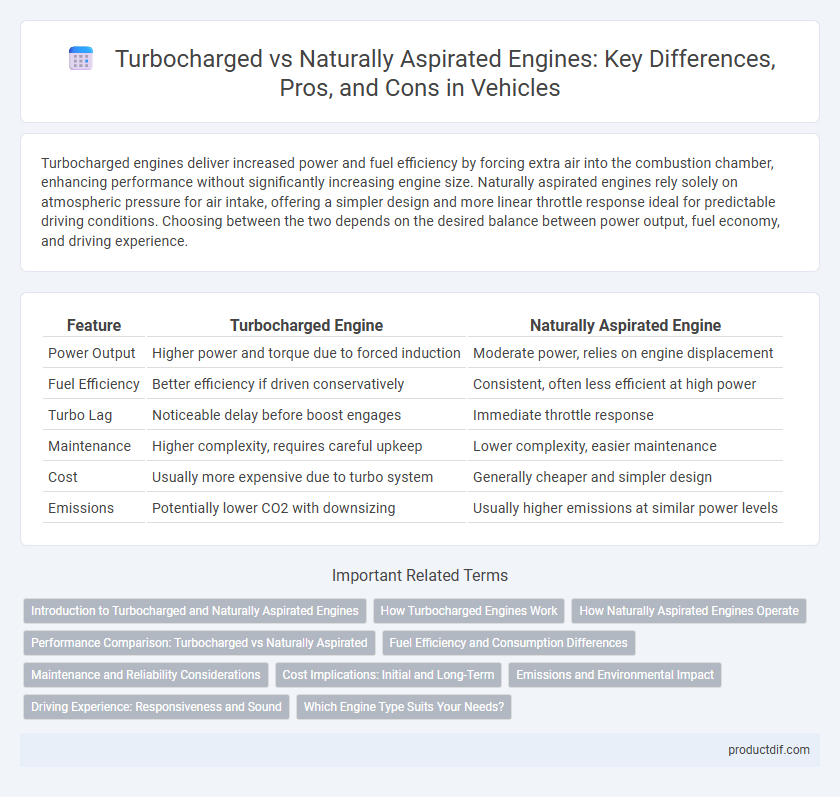
Turbocharged engines deliver increased power and fuel efficiency by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber, enhancing performance without significantly increasing engine size. Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure for air intake, offering a simpler design and more linear throttle response ideal for predictable driving conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance between power output, fuel economy, and driving experience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Turbocharged Engine | Naturally Aspirated Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Higher power and torque due to forced induction | Moderate power, relies on engine displacement |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better efficiency if driven conservatively | Consistent, often less efficient at high power |
| Turbo Lag | Noticeable delay before boost engages | Immediate throttle response |
| Maintenance | Higher complexity, requires careful upkeep | Lower complexity, easier maintenance |
| Cost | Usually more expensive due to turbo system | Generally cheaper and simpler design |
| Emissions | Potentially lower CO2 with downsizing | Usually higher emissions at similar power levels |
Introduction to Turbocharged and Naturally Aspirated Engines
Turbocharged engines use a turbine-driven forced induction system to compress air entering the engine, increasing power output and efficiency compared to naturally aspirated engines, which rely solely on atmospheric pressure for air intake. Turbochargers enhance performance by recycling exhaust gases to spin a turbine that forces more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in higher horsepower and torque. Naturally aspirated engines offer simpler design and more linear throttle response but generally provide less power and lower fuel efficiency than turbocharged counterparts.
How Turbocharged Engines Work
Turbocharged engines utilize a turbine driven by exhaust gases to compress incoming air, significantly increasing the oxygen content entering the combustion chamber. This process enables more fuel to be burned efficiently, resulting in higher power output and improved engine performance compared to naturally aspirated engines. The turbocharger's ability to recycle exhaust energy enhances fuel economy and reduces emissions, making it a key component in modern high-performance and fuel-efficient vehicles.
How Naturally Aspirated Engines Operate
Naturally aspirated engines operate by drawing air into the combustion chamber solely through atmospheric pressure without the aid of forced induction like turbochargers or superchargers. The engine relies on the vacuum created during the intake stroke to pull air through the intake manifold and into the cylinders. This process results in a linear throttle response and typically lower complexity compared to turbocharged engines, though it may limit maximum power output due to less air density at higher altitudes or engine speeds.
Performance Comparison: Turbocharged vs Naturally Aspirated
Turbocharged engines deliver significantly higher power and torque by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, improving acceleration and overall performance compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines provide linear power delivery and lower complexity, but they often lack the high-end thrust and fuel efficiency benefits of turbocharged systems. Performance metrics typically show turbocharged engines achieving up to 30% more power output and better fuel economy under similar displacement conditions.
Fuel Efficiency and Consumption Differences
Turbocharged engines provide improved fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for a smaller engine displacement while maintaining power output. Naturally aspirated engines typically consume more fuel as they rely solely on air intake at atmospheric pressure, resulting in less efficient combustion at higher power demands. Studies show turbocharged engines can achieve up to 20% better fuel economy compared to naturally aspirated counterparts under similar driving conditions.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Turbocharged engines require more frequent oil changes and use higher-quality synthetic oils due to increased operating temperatures and pressures, which can affect overall maintenance costs and intervals. Naturally aspirated engines exhibit simpler designs with fewer components prone to failure, resulting in generally lower maintenance requirements and enhanced long-term reliability. The complexity of turbo systems and potential turbocharger wear necessitate careful monitoring to prevent issues such as boost leaks or turbo lag, impacting engine durability.
Cost Implications: Initial and Long-Term
Turbocharged engines generally have higher initial costs due to advanced components like turbochargers and intercoolers, increasing manufacturing complexity. Long-term maintenance expenses also tend to rise with turbocharged engines, involving pricier repairs for turbo units and associated cooling systems. Naturally aspirated engines offer lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance, often resulting in reduced long-term financial commitments for owners.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Turbocharged engines deliver improved fuel efficiency and lower CO2 emissions by optimizing air intake and combustion compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines typically produce higher emissions due to less efficient fuel usage and incomplete combustion at varying RPMs. Advances in turbocharging technology contribute to reduced environmental impact by enabling smaller engine sizes without sacrificing power output.
Driving Experience: Responsiveness and Sound
Turbocharged engines deliver rapid throttle response and increased torque, enhancing acceleration and overall driving excitement. Naturally aspirated engines offer a linear power delivery with immediate feedback, prized for precise control and a more natural engine sound. The distinct auditory experience of turbocharged engines includes turbo whine and blow-off valve sounds, while naturally aspirated engines often provide a richer, more mechanical exhaust note.
Which Engine Type Suits Your Needs?
Choosing between a turbocharged engine and a naturally aspirated engine depends on your driving preferences and performance needs. Turbocharged engines deliver higher power and fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, making them ideal for enthusiasts seeking acceleration and better fuel economy. Naturally aspirated engines offer simpler mechanics and more linear power delivery, which suits drivers valuing reliability and predictability in everyday driving conditions.
Turbocharged Engine vs Naturally Aspirated Engine Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com