistent EV readiness without the premium infrastructure requirements of DC fast chargers.
Home vs Public Charging Solutions
Fast charging offers rapid energy replenishment, ideal for public charging stations where drivers prioritize minimal downtime during long trips. Level 2 charging, delivering slower energy transfer rates, suits home environments by providing a cost-effective and convenient overnight solution for electric vehicles. Public charging infrastructure emphasizes speed and accessibility, while home setups optimize energy efficiency and user control over charging schedules.
Future Trends in EV Charging Technology
Fast charging technology continues to evolve with ultra-fast chargers capable of delivering up to 350 kW, reducing electric vehicle charging times to under 20 minutes, while Level 2 charging remains essential for residential and workplace settings due to its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. Future trends emphasize integrating smart grid technology and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities, allowing EVs to not only charge efficiently but also serve as energy storage and supply units during peak demand. Advances in solid-state batteries and improved thermal management systems are projected to enhance charging speeds and battery longevity, making fast charging more practical for everyday use.
Fast Charging vs Level 2 Charging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com