Hydraulic tools deliver higher power and precision by using fluid pressure, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and industrial maintenance. Pneumatic tools rely on compressed air, offering lighter weight and faster operation, which is advantageous for tasks requiring mobility and speed. Choosing between hydraulic and pneumatic tools depends on the required force, application environment, and portability needs.
Table of Comparison
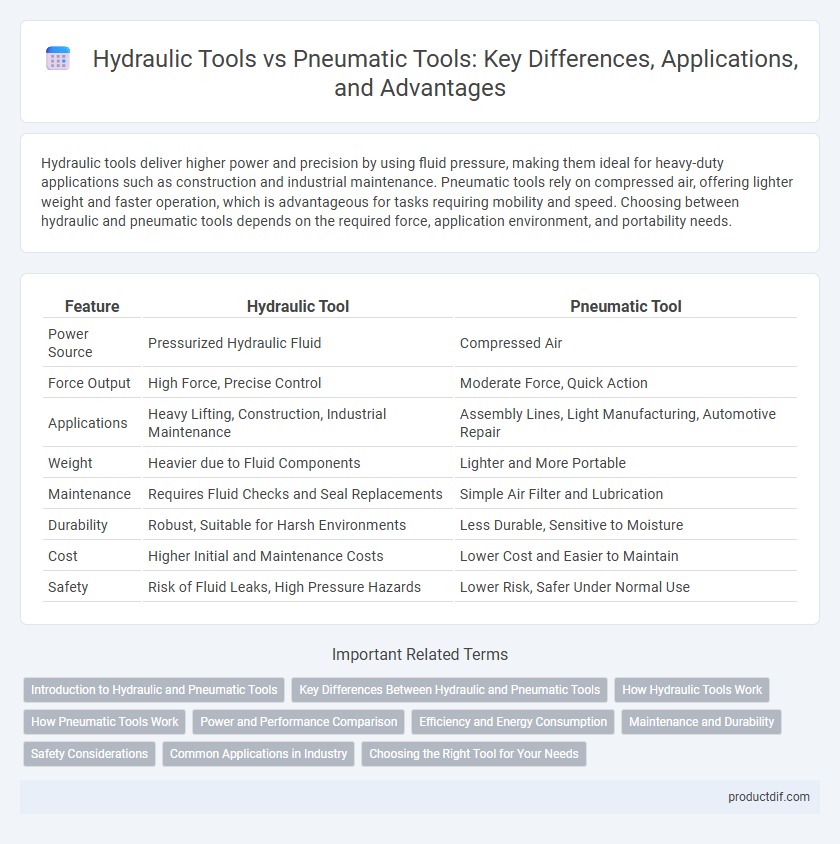
| Feature | Hydraulic Tool | Pneumatic Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Pressurized Hydraulic Fluid | Compressed Air |
| Force Output | High Force, Precise Control | Moderate Force, Quick Action |
| Applications | Heavy Lifting, Construction, Industrial Maintenance | Assembly Lines, Light Manufacturing, Automotive Repair |
| Weight | Heavier due to Fluid Components | Lighter and More Portable |
| Maintenance | Requires Fluid Checks and Seal Replacements | Simple Air Filter and Lubrication |
| Durability | Robust, Suitable for Harsh Environments | Less Durable, Sensitive to Moisture |
| Cost | Higher Initial and Maintenance Costs | Lower Cost and Easier to Maintain |
| Safety | Risk of Fluid Leaks, High Pressure Hazards | Lower Risk, Safer Under Normal Use |
Introduction to Hydraulic and Pneumatic Tools
Hydraulic tools utilize fluid pressure to generate powerful and precise force, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and industrial machinery. Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, offering lightweight, versatile solutions commonly used in automotive and assembly line tasks. Both systems provide efficient energy transfer but differ in power delivery, maintenance requirements, and suitable environments.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Tools
Hydraulic tools operate using fluid pressure, providing higher force output and precision ideal for heavy-duty applications, while pneumatic tools rely on compressed air, offering lighter weight and faster operation suited for repetitive tasks. Hydraulic systems are generally more powerful with slower response times, whereas pneumatic tools excel in speed and ease of maintenance but deliver less torque. Understanding the pressure source, force capacity, response time, and maintenance complexity highlights crucial distinctions between hydraulic and pneumatic tools for optimal tool selection.
How Hydraulic Tools Work
Hydraulic tools operate by utilizing pressurized fluid, typically oil, to generate force and motion through cylinders and pistons, enabling powerful and precise applications. This fluid power mechanism allows hydraulic tools to deliver higher torque and lifting capacity compared to pneumatic tools, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks such as construction and industrial machinery maintenance. The efficiency of hydraulic systems comes from the incompressibility of fluids, which ensures consistent and controlled power output under varying load conditions.
How Pneumatic Tools Work
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air delivered through a hose from an air compressor, which powers the tool's internal motor or piston to perform tasks like drilling, grinding, or fastening. The air pressure converts energy into mechanical work by driving a piston or turbine, enabling consistent and powerful tool operation. This mechanism offers advantages in speed, torque, and lightweight design compared to hydraulic tools, which rely on fluid pressure.
Power and Performance Comparison
Hydraulic tools deliver higher power and torque compared to pneumatic tools due to their use of pressurized fluid, enabling more precise control and greater force output for heavy-duty applications. Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, providing faster speed but less torque, making them ideal for lighter tasks and rapid tool cycling. The choice between hydraulic and pneumatic tools depends on performance requirements, with hydraulics favored for maximum power and durability in demanding environments.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Hydraulic tools deliver higher efficiency by generating greater force through incompressible fluid, resulting in more precise and powerful performance compared to pneumatic tools, which rely on compressed air. Energy consumption in hydraulic systems tends to be lower since they maintain consistent pressure without significant losses, whereas pneumatic tools often experience energy inefficiencies due to air compression and leakage. Choosing hydraulic tools can optimize energy usage and operational efficiency in heavy-duty applications where sustained power is critical.
Maintenance and Durability
Hydraulic tools require regular inspection of hydraulic fluid levels and seals to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance, which contributes to longer durability under heavy loads. Pneumatic tools demand frequent lubrication of air motors and filters to avoid moisture buildup and wear, affecting their maintenance frequency but offering lightweight operation. Both tools benefit from proper upkeep, but hydraulic tools typically offer greater durability in high-pressure environments due to their robust construction.
Safety Considerations
Hydraulic tools operate under high pressure using incompressible fluids, posing risks of fluid injection injuries and requiring robust containment to prevent leaks, while pneumatic tools use compressed air, which significantly reduces the risk of hazardous leaks but can cause flying debris or noise-related hazards. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and eye protection is essential for both tool types due to the potential for sudden tool movement or pressure release. Regular inspection and maintenance of seals, hoses, and fittings in hydraulic tools are critical to prevent dangerous failures, whereas ensuring proper air pressure regulation in pneumatic tools minimizes the chances of accidental tool ejections or hose whip.
Common Applications in Industry
Hydraulic tools excel in heavy-duty applications such as construction, mining, and industrial manufacturing due to their high force output and precise control. Pneumatic tools are commonly used in automotive repair, assembly lines, and light manufacturing for tasks like fastening, grinding, and drilling because of their lightweight design and ease of maintenance. Both tool types are integral to industrial operations where efficiency and reliability are critical.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Hydraulic tools offer superior power and precision by using pressurized fluid, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring consistent force. Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, providing lightweight, portable options suited for tasks demanding speed and flexibility. Choosing the right tool depends on factors like required torque, portability, maintenance, and the specific application environment.
Hydraulic Tool vs Pneumatic Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com