White Label software offers businesses fully developed products that can be rebranded and marketed as their own, streamlining time-to-market and reducing development costs. OEM software involves integrating pre-built software components into a company's own product, allowing customization while leveraging established technology for reliability. Choosing between White Label and OEM solutions depends on the desired level of branding control, customization needs, and resource availability.
Table of Comparison
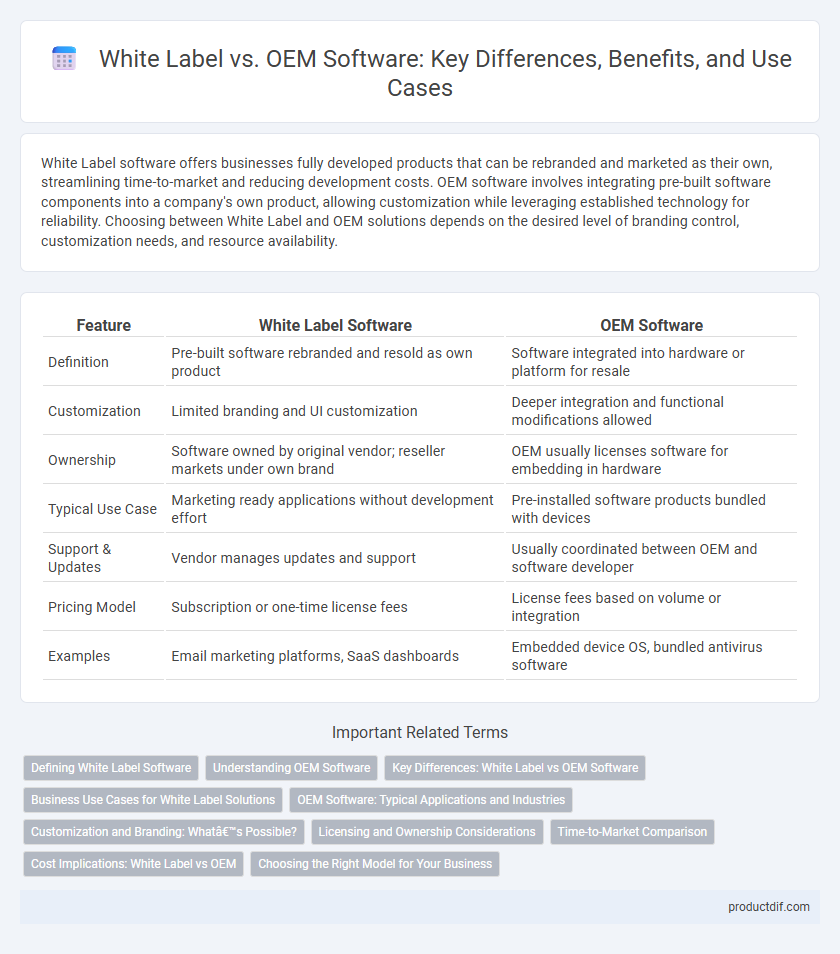
| Feature | White Label Software | OEM Software |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built software rebranded and resold as own product | Software integrated into hardware or platform for resale |
| Customization | Limited branding and UI customization | Deeper integration and functional modifications allowed |
| Ownership | Software owned by original vendor; reseller markets under own brand | OEM usually licenses software for embedding in hardware |
| Typical Use Case | Marketing ready applications without development effort | Pre-installed software products bundled with devices |
| Support & Updates | Vendor manages updates and support | Usually coordinated between OEM and software developer |
| Pricing Model | Subscription or one-time license fees | License fees based on volume or integration |
| Examples | Email marketing platforms, SaaS dashboards | Embedded device OS, bundled antivirus software |
Defining White Label Software
White label software is a fully developed application created by one company and rebranded by another to appear as their own product. This software allows businesses to offer customized solutions without investing in the development process, enhancing brand presence and reducing time to market. Unlike OEM software, white label solutions provide extensive branding flexibility while maintaining the underlying functionality from the original developer.
Understanding OEM Software
OEM software is pre-installed or integrated into hardware products by the original equipment manufacturer before sale, allowing businesses to offer branded solutions without developing software from scratch. This software often comes with licensing agreements restricting modification and resale, emphasizing seamless compatibility and optimized performance with specific devices. Understanding OEM software requires recognizing its role in enhancing product value while streamlining distribution and support channels for manufacturers.
Key Differences: White Label vs OEM Software
White Label software is fully developed by one company and rebranded by another to create the appearance of their own product, whereas OEM software is created by a manufacturer to be integrated into hardware or other software products for resale. White Label solutions offer extensive customization and branding flexibility, while OEM products tend to have limited modifications and are often bundled with specific devices. Understanding the licensing agreements and support responsibilities is crucial, as White Label licenses typically allow more control over updates compared to OEM licenses, which depend on the original manufacturer.
Business Use Cases for White Label Solutions
White label software enables businesses to quickly expand their product portfolio by rebranding and reselling fully developed applications, reducing time-to-market and development costs. It supports various enterprise use cases, including customized CRM platforms, marketing automation tools, and e-commerce solutions tailored to specific industry needs. Companies leverage white label solutions to maintain brand consistency while offering advanced features without investing in extensive software development.
OEM Software: Typical Applications and Industries
OEM software is extensively used in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and consumer electronics, where it is integrated into hardware products for enhanced functionality. Typical applications include embedded operating systems, specialized drivers, and firmware tailored to specific devices, enabling seamless hardware-software synergy. This approach allows manufacturers to customize software solutions for original equipment, improving performance and user experience while reducing time-to-market.
Customization and Branding: What’s Possible?
White label software allows businesses to fully customize the user interface, logos, and features to match their brand identity, offering seamless integration without revealing the original developer. OEM software typically provides a base product with limited customization options, enabling companies to rebrand the software under their name but often with constraints on feature modifications. Customization and branding in white label solutions deliver greater flexibility for unique user experiences, while OEM focuses on cost-efficiency and quicker market deployment with standardized offerings.
Licensing and Ownership Considerations
White label software licensing typically grants resellers extensive branding rights while maintaining the original developer's ownership, allowing customization without transferring intellectual property. OEM software licensing involves embedding or bundling the software with hardware or other products, often accompanied by stricter usage restrictions and limited control over branding or redistribution. Understanding these distinctions in licensing and ownership is crucial for businesses to align their software deployment strategy with legal and commercial objectives.
Time-to-Market Comparison
White Label software offers a faster time-to-market by providing ready-made solutions that can be easily rebranded and deployed without significant development. OEM software requires more extensive integration and customization, which typically extends the product launch timeline. Companies seeking rapid market entry often prefer White Label options to capitalize on immediate branding opportunities and reduce development overhead.
Cost Implications: White Label vs OEM
White Label software typically involves lower upfront costs as it allows companies to rebrand existing solutions without extensive development, reducing initial investment. OEM software often requires licensing fees and potential customization expenses that can increase total cost, but may offer deeper integration and unique features tailored to the buyer's hardware or platform. Evaluating ongoing support, maintenance, and scalability costs is crucial to accurately compare the financial impact of White Label versus OEM software options.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing between white label and OEM software depends on your business goals and customization needs; white label software allows rebranding with minimal changes, ideal for companies seeking quick market entry. OEM software offers deeper integration and customization, making it suitable for businesses requiring unique features embedded into their hardware or existing solutions. Assess factors such as development resources, branding control, and long-term scalability to select the most effective software model for your business growth.
White Label vs OEM Software Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com