Feature creep occurs when additional functionalities are continuously added to a software project beyond the original scope, leading to delays and increased complexity. Scope freeze, in contrast, involves locking the project requirements early to prevent changes, ensuring timely delivery but potentially overlooking valuable enhancements. Balancing feature creep and scope freeze is crucial for maintaining project agility while meeting deadlines and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
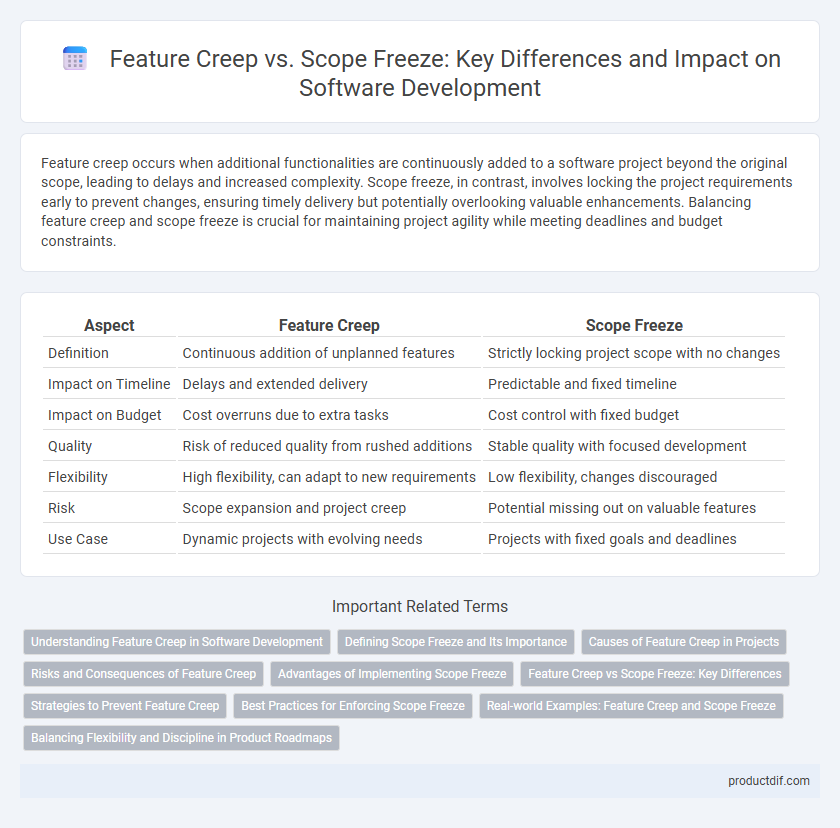
| Aspect | Feature Creep | Scope Freeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous addition of unplanned features | Strictly locking project scope with no changes |
| Impact on Timeline | Delays and extended delivery | Predictable and fixed timeline |
| Impact on Budget | Cost overruns due to extra tasks | Cost control with fixed budget |
| Quality | Risk of reduced quality from rushed additions | Stable quality with focused development |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, can adapt to new requirements | Low flexibility, changes discouraged |
| Risk | Scope expansion and project creep | Potential missing out on valuable features |
| Use Case | Dynamic projects with evolving needs | Projects with fixed goals and deadlines |
Understanding Feature Creep in Software Development
Feature creep refers to the continuous addition of new features to software beyond the original scope, often leading to increased complexity, project delays, and budget overruns. It disrupts development cycles by expanding requirements without adequate planning or resource allocation. Recognizing and controlling feature creep is essential to maintain project focus, ensure timely delivery, and uphold software quality.
Defining Scope Freeze and Its Importance
Scope Freeze is the practice of locking project requirements and functionalities to prevent further changes, ensuring that development remains focused and deadlines are met. This approach minimizes risks associated with feature creep, such as increased costs, extended timelines, and compromised quality. Maintaining scope freeze enhances team alignment, resource allocation, and predictable delivery in software development projects.
Causes of Feature Creep in Projects
Feature creep in software projects often stems from unclear initial requirements and continuous stakeholder demands for additions beyond the original scope. Frequent changes in user needs and competitive market pressure also drive uncontrolled feature expansion. Inadequate project management and poor communication between development teams and clients further exacerbate the tendency to add unnecessary features.
Risks and