Corded tools provide consistent power and unlimited runtime, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and prolonged use without interruption. Cordless tools offer enhanced portability and convenience, allowing for easy maneuverability and use in remote locations without access to electrical outlets. Choosing between corded and cordless tools depends on the balance between power needs and mobility requirements for specific pet care tasks.
Table of Comparison
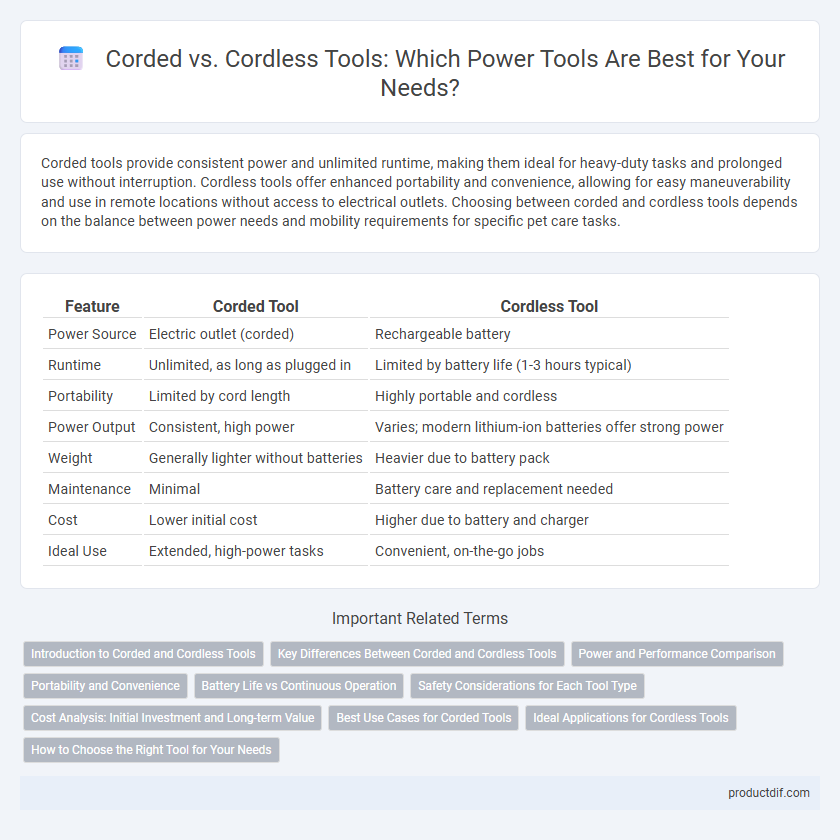
| Feature | Corded Tool | Cordless Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric outlet (corded) | Rechargeable battery |
| Runtime | Unlimited, as long as plugged in | Limited by battery life (1-3 hours typical) |
| Portability | Limited by cord length | Highly portable and cordless |
| Power Output | Consistent, high power | Varies; modern lithium-ion batteries offer strong power |
| Weight | Generally lighter without batteries | Heavier due to battery pack |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Battery care and replacement needed |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher due to battery and charger |
| Ideal Use | Extended, high-power tasks | Convenient, on-the-go jobs |
Introduction to Corded and Cordless Tools
Corded tools rely on a continuous power supply through an electric cord, providing consistent energy for extended use without downtime. Cordless tools operate on rechargeable batteries, offering enhanced portability and flexibility, especially in locations without easy access to power outlets. Both types serve essential roles in various tasks, with corded tools excelling in power demands and cordless tools in convenience and mobility.
Key Differences Between Corded and Cordless Tools
Corded tools provide consistent power and unlimited runtime due to their direct connection to electrical outlets, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Cordless tools offer enhanced portability and convenience with rechargeable batteries, but their performance depends on battery life and charge cycles. Choosing between corded and cordless tools hinges on the balance between power needs and mobility requirements for specific applications.
Power and Performance Comparison
Corded tools deliver consistent, high voltage power directly from an electrical outlet, ensuring sustained performance during extended use without power loss. Cordless tools rely on rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, offering portability but often sacrificing runtime and power intensity compared to corded models. For heavy-duty tasks requiring continuous, high torque output, corded tools typically outperform cordless alternatives, while cordless tools provide greater flexibility for light to medium-duty applications.
Portability and Convenience
Cordless tools offer superior portability by eliminating the need for power outlets, enabling use in remote or tight locations without restriction. Corded tools, while often providing consistent power and extended runtime, limit mobility due to dependency on electrical cords. For tasks requiring mobility and ease of use, cordless tools deliver unmatched convenience and flexibility.
Battery Life vs Continuous Operation
Corded tools provide unlimited continuous operation since they draw power directly from an electrical outlet, eliminating concerns about battery life or charging interruptions. Cordless tools rely on rechargeable batteries, which require periodic recharging and can limit usage time depending on battery capacity and power consumption. Battery advancements have improved cordless tool runtime, but corded tools remain ideal for tasks demanding extended, uninterrupted operation.
Safety Considerations for Each Tool Type
Corded tools offer consistent power without battery concerns but require careful management of cords to prevent tripping hazards and electrical shocks, especially in wet environments. Cordless tools enhance mobility and reduce cord entanglement risks, yet users must monitor battery condition to avoid sudden power loss and potential tool malfunction. Proper use of grounding, insulation, and battery maintenance is essential to ensure safety when operating either corded or cordless power tools.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Value
Corded tools typically have a lower initial investment compared to cordless tools due to their simpler design and absence of battery technology. Cordless tools incur higher upfront costs because of rechargeable batteries and advanced electronics but offer greater long-term value through portability and convenience. Evaluating cost effectiveness involves considering battery lifespan, replacement expenses, and potential productivity gains over time.
Best Use Cases for Corded Tools
Corded tools excel in applications demanding continuous power and high torque, such as heavy-duty drilling, cutting, and grinding tasks in construction and manufacturing industries. These tools are ideal for indoor projects or workshops where access to power outlets is reliable, enabling extended operation without battery interruptions. They outperform cordless alternatives in situations requiring sustained energy output and consistent performance, making them essential for professionals handling intensive workloads.
Ideal Applications for Cordless Tools
Cordless tools excel in applications requiring mobility and convenience, such as outdoor projects, remote job sites, and tasks without easy access to power outlets. Their battery-powered design allows for quick maneuvering in tight spaces and reduces downtime caused by cord management. Ideal uses include light to medium-duty tasks like drilling, fastening, and trimming, where flexibility and portability are essential.
How to Choose the Right Tool for Your Needs
Selecting between a corded tool and a cordless tool depends primarily on your work environment and power requirements. Corded tools provide consistent power and are ideal for long-duration tasks or heavy-duty projects, while cordless tools offer portability and convenience for quick, mobile jobs. Assess factors like battery life, power output, and task complexity to make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs.
Corded Tool vs Cordless Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com