Fleet sales typically involve bulk transactions where vehicles are sold to organizations, businesses, or government agencies, often at discounted rates due to volume purchases. Retail sales focus on individual consumers seeking personalized services and options tailored to personal preferences and needs. Understanding the differences between fleet and retail sales is crucial for manufacturers and dealers to optimize marketing strategies and pricing models.
Table of Comparison
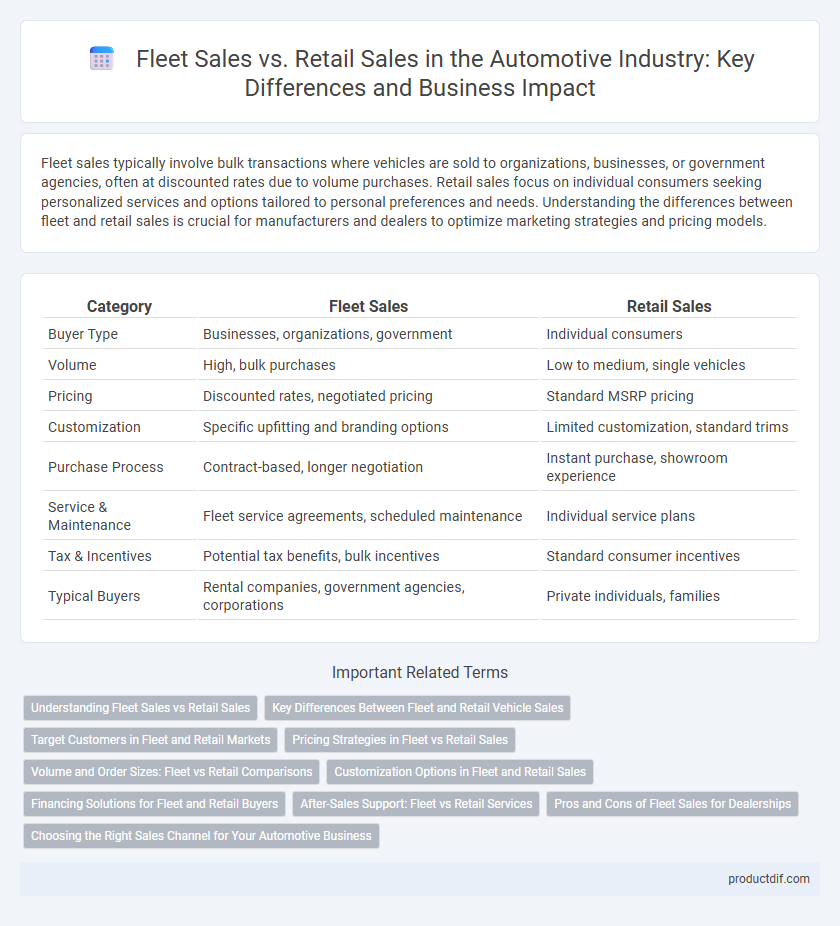
| Category | Fleet Sales | Retail Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Type | Businesses, organizations, government | Individual consumers |
| Volume | High, bulk purchases | Low to medium, single vehicles |
| Pricing | Discounted rates, negotiated pricing | Standard MSRP pricing |
| Customization | Specific upfitting and branding options | Limited customization, standard trims |
| Purchase Process | Contract-based, longer negotiation | Instant purchase, showroom experience |
| Service & Maintenance | Fleet service agreements, scheduled maintenance | Individual service plans |
| Tax & Incentives | Potential tax benefits, bulk incentives | Standard consumer incentives |
| Typical Buyers | Rental companies, government agencies, corporations | Private individuals, families |
Understanding Fleet Sales vs Retail Sales
Fleet sales involve the bulk purchase of vehicles by businesses or organizations for operational use, often resulting in discounted pricing due to volume. Retail sales target individual consumers who buy vehicles for personal use, typically involving customized options and financing plans. Understanding the differences in target buyers, transaction volume, and pricing strategies is crucial for optimizing automotive sales approaches.
