Release Train software follows a scheduled update cycle, ensuring consistent and predictable deployments, which helps organizations plan and manage releases more effectively. Rolling Release provides continuous updates with the latest features and fixes, eliminating the need for major upgrades and reducing downtime. Choosing between Release Train and Rolling Release depends on an organization's preference for stability versus rapid access to new capabilities.
Table of Comparison
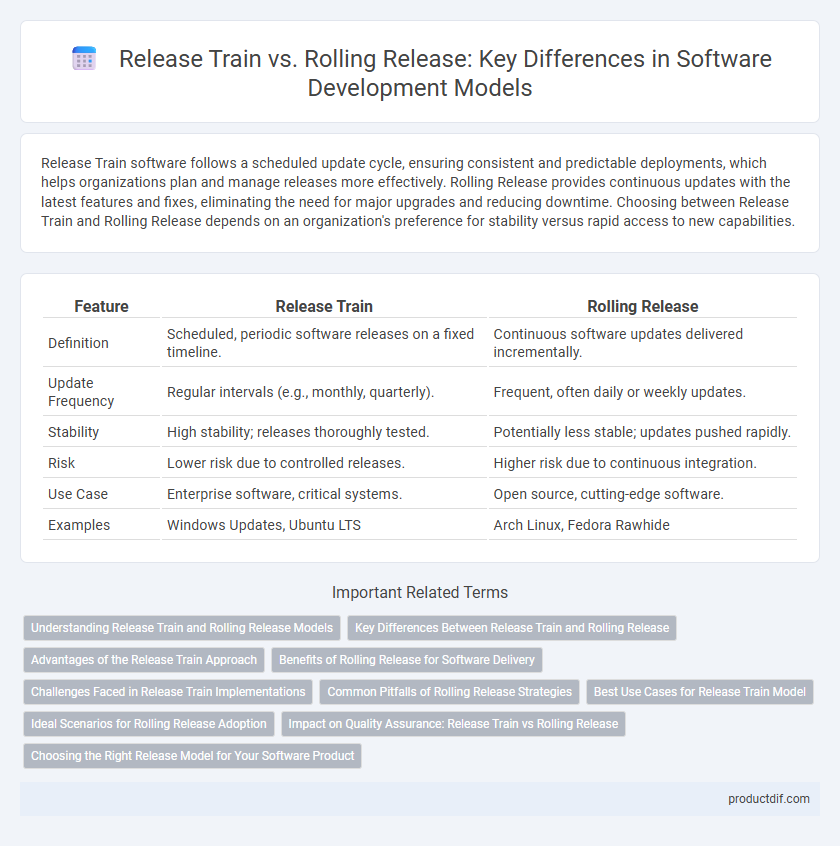
| Feature | Release Train | Rolling Release |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled, periodic software releases on a fixed timeline. | Continuous software updates delivered incrementally. |
| Update Frequency | Regular intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly). | Frequent, often daily or weekly updates. |
| Stability | High stability; releases thoroughly tested. | Potentially less stable; updates pushed rapidly. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to controlled releases. | Higher risk due to continuous integration. |
| Use Case | Enterprise software, critical systems. | Open source, cutting-edge software. |
| Examples | Windows Updates, Ubuntu LTS | Arch Linux, Fedora Rawhide |
Understanding Release Train and Rolling Release Models
Release Train models follow a scheduled, predictable timeline where software updates are bundled and released at fixed intervals, ensuring stability and coordinated feature deployment. Rolling Release models deliver continuous, incremental updates without fixed schedules, allowing users to receive the latest improvements and bug fixes as soon as they are ready. Understanding these models helps in choosing between the reliability of periodic releases and the agility of continuous updates in software development cycles.
Key Differences Between Release Train and Rolling Release
Release Train software development follows a fixed schedule, delivering updates at predetermined intervals to ensure predictability and stability, whereas Rolling Release continuously updates software with incremental improvements, providing the latest features without waiting for a full new version. Release Train emphasizes coordinated, synchronized releases across teams, promoting thorough testing and integration prior to deployment, while Rolling Release focuses on rapid, iterative deployment with ongoing integration and testing. Key differences lie in release frequency, predictability, stability, and update management, impacting user experience and development workflow.
Advantages of the Release Train Approach
The Release Train approach offers predictable, scheduled software updates that enhance project planning and delivery consistency for development teams. By synchronizing feature integration and testing across multiple teams, it reduces integration issues and improves software stability upon release. This method supports better stakeholder communication and risk management through fixed release cadences and comprehensive quality checks.
Benefits of Rolling Release for Software Delivery
Rolling release models enable continuous integration of updates, ensuring users access the latest features and security patches without waiting for scheduled releases. This approach reduces downtime and promotes rapid feedback, accelerating bug fixes and feature enhancements. Frequent, incremental updates foster agile software delivery, enhancing overall user satisfaction and system stability.
Challenges Faced in Release Train Implementations
Release Train implementations often face challenges such as coordinating multiple teams to align on fixed schedule deadlines, managing dependencies across diverse codebases, and ensuring quality assurance within constrained release windows. The rigidity of synchronized releases can lead to bottlenecks when unexpected bugs or integration issues arise, causing delays and impacting overall delivery timelines. Resource allocation and maintaining consistent communication across distributed development teams also pose significant hurdles in effective Release Train execution.
Common Pitfalls of Rolling Release Strategies
Rolling release strategies often lead to instability due to frequent updates that can introduce untested bugs or compatibility issues, disrupting user environments. Lack of clear versioning confuses users and complicates support, as software states continuously evolve without fixed milestones. Furthermore, dependency conflicts arise more frequently in rolling releases, increasing maintenance overhead and risking system breakages.
Best Use Cases for Release Train Model
The Release Train model is best suited for complex software projects requiring predictable schedules and coordinated feature delivery across multiple teams. This approach ensures stability and quality by grouping features into fixed release cycles, ideal for enterprise environments with strict compliance and documentation needs. Organizations emphasizing reliability and synchronized updates benefit most from the structured cadence of the Release Train system.
Ideal Scenarios for Rolling Release Adoption
Rolling release is ideal for software projects requiring continuous integration and frequent updates, such as development tools, Linux distributions like Arch Linux, and applications with active developer communities. It ensures users have immediate access to the latest features and security patches without waiting for scheduled release cycles. This model suits environments where stability can be balanced with rapid innovation and real-time bug fixes.
Impact on Quality Assurance: Release Train vs Rolling Release
Release Train models offer predictable, scheduled software updates that enable thorough quality assurance testing cycles, reducing the risk of defects reaching production. Rolling Release delivers continuous updates with smaller, incremental changes, requiring automated testing strategies to maintain quality without delays. The choice between these models directly influences QA resource allocation, testing methodologies, and defect management processes.
Choosing the Right Release Model for Your Software Product
Choosing between a Release Train and Rolling Release model depends on your software product's stability requirements and update frequency. Release Train offers predictable, scheduled updates ideal for enterprise environments demanding rigorous testing and user readiness, while Rolling Release provides continuous, incremental updates suited for agile teams prioritizing rapid feature delivery and real-time bug fixes. Assessing your development workflow, user base tolerance for change, and deployment infrastructure ensures optimal alignment with the chosen release strategy.
Release Train vs Rolling Release Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com