AWD systems provide continuous power to all wheels for improved traction and handling in various driving conditions, making them ideal for on-road use and light off-roading. 4WD systems offer selectable power distribution, enhancing performance in rugged terrain and challenging off-road environments by delivering maximum torque to the wheels that need it. Choosing AWD or 4WD depends on the typical driving conditions and the level of off-road capability required.
Table of Comparison
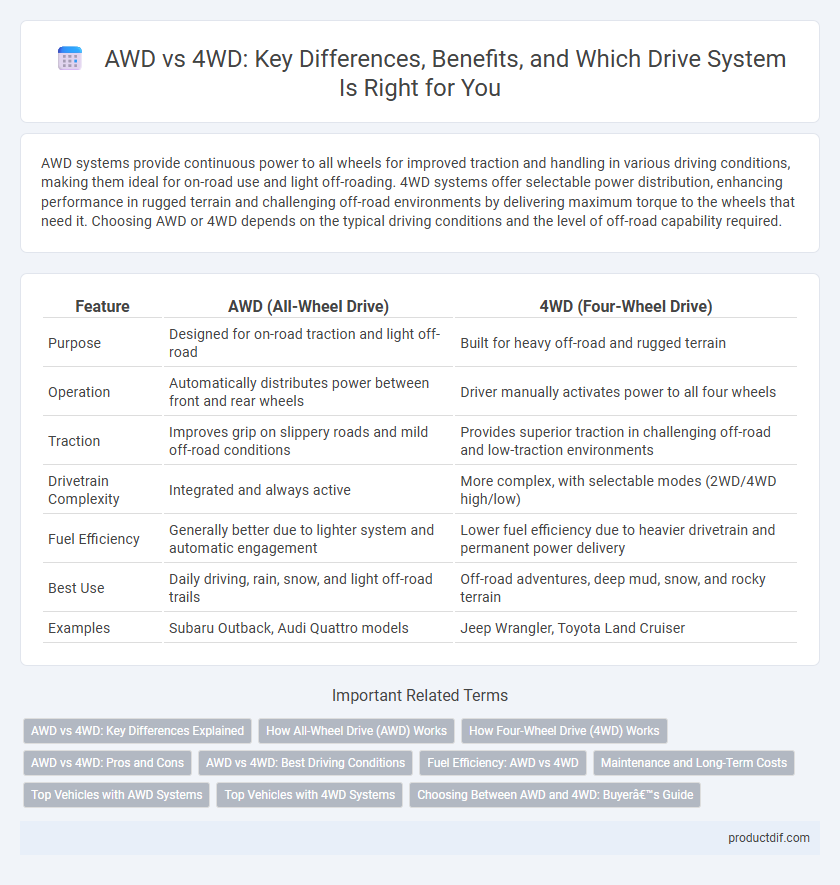
| Feature | AWD (All-Wheel Drive) | 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for on-road traction and light off-road | Built for heavy off-road and rugged terrain |
| Operation | Automatically distributes power between front and rear wheels | Driver manually activates power to all four wheels |
| Traction | Improves grip on slippery roads and mild off-road conditions | Provides superior traction in challenging off-road and low-traction environments |
| Drivetrain Complexity | Integrated and always active | More complex, with selectable modes (2WD/4WD high/low) |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally better due to lighter system and automatic engagement | Lower fuel efficiency due to heavier drivetrain and permanent power delivery |
| Best Use | Daily driving, rain, snow, and light off-road trails | Off-road adventures, deep mud, snow, and rocky terrain |
| Examples | Subaru Outback, Audi Quattro models | Jeep Wrangler, Toyota Land Cruiser |
AWD vs 4WD: Key Differences Explained
AWD (All-Wheel Drive) delivers constant power to all four wheels for enhanced traction on various road conditions, ideal for on-road driving and light off-road use. In contrast, 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive) provides power to all wheels but can be manually engaged or disengaged, offering superior performance in rugged off-road terrain. AWD systems prioritize convenience and stability, while 4WD systems emphasize control and capability in challenging environments.
