Fast charging significantly reduces the time required to recharge electric vehicle batteries, enabling longer trips with minimal downtime. Slow charging, while less convenient for immediate needs, is gentler on battery health and can extend the overall lifespan by minimizing heat generation and stress. Choosing between fast and slow charging depends on balancing urgent energy demands with long-term battery maintenance.
Table of Comparison
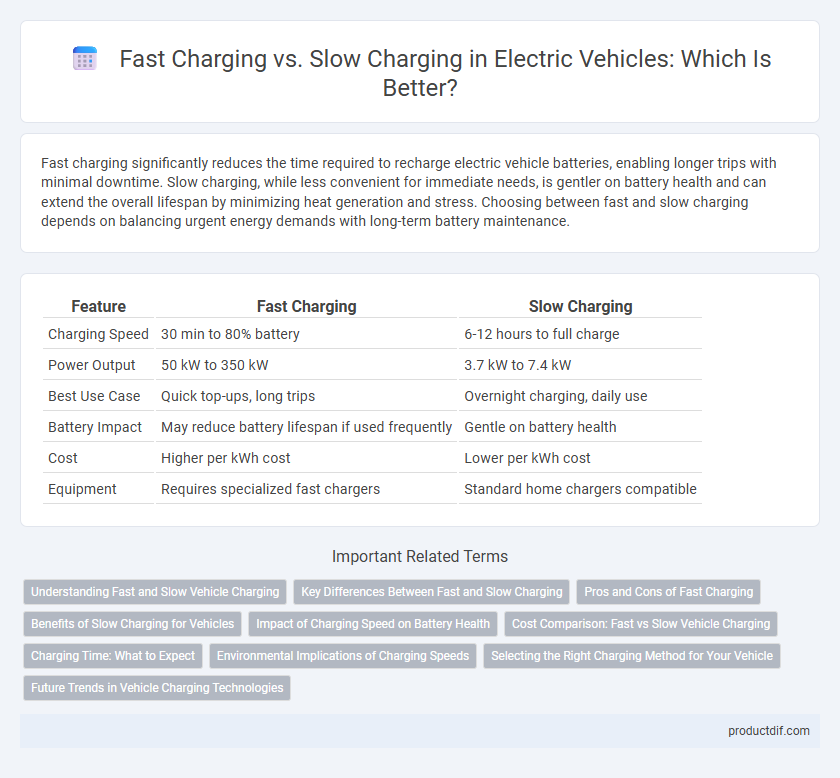
| Feature | Fast Charging | Slow Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | 30 min to 80% battery | 6-12 hours to full charge |
| Power Output | 50 kW to 350 kW | 3.7 kW to 7.4 kW |
| Best Use Case | Quick top-ups, long trips | Overnight charging, daily use |
| Battery Impact | May reduce battery lifespan if used frequently | Gentle on battery health |
| Cost | Higher per kWh cost | Lower per kWh cost |
| Equipment | Requires specialized fast chargers | Standard home chargers compatible |
Understanding Fast and Slow Vehicle Charging
Fast charging significantly reduces electric vehicle (EV) charging time by delivering high power levels, typically between 50 kW and 350 kW, enabling up to 80% charge within 20 to 40 minutes. Slow charging operates at lower power rates, generally 3.3 kW to 7.7 kW, ideal for overnight or long-duration charging sessions, preserving battery health and reducing thermal stress. Choosing between fast and slow charging depends on usage patterns, battery capacity, and the availability of charging infrastructure, balancing convenience with battery longevity.
Key Differences Between Fast and Slow Charging
Fast charging delivers high power output, typically ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, enabling electric vehicles (EVs) to reach 80% charge in 20-40 minutes, while slow charging usually offers 3 to 7 kW and requires 6-12 hours for a full charge. Fast charging generates more heat and may accelerate battery degradation due to higher current stress, whereas slow charging is gentler on battery health and optimal for overnight charging. Infrastructure cost and accessibility also differ, with fast chargers being more expensive to install and more commonly found at public stations compared to affordable and widely available slow chargers suited for home use.
