Feature flags enable developers to control software functionality dynamically, allowing selective user access and gradual rollouts without redeploying code. Hard releases deploy new features to all users simultaneously, increasing risk and reducing flexibility in managing potential issues. Leveraging feature flags improves testing, rollback capabilities, and user experience by minimizing disruptions during software updates.
Table of Comparison
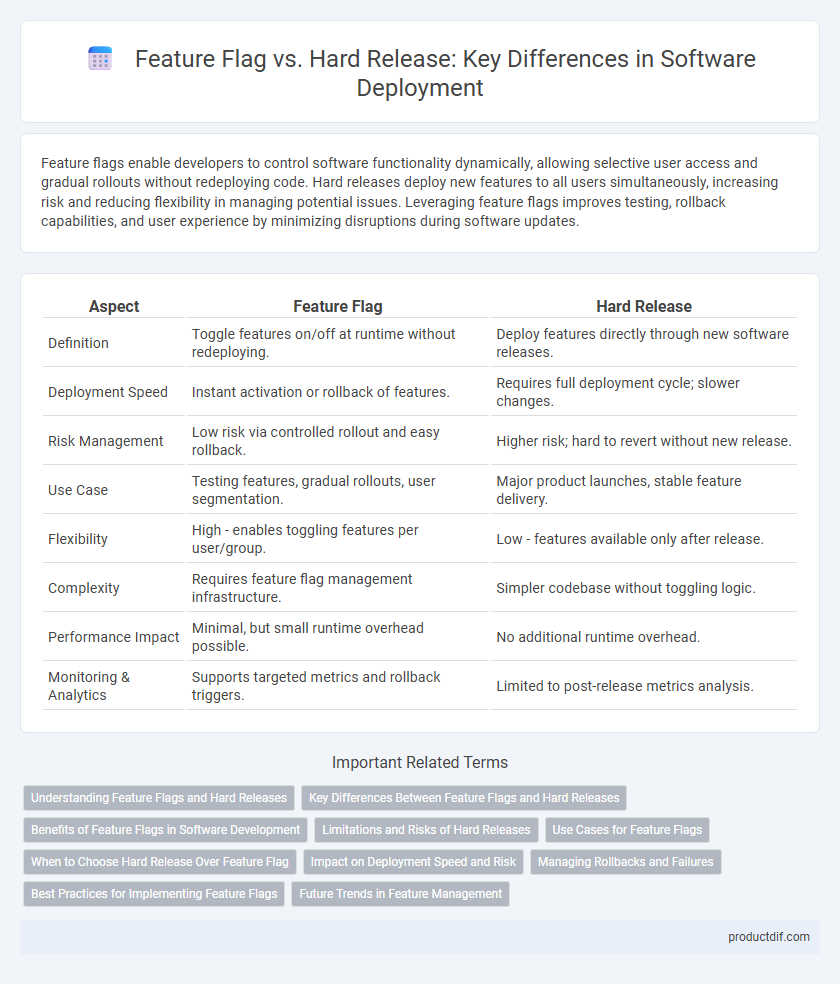
| Aspect | Feature Flag | Hard Release |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toggle features on/off at runtime without redeploying. | Deploy features directly through new software releases. |
| Deployment Speed | Instant activation or rollback of features. | Requires full deployment cycle; slower changes. |
| Risk Management | Low risk via controlled rollout and easy rollback. | Higher risk; hard to revert without new release. |
| Use Case | Testing features, gradual rollouts, user segmentation. | Major product launches, stable feature delivery. |
| Flexibility | High - enables toggling features per user/group. | Low - features available only after release. |
| Complexity | Requires feature flag management infrastructure. | Simpler codebase without toggling logic. |
| Performance Impact | Minimal, but small runtime overhead possible. | No additional runtime overhead. |
| Monitoring & Analytics | Supports targeted metrics and rollback triggers. | Limited to post-release metrics analysis. |
Understanding Feature Flags and Hard Releases
Feature flags enable developers to toggle features on or off in real-time, allowing for gradual rollouts, targeted testing, and quick rollbacks without redeploying code. Hard releases involve deploying features directly to all users at once, often increasing the risk of widespread issues due to lack of incremental control. Understanding the strategic use of feature flags versus hard releases is essential for balancing risk, user experience, and deployment agility.
