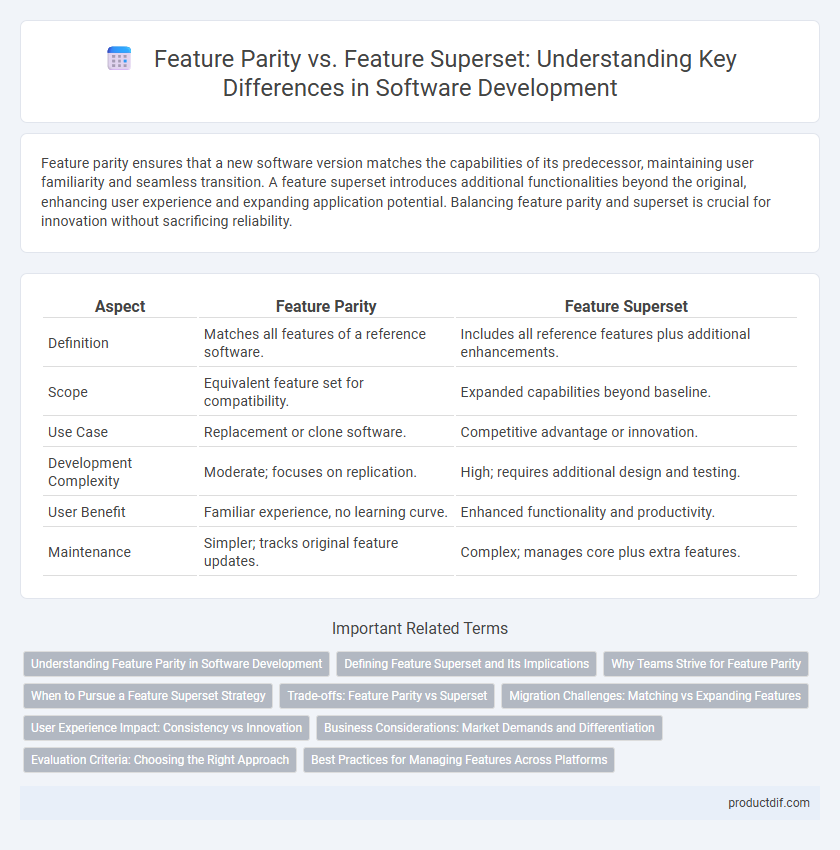
Feature parity ensures that a new software version matches the capabilities of its predecessor, maintaining user familiarity and seamless transition. A feature superset introduces additional functionalities beyond the original, enhancing user experience and expanding application potential. Balancing feature parity and superset is crucial for innovation without sacrificing reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Feature Parity | Feature Superset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matches all features of a reference software. | Includes all reference features plus additional enhancements. |
| Scope | Equivalent feature set for compatibility. | Expanded capabilities beyond baseline. |
| Use Case | Replacement or clone software. | Competitive advantage or innovation. |
| Development Complexity | Moderate; focuses on replication. | High; requires additional design and testing. |
| User Benefit | Familiar experience, no learning curve. | Enhanced functionality and productivity. |
| Maintenance | Simpler; tracks original feature updates. | Complex; manages core plus extra features. |
Understanding Feature Parity in Software Development
Feature parity in software development ensures that a new product or version matches the capabilities of its predecessor, providing users with a familiar experience and full compatibility. Achieving feature parity is critical for seamless migration, minimizing user disruption, and maintaining functional consistency across platforms or versions. Emphasizing thorough requirement analysis and rigorous testing supports the successful realization of feature parity before pursuing enhancements or feature supersets.
Defining Feature Superset and Its Implications
Feature superset refers to a software version that includes all functionalities of a predecessor (feature parity) plus additional capabilities or enhancements that extend the original scope. This approach drives innovation by enabling broader use cases and improving user experience beyond replicated features. Implementing a feature superset requires careful design to ensure backward compatibility while delivering new value propositions to the target audience.
Why Teams Strive for Feature Parity
Teams strive for feature parity to ensure consistent user experience across different platforms and reduce development complexity, enabling seamless functionality regardless of the device or operating system. Achieving feature parity helps maintain competitive positioning by meeting user expectations uniformly and facilitates easier maintenance and testing due to uniform codebases. This approach accelerates adoption rates and minimizes user frustration linked to missing features, ultimately driving product reliability and customer satisfaction.
When to Pursue a Feature Superset Strategy
Pursuing a feature superset strategy is ideal when targeting advanced user segments or entering highly competitive markets where differentiation drives adoption. This approach ensures a comprehensive offering that surpasses competitors by integrating additional functionalities, increasing user retention and satisfaction. Prioritize superset features when scalability and long-term product roadmap flexibility are critical for business growth.
Trade-offs: Feature Parity vs Superset
Feature parity ensures consistent user experience by matching functionalities across different software versions, minimizing learning curves and support issues. Feature supersets introduce advanced capabilities that differentiate products but risk increased complexity and potential user confusion. Organizations must balance maintaining familiar interfaces with innovating to meet evolving user demands and competitive pressures.
Migration Challenges: Matching vs Expanding Features
Migration challenges arise when aiming for feature parity, as developers must ensure new software replicates all existing functionalities precisely, demanding thorough testing and compatibility checks. Expanding features in a feature superset approach involves integrating novel capabilities while maintaining core functions, which can increase complexity and risk of introducing bugs or user confusion. Balancing the need for seamless user experience with innovation requires careful planning, resource allocation, and iterative validation during the migration process.
User Experience Impact: Consistency vs Innovation
Feature parity ensures a consistent user experience by replicating existing functionalities across platforms, maintaining familiarity and reducing learning curves. Feature supersets drive innovation by introducing advanced capabilities that enhance usability and differentiate the product, potentially improving efficiency and satisfaction. Balancing consistency with novelty is critical to optimizing user engagement and maintaining competitive advantage in software development.
Business Considerations: Market Demands and Differentiation
Feature parity ensures a software product meets baseline market demands by matching competitor functionalities, which is essential for user retention and satisfaction. A feature superset, on the other hand, strategically introduces advanced or unique capabilities that drive differentiation, positioning the product as a market leader and enabling premium pricing. Balancing feature parity with a superset approach supports both competitive viability and innovative growth in dynamic software markets.
Evaluation Criteria: Choosing the Right Approach
Evaluating feature parity versus a feature superset hinges on aligning software capabilities with user needs, project scope, and resource availability. Prioritizing feature parity ensures consistent user experience and easier adoption when replacing or upgrading software, while a feature superset can drive innovation and competitive advantage by exceeding current functionality. Critical criteria include market demands, development costs, time-to-market, and long-term maintenance implications.
Best Practices for Managing Features Across Platforms
Ensuring feature parity across platforms maintains consistent user experience and functionality, reducing confusion and support issues. Implementing a feature superset strategy allows leveraging unique platform capabilities to enhance overall product value without compromising core features. Regular cross-functional reviews and automated testing frameworks help effectively manage feature alignment while accommodating platform-specific innovations.
Feature Parity vs Feature Superset Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com