Public cloud offers scalable resources and cost-efficiency by sharing infrastructure across multiple users, ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads and limited IT management. Private cloud provides enhanced security and customization through dedicated resources tailored to an organization's specific needs, suitable for industries with strict compliance requirements. Choosing between public and private cloud depends on factors like data sensitivity, control needs, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
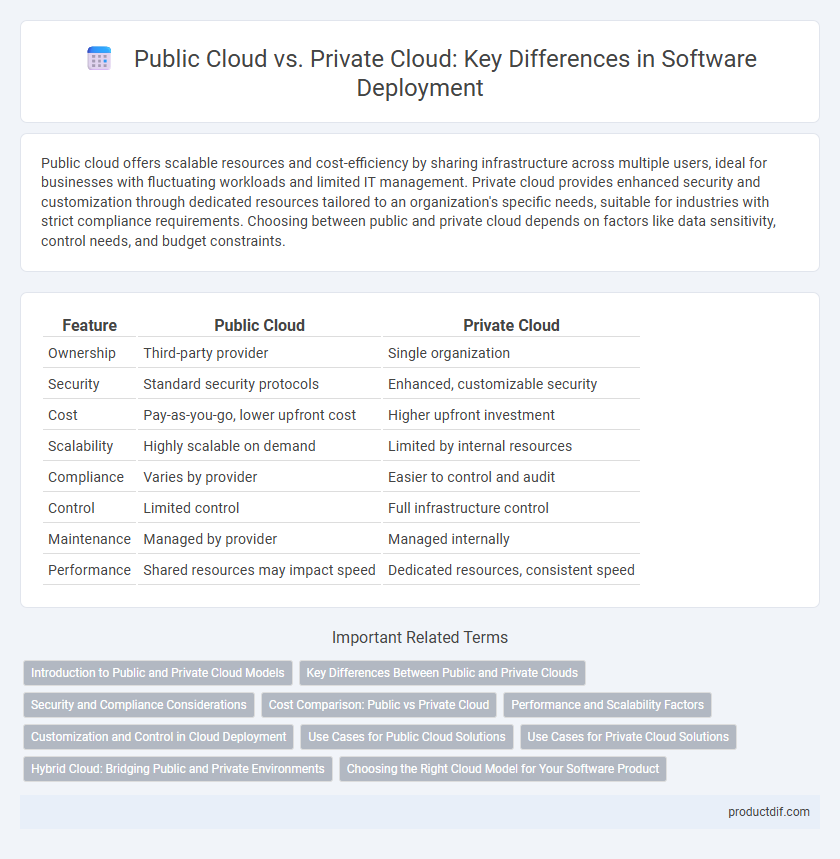
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Third-party provider | Single organization |
| Security | Standard security protocols | Enhanced, customizable security |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, lower upfront cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Scalability | Highly scalable on demand | Limited by internal resources |
| Compliance | Varies by provider | Easier to control and audit |
| Control | Limited control | Full infrastructure control |
| Maintenance | Managed by provider | Managed internally |
| Performance | Shared resources may impact speed | Dedicated resources, consistent speed |
Introduction to Public and Private Cloud Models
Public cloud models offer scalable, on-demand computing resources hosted by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, delivering cost efficiency and flexibility for diverse workloads. Private cloud models involve dedicated infrastructure managed internally or by a third-party provider, ensuring enhanced security, compliance, and control suitable for organizations with strict regulatory requirements. Hybrid cloud strategies often integrate both public and private clouds, optimizing performance, cost, and data governance across IT ecosystems.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Clouds
Public clouds offer scalable, multi-tenant environments managed by third-party providers, enabling cost-effective resource allocation and ease of access. Private clouds provide dedicated infrastructure with enhanced security and customization options, suitable for organizations with strict compliance and data privacy requirements. Key differences include ownership, level of control, security measures, and cost structure, impacting deployment choices based on operational needs.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Public cloud environments offer extensive security measures including advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring, but may present compliance challenges depending on industry-specific regulations like HIPAA or GDPR due to data residency and control limitations. Private clouds provide enhanced control over security protocols and data governance, making them preferable for organizations with stringent compliance requirements or sensitive data handling. Understanding the trade-offs between scalability in public clouds and customized security in private clouds is critical for aligning cloud strategy with regulatory mandates.
Cost Comparison: Public vs Private Cloud
Public cloud services typically offer lower upfront costs due to their pay-as-you-go pricing model, reducing the need for significant capital investment in hardware. Private clouds often involve higher initial expenses for infrastructure setup and ongoing maintenance, but provide better cost predictability and control over resource allocation. Organizations weighing public vs private cloud costs should consider scalability needs, security requirements, and long-term operational expenses to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Performance and Scalability Factors
Public cloud platforms offer high scalability with virtually unlimited resources, enabling dynamic performance adjustments based on demand through multi-tenant architectures and automated resource allocation. Private cloud environments deliver more consistent performance by dedicating hardware solely to one organization, reducing latency and enhancing security but often with limited scalability compared to public options. Performance optimization in public clouds relies on elasticity and global distribution, while private clouds emphasize control and predictability, making the choice dependent on specific workload and scalability requirements.
Customization and Control in Cloud Deployment
Public cloud platforms offer scalable resources with standardized configurations, limiting deep customization and granular control over the environment. Private cloud solutions provide enhanced customization options and full control over hardware, software, and security settings, making them ideal for organizations with specific compliance and performance requirements. Enterprises seeking tailored cloud deployments prioritize private clouds to meet stringent governance and operational needs.
Use Cases for Public Cloud Solutions
Public cloud solutions excel in scalability and cost efficiency, making them ideal for web hosting, SaaS applications, and disaster recovery. Businesses leverage their global accessibility and rapid provisioning to support dynamic workloads and fluctuating demand. Industries such as e-commerce, media streaming, and startups benefit from the pay-as-you-go model of public cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Use Cases for Private Cloud Solutions
Private cloud solutions are ideal for enterprises requiring enhanced security, compliance, and control over sensitive data, such as financial institutions and healthcare providers. Organizations with predictable workloads benefit from private clouds due to customizable infrastructure and dedicated resources that ensure consistent performance. Use cases also include development and testing environments, where isolation from public cloud variability helps maintain reliability and security during software lifecycle processes.
Hybrid Cloud: Bridging Public and Private Environments
Hybrid cloud integrates public cloud services with private cloud infrastructure, enabling seamless data and application portability across environments. This architecture enhances scalability by leveraging public cloud resources while maintaining security and compliance through private cloud control. Enterprises benefit from optimized workload distribution, improved disaster recovery options, and cost-efficiency by dynamically allocating resources between public and private clouds.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Software Product
Selecting the appropriate cloud model for your software product hinges on factors such as security requirements, scalability, and budget constraints. Public clouds offer cost-effective scalability and ease of access, making them ideal for startups and applications with variable workloads, whereas private clouds provide enhanced security and control suited for enterprises handling sensitive data. Hybrid cloud solutions combine the advantages of both models, enabling flexible resource allocation while maintaining strict compliance and performance standards.
Public Cloud vs Private Cloud Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com