Key Differences Between Fleet and Retail Vehicle Sales
Fleet sales involve bulk transactions of vehicles typically purchased by businesses, government agencies, or rental companies at discounted rates, while retail sales target individual consumers buying single vehicles at standard market prices. Fleet transactions often emphasize cost efficiency, long-term service agreements, and standardized vehicle models, whereas retail sales prioritize customization, options, and financing flexibility. The sales process for fleets is typically faster and more volume-driven, contrasting with the personalized, relationship-based approach characteristic of retail sales.
Target Customers in Fleet and Retail Markets
Fleet sales primarily target businesses, government agencies, and organizations seeking to purchase multiple vehicles for operational use, emphasizing bulk discounts and customized fleet management solutions. Retail sales focus on individual consumers or families looking for personal vehicles, prioritizing features like comfort, style, and financing options. Fleet customers demand durability, lower total cost of ownership, and service agreements, while retail customers prioritize brand preference, aesthetic appeal, and after-sales support.
Pricing Strategies in Fleet vs Retail Sales
Fleet sales pricing strategies emphasize volume discounts, negotiated contracts, and reduced per-unit costs to attract large buyers such as corporations, government agencies, and rental companies. Retail sales pricing targets individual consumers with fixed MSRP, promotional offers, and seasonal incentives tailored to maximize profit margins and appeal to demand fluctuations. Efficient pricing in fleet sales often leverages economies of scale, while retail sales rely on competitive pricing and financing options to drive consumer purchases.
Volume and Order Sizes: Fleet vs Retail Comparisons
Fleet sales typically involve large-volume orders from businesses or organizations, resulting in fewer transactions but higher overall unit volumes compared to retail sales. Retail sales focus on individual customers purchasing single vehicles or small quantities, leading to higher transaction frequency but lower average order sizes. The bulk nature of fleet orders often provides manufacturers with stable demand forecasts and economies of scale, whereas retail sales rely on market trends and consumer preferences to drive volume.
Customization Options in Fleet and Retail Sales
Fleet sales typically offer limited customization options focused on standard configurations and bulk orders to streamline production and reduce costs. Retail sales provide extensive customization choices, including trim levels, color options, and advanced features catering to individual buyer preferences. Customization in retail emphasizes personalization, whereas fleet sales prioritize functionality and consistency across vehicles.
Financing Solutions for Fleet and Retail Buyers
Fleet sales offer tailored financing solutions that accommodate bulk purchasing, flexible payment terms, and customized lease options to optimize cash flow for businesses managing multiple vehicles. Retail sales financing typically involves standardized loan products and lease agreements designed for individual buyers, emphasizing competitive interest rates and manageable monthly payments. Both sectors benefit from specialized financing programs, but fleet sales prioritize scalability and operational efficiency while retail solutions focus on personalization and affordability for single consumers.
After-Sales Support: Fleet vs Retail Services
Fleet sales typically include comprehensive after-sales support packages designed to minimize vehicle downtime through prioritized maintenance schedules and dedicated service teams. Retail sales often rely on standard after-sales services with flexible options tailored to individual customer needs and less predictable service intervals. Fleet after-sales support emphasizes cost-efficiency and operational continuity, while retail services focus on personalized care and customer convenience.
Pros and Cons of Fleet Sales for Dealerships
Fleet sales offer dealerships the advantage of selling high-volume vehicle orders to businesses, generating steady revenue and reducing marketing costs. However, these sales often come with lower profit margins per unit and limited opportunities for upselling additional features or services. While fleet clients typically require standardized vehicle configurations, retail sales allow dealerships to cater to individual preferences, potentially leading to higher overall profitability.
Choosing the Right Sales Channel for Your Automotive Business
Choosing the right sales channel for your automotive business depends on your target market, sales volume, and customer relationship strategy. Fleet sales involve bulk selling to corporations or government agencies, providing higher volume but often lower margins and longer payment cycles, while retail sales focus on individual customers, offering higher per-unit profits and direct customer interaction. Understanding these differences helps optimize inventory management, marketing efforts, and revenue streams for sustainable business growth.
Fleet Sales vs Retail Sales Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com