Key Differences Between Feature Flags and Hard Releases
Feature flags allow developers to enable or disable features dynamically without deploying new code, offering granular control over feature rollout and user segmentation. Hard releases require full deployment of new code versions, making feature changes less flexible and increasing the risk of introducing bugs to all users simultaneously. Feature flags improve continuous delivery by enabling incremental feature testing and rollback, whereas hard releases follow a more rigid deployment cycle with less operational agility.
Benefits of Feature Flags in Software Development
Feature flags enable rapid and controlled feature deployment by toggling functionalities without full-scale releases, reducing risk and improving continuous integration workflows. They facilitate targeted testing and gradual rollouts, enhancing user feedback and minimizing disruptions. This approach accelerates innovation while maintaining system stability and improving overall release management efficiency.
Limitations and Risks of Hard Releases
Hard releases in software deployment pose significant limitations and risks, including the inability to quickly rollback changes if new features cause failures or performance degradation. They require extensive pre-release testing and coordination, increasing the chance of deployment errors and extended downtime. Lack of flexibility in hard releases also leads to challenges in gradual user exposure, potentially resulting in widespread impact from undetected bugs or compatibility issues.
Use Cases for Feature Flags
Feature flags enable granular control over feature rollout, allowing developers to test new functionality in production with minimal risk and quickly toggle features on or off based on user feedback or performance metrics. They support targeted releases to specific user segments, enhancing A/B testing, canary deployments, and continuous integration workflows without requiring full application redeployments. This method improves agility in software delivery, reduces downtime, and facilitates safer, incremental updates compared to traditional hard releases.
When to Choose Hard Release Over Feature Flag
Hard release is preferred when deploying minor updates with minimal risk or when the development team lacks the infrastructure for feature flag management. It suits scenarios requiring immediate, full-feature availability without incremental rollouts. Opt for hard releases in environments prioritizing simplicity and rapid deployment over granular control.
Impact on Deployment Speed and Risk
Feature flags enable incremental deployment by toggling functionality on or off, significantly accelerating deployment speed while minimizing risk through controlled rollouts and immediate rollback options. Hard releases require fully completed code, often resulting in longer deployment cycles and increased risk due to the absence of gradual exposure or easy rollback mechanisms. Leveraging feature flags reduces downtime and mitigates the impact of potential bugs, enhancing continuous integration and delivery processes.
Managing Rollbacks and Failures
Feature flags enable granular control over software rollouts, allowing teams to disable specific features instantly without redeploying code, which simplifies managing rollbacks and minimizing downtime. In contrast, hard releases require full version rollbacks in case of failures, often leading to longer recovery times and increased risk of user disruption. Implementing feature flags enhances failure isolation and accelerates issue resolution, improving overall release robustness.
Best Practices for Implementing Feature Flags
Feature flags enable continuous delivery by allowing developers to toggle features on or off without deploying new code, reducing risks associated with hard releases. Best practices include implementing granular flag management, establishing clear ownership and lifecycle policies, and integrating feature flags with automated testing and monitoring systems. Maintaining a cleanup strategy to remove obsolete flags prevents technical debt and ensures scalable, maintainable software development workflows.
Future Trends in Feature Management
Feature flag technology is rapidly evolving, enabling dynamic, granular control over software deployment and user experience customization that surpasses traditional hard release methods. Anticipated future trends highlight increased integration of AI-driven analytics to predict feature impact and optimize rollout strategies, enhancing continuous delivery environments. Emphasis on security, compliance, and real-time performance monitoring will further transform feature management into a proactive, data-driven process.
Feature Flag vs Hard Release Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com