Connected cars leverage real-time data exchange through internet and cloud services, enhancing navigation, diagnostics, and safety features compared to standalone systems that operate independently without external communication. Standalone systems rely solely on onboard sensors and internal processing, limiting their ability to access live updates or interact with other vehicles and infrastructure. The integration of connected technology enables smarter, more responsive driving experiences that standalone systems cannot match.
Table of Comparison
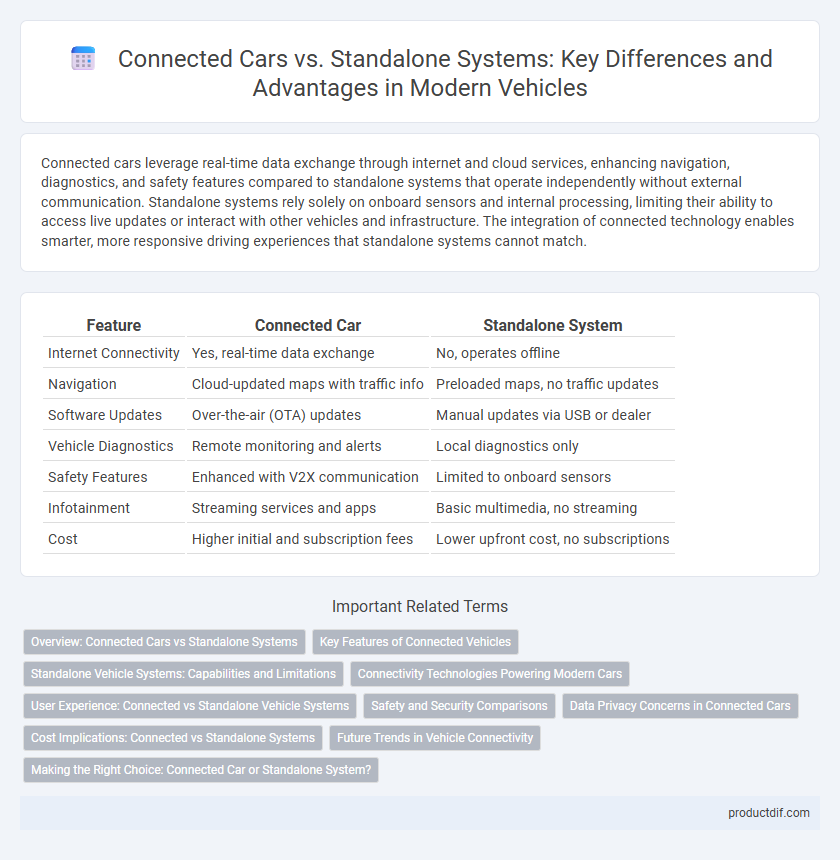
| Feature | Connected Car | Standalone System |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Connectivity | Yes, real-time data exchange | No, operates offline |
| Navigation | Cloud-updated maps with traffic info | Preloaded maps, no traffic updates |
| Software Updates | Over-the-air (OTA) updates | Manual updates via USB or dealer |
| Vehicle Diagnostics | Remote monitoring and alerts | Local diagnostics only |
| Safety Features | Enhanced with V2X communication | Limited to onboard sensors |
| Infotainment | Streaming services and apps | Basic multimedia, no streaming |
| Cost | Higher initial and subscription fees | Lower upfront cost, no subscriptions |
Overview: Connected Cars vs Standalone Systems
Connected cars leverage real-time data exchange through wireless networks, enabling features like remote diagnostics, navigation updates, and enhanced safety via Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, while standalone systems operate independently without continuous connectivity. Connected car technologies integrate cloud computing, over-the-air updates, and Internet of Things (IoT) frameworks to provide dynamic and personalized user experiences. Standalone systems rely on built-in sensors and onboard computing power, offering reliable but limited functionality compared to the adaptive capabilities of connected car platforms.