How All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Works
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) systems continuously distribute power to all four wheels, using sensors to detect traction levels and adjust torque accordingly for optimal grip. Unlike traditional 4WD, AWD operates automatically without driver input, enhancing stability and control on varying road conditions. This seamless torque management improves handling during acceleration, cornering, and slippery surfaces, making AWD ideal for everyday driving and moderate off-road use.
How Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) Works
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) engages all four wheels simultaneously by distributing torque evenly through a transfer case, improving traction on off-road and slippery conditions. The system often includes low-range gearing, allowing enhanced torque multiplication for challenging terrains like mud, rocks, or steep inclines. Unlike All-Wheel Drive (AWD), 4WD systems are usually manually activated and designed for rugged environments, providing maximum control and power delivery to each wheel.
AWD vs 4WD: Pros and Cons
AWD systems provide continuous power to all wheels, enhancing traction on slippery or uneven surfaces without driver intervention, making them ideal for everyday driving and mixed road conditions. 4WD offers superior off-road capability and better performance in rugged terrain by allowing the driver to manually engage power to all wheels, but it often adds weight and reduces fuel efficiency. AWD excels in convenience and on-road stability, while 4WD is preferred for heavy-duty use and extreme off-road situations.
AWD vs 4WD: Best Driving Conditions
AWD (All-Wheel Drive) is best suited for on-road driving in various weather conditions such as rain, snow, and light off-road terrain due to its continuous power delivery to all wheels. 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive) excels in off-road, rugged environments where maximum traction is needed, especially in deep snow, mud, or rocky trails. AWD systems provide better handling and stability on pavement while 4WD offers superior performance on challenging, uneven surfaces.
Fuel Efficiency: AWD vs 4WD
AWD systems generally offer better fuel efficiency compared to 4WD because they are designed to operate primarily in two-wheel drive mode and engage all wheels only when needed, reducing energy consumption. In contrast, 4WD systems tend to be heavier and mechanically complex, resulting in higher fuel consumption even when off-road capability is not required. Modern AWD vehicles often incorporate electronic controls and lighter materials, further enhancing fuel economy over traditional 4WD setups.
Maintenance and Long-Term Costs
AWD systems generally require less maintenance than 4WD due to their simpler design and permanent engagement, reducing the risk of drivetrain damage from improper use. 4WD systems often demand regular servicing of components like transfer cases and locking differentials, leading to higher long-term costs. Choosing AWD can result in lower maintenance expenses and improved reliability, especially for everyday driving conditions.
Top Vehicles with AWD Systems
Top vehicles with AWD systems include the Subaru Outback, Audi Q5, and Tesla Model Y, renowned for enhanced traction and stability on various terrains. AWD systems deliver continuous power to all wheels, improving handling in wet or icy conditions without driver intervention. These vehicles combine advanced AWD technology with fuel efficiency and performance, making them popular choices for urban and off-road driving.
Top Vehicles with 4WD Systems
Top vehicles with 4WD systems include the Jeep Wrangler, Toyota Land Cruiser, and Ford Bronco, known for their robust off-road capabilities and rugged terrain adaptability. These models utilize part-time or full-time 4WD systems, providing superior traction in challenging conditions such as mud, snow, and steep inclines. Advanced 4WD technology in these vehicles often features low-range gearing and locking differentials, enhancing control and performance on demanding trails.
Choosing Between AWD and 4WD: Buyer’s Guide
AWD systems provide automatic traction control on all wheels, ideal for varied on-road conditions and light off-roading, making them suitable for daily commuters and mixed terrains. 4WD systems offer manual control of power distribution to all wheels, delivering superior performance in challenging off-road environments like mud, snow, and rocky trails, preferred by serious off-road enthusiasts. Buyers should consider driving habits, terrain, and vehicle purpose when choosing between AWD and 4WD to optimize safety, performance, and fuel efficiency.
AWD vs 4WD Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com