Connected cars enhance driving experiences by integrating internet access and smart features that provide real-time traffic updates, safety alerts, and vehicle diagnostics. Autonomous vehicles, equipped with advanced sensors and AI, enable self-driving capabilities, reducing human error and increasing road safety. While connected cars depend on driver interaction, autonomous vehicles aim to fully automate driving functions for greater convenience and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
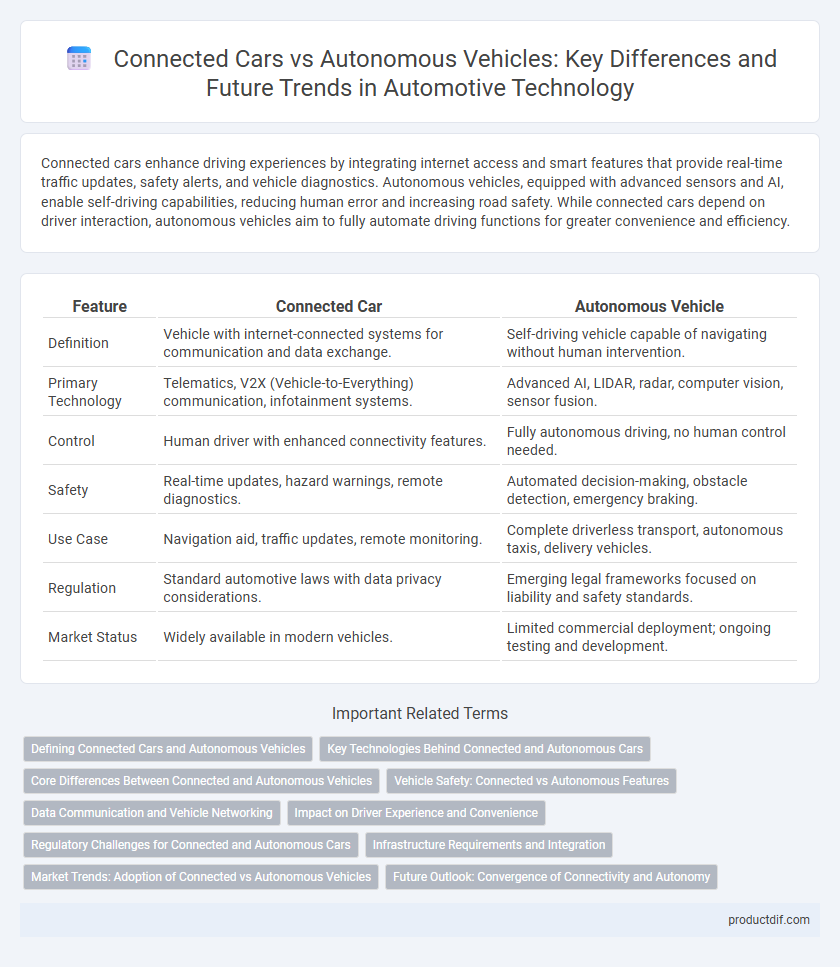
| Feature | Connected Car | Autonomous Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicle with internet-connected systems for communication and data exchange. | Self-driving vehicle capable of navigating without human intervention. |
| Primary Technology | Telematics, V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication, infotainment systems. | Advanced AI, LIDAR, radar, computer vision, sensor fusion. |
| Control | Human driver with enhanced connectivity features. | Fully autonomous driving, no human control needed. |
| Safety | Real-time updates, hazard warnings, remote diagnostics. | Automated decision-making, obstacle detection, emergency braking. |
| Use Case | Navigation aid, traffic updates, remote monitoring. | Complete driverless transport, autonomous taxis, delivery vehicles. |
| Regulation | Standard automotive laws with data privacy considerations. | Emerging legal frameworks focused on liability and safety standards. |
| Market Status | Widely available in modern vehicles. | Limited commercial deployment; ongoing testing and development. |
Defining Connected Cars and Autonomous Vehicles
Connected cars utilize internet connectivity and wireless networks to exchange data with other devices, infrastructure, and cloud services, enhancing navigation, safety, and infotainment features. Autonomous vehicles rely on advanced sensors, machine learning, and AI to independently perceive the environment, make driving decisions, and control the vehicle without human intervention. While connected cars emphasize communication and data sharing, autonomous vehicles prioritize self-driving capabilities and operational autonomy.