Pros and Cons of Fast Charging
Fast charging significantly reduces electric vehicle (EV) charging time, often reaching 80% battery capacity within 30 minutes, making it ideal for long trips and quick turnarounds. However, frequent use of fast chargers can accelerate battery degradation, potentially shortening overall battery lifespan compared to slow charging methods. While slow charging preserves battery health through lower heat generation, it requires several hours to fully recharge, limiting convenience for drivers needing rapid energy replenishment.
Benefits of Slow Charging for Vehicles
Slow charging benefits electric vehicles by promoting battery longevity through reduced heat generation and stress on cells, leading to extended battery life and reliability. It also allows for cost-effective energy use by charging during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, maximizing efficiency. Furthermore, slow charging is ideal for overnight or long-duration parking, providing a convenient and safe method to fully recharge vehicles without the need for high-power infrastructure.
Impact of Charging Speed on Battery Health
Fast charging delivers high voltage and current to quickly replenish electric vehicle batteries but can accelerate battery degradation by increasing heat and causing lithium plating. Slow charging uses lower power levels, reducing thermal stress and promoting longer battery lifespan through more stable electrochemical reactions. Choosing the appropriate charging speed balances convenience with preserving battery capacity and overall vehicle performance.
Cost Comparison: Fast vs Slow Vehicle Charging
Fast vehicle charging typically incurs higher electricity rates due to peak demand pricing and increased infrastructure costs, making it more expensive per kWh compared to slow charging methods. Slow charging utilizes off-peak hours and standard residential electrical setups, resulting in lower operational costs and reduced wear on the vehicle battery. Cost efficiency depends on usage patterns, with slow charging favored for overnight home charging and fast charging suited for urgent, on-the-go energy replenishment despite its premium cost.
Charging Time: What to Expect
Fast charging technology can recharge electric vehicles (EVs) up to 80% battery capacity in 20 to 40 minutes, significantly reducing downtime compared to slow charging, which typically takes 6 to 12 hours for a full charge. Slow charging, using Level 1 or Level 2 chargers, provides a steady and battery-friendly charge, making it ideal for overnight home charging but less practical for quick turnarounds. Understanding the balance between fast charging speed and battery health impacts helps EV owners optimize their charging routines according to their daily driving needs.
Environmental Implications of Charging Speeds
Fast charging electric vehicles (EVs) demand higher energy output, often sourced from non-renewable grids, which can increase carbon emissions compared to slow charging that better aligns with off-peak renewable energy availability. Slow charging reduces strain on grid infrastructure, enabling more efficient integration of solar, wind, and other renewables, thus lowering overall environmental impact. Choosing slow charging also minimizes battery degradation, extending EV lifespan and reducing resource consumption associated with battery production.
Selecting the Right Charging Method for Your Vehicle
Fast charging offers rapid energy replenishment ideal for long trips or urgent travel, utilizing high-power DC chargers that can charge a typical electric vehicle (EV) battery to 80% in 30 minutes. Slow charging, typically using Level 1 or Level 2 chargers, provides a gentler charge that preserves battery longevity and is well-suited for overnight home charging or daily commutes. Selecting the right charging method depends on your driving patterns, battery health priorities, and access to charging infrastructure to balance convenience and efficiency.
Future Trends in Vehicle Charging Technologies
Fast charging technologies are rapidly advancing with innovations like ultra-high power chargers exceeding 350 kW, significantly reducing electric vehicle (EV) charging times to under 15 minutes. Wireless charging and smart grid integration are emerging trends, enabling seamless energy transfer and efficient load balancing to support widespread EV adoption. Battery advancements, such as solid-state batteries, promise to enhance charging speeds and durability, shaping the future landscape of vehicle charging infrastructure.
Fast charging vs Slow charging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com