Key Features of Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles integrate advanced telematics, real-time data exchange, and cloud-based computing to enhance safety, navigation, and driver assistance. Key features include Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, over-the-air software updates, and integration with smart infrastructure. These capabilities enable predictive maintenance, improved traffic management, and seamless infotainment systems, distinguishing connected cars from standalone vehicles that rely solely on onboard sensors and limited computing power.
Standalone Vehicle Systems: Capabilities and Limitations
Standalone vehicle systems operate independently without relying on external connectivity, utilizing onboard sensors, cameras, and processors to manage driving functions such as navigation, safety alerts, and basic autopilot features. These systems offer enhanced privacy and security by minimizing data transmission but face limitations in real-time traffic updates, remote diagnostics, and over-the-air software updates. Their capabilities are often constrained to pre-programmed scenarios, reducing adaptability compared to connected cars that leverage cloud-based data for dynamic decision-making.
Connectivity Technologies Powering Modern Cars
Connected cars leverage advanced connectivity technologies such as 5G, LTE, and dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) to enable real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud services. Standalone systems, in contrast, operate independently without external network integration, relying solely on onboard sensors and processors for functionality. The integration of V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication protocols significantly enhances the capabilities of connected cars by improving safety, navigation, and infotainment features.
User Experience: Connected vs Standalone Vehicle Systems
Connected car systems enhance user experience by offering real-time traffic updates, seamless smartphone integration, and remote vehicle diagnostics, enabling smarter and more efficient driving. Standalone vehicle systems, while reliable for basic functions like navigation and entertainment, lack the dynamic data exchange and personalization features that connected systems provide. The integration of cloud-based services in connected cars transforms user interaction by delivering tailored content, over-the-air updates, and enhanced safety alerts, surpassing the limitations of standalone systems.
Safety and Security Comparisons
Connected cars leverage real-time data exchange and cloud-based analytics to enhance safety features such as collision avoidance and emergency response, outperforming standalone systems that rely solely on onboard sensors. Standalone systems provide a controlled environment with reduced exposure to cyber threats but lack the adaptive security updates and predictive analytics available in connected car platforms. The integration of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication in connected cars significantly improves situational awareness, while standalone systems depend on limited local inputs, affecting their ability to proactively mitigate security risks.
Data Privacy Concerns in Connected Cars
Connected cars continuously exchange data with external networks, raising significant privacy concerns due to potential unauthorized access and data breaches. Standalone systems operate without constant connectivity, reducing exposure to cyber threats but limiting real-time updates and remote diagnostics. Ensuring robust encryption and stringent data handling policies is critical to safeguarding user information in connected vehicle environments.
Cost Implications: Connected vs Standalone Systems
Connected car systems typically incur higher upfront costs due to integrated telematics, real-time data processing, and cloud connectivity infrastructure, but they offer long-term savings through enhanced predictive maintenance and over-the-air updates. Standalone systems have lower initial expenses since they operate independently without continuous network connections, yet they may require more frequent manual updates and repairs, increasing overall maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that connected systems optimize operational efficiency while standalone systems present budget-friendly solutions for basic vehicle functionality.
Future Trends in Vehicle Connectivity
Connected cars leverage integrated telecommunications and internet access to enable real-time data exchange, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, and enhanced driver assistance systems, driving the future of autonomous and smart transportation. Standalone systems operate independently without continuous network connectivity, limiting features like over-the-air updates and cloud-based diagnostics. Future trends prioritize 5G-enabled connected vehicles, edge computing for low-latency processing, and AI-driven predictive maintenance to create safer, smarter, and more efficient roadways.
Making the Right Choice: Connected Car or Standalone System?
Choosing between a connected car and a standalone system depends on the desired level of connectivity, data accessibility, and user control. Connected cars offer real-time data exchange, enhanced navigation, and over-the-air updates, leveraging IoT integration for an improved driving experience. Standalone systems provide localized functionality without reliance on cloud networks, offering greater privacy and reliability in isolated environments.
Connected Car vs Standalone System Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com