Key Technologies Behind Connected and Autonomous Cars
Connected cars utilize advanced telematics systems, 5G communication networks, and IoT sensors to enable real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud platforms. Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on LiDAR, radar, computer vision, and artificial intelligence algorithms for environment perception, path planning, and decision-making without human intervention. Both technologies integrate GPS navigation and machine learning, but connected cars emphasize connectivity, whereas autonomous vehicles prioritize self-driving capabilities.
Core Differences Between Connected and Autonomous Vehicles
Connected cars rely on external data networks to communicate with other devices, infrastructure, and services, enhancing safety and convenience through real-time information exchange. Autonomous vehicles, equipped with advanced sensors and AI, independently perceive their environment and make driving decisions without human intervention. The core difference lies in connected cars augmenting driver awareness while autonomous vehicles replace human control entirely.
Vehicle Safety: Connected vs Autonomous Features
Connected cars enhance vehicle safety by enabling real-time communication with other vehicles and infrastructure to prevent accidents through features like collision warnings and traffic updates. Autonomous vehicles rely on advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to independently detect obstacles, make decisions, and control the vehicle, reducing human error as a primary cause of crashes. While connected car technology improves situational awareness, autonomous vehicles aim to achieve a higher safety standard by fully automating driving tasks and responses in complex environments.
Data Communication and Vehicle Networking
Connected cars utilize advanced data communication networks such as 5G, V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything), and cloud platforms to enable real-time information exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and mobile devices. Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on high-bandwidth vehicle networking systems combining LiDAR, radar, cameras, and edge computing to process sensor data locally while communicating critical updates with other vehicles and traffic management systems. Efficient integration of these technologies improves safety, traffic flow, and predictive maintenance by creating an intelligent transportation ecosystem.
Impact on Driver Experience and Convenience
Connected cars enhance the driver experience by providing real-time traffic updates, seamless smartphone integration, and advanced safety alerts, increasing convenience and situational awareness. Autonomous vehicles, on the other hand, redefine convenience by enabling hands-free driving and reducing driver effort, potentially transforming commuting into a more relaxed and productive activity. Both technologies significantly improve safety, but autonomous vehicles offer the benefit of eliminating driver error entirely, reshaping the future of mobility.
Regulatory Challenges for Connected and Autonomous Cars
Regulatory challenges for connected and autonomous vehicles include data privacy, cybersecurity, and liability frameworks that currently lack comprehensive standardization across jurisdictions. Ensuring compliance with evolving safety protocols and communication standards like V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) technology poses significant hurdles for manufacturers and policymakers. Harmonizing regulations internationally is critical to enable widespread adoption and safe integration of these advanced vehicular technologies on public roads.
Infrastructure Requirements and Integration
Connected cars require robust communication networks such as 5G and dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) to enable real-time data exchange with infrastructure and other vehicles. Autonomous vehicles depend heavily on advanced sensor integration, high-definition mapping, and edge computing infrastructure to process environmental data for safe navigation. Seamless integration of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technology with urban traffic management systems is critical to support both connected and autonomous vehicle functionalities.
Market Trends: Adoption of Connected vs Autonomous Vehicles
Connected cars are experiencing rapid market growth due to increasing consumer demand for enhanced infotainment, safety features, and real-time diagnostics, with global adoption expected to exceed 300 million units by 2027. Autonomous vehicles face slower adoption, constrained by regulatory hurdles and technological challenges, though strategic investments by leading automakers and tech firms forecast autonomous vehicle market valuations surpassing $60 billion by 2030. The convergence of IoT integration, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and 5G connectivity continues to drive differentiated growth trajectories within connected and autonomous vehicle segments.
Future Outlook: Convergence of Connectivity and Autonomy
Connected cars and autonomous vehicles are increasingly converging through advancements in AI, 5G networks, and sensor technology, enabling seamless communication between vehicles and infrastructure. The future outlook emphasizes integrated systems that enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience by combining real-time data sharing with autonomous decision-making capabilities. Industry projections estimate that this convergence will drive a significant reduction in traffic accidents and foster the growth of smart cities by 2030.
Connected Car vs Autonomous Vehicle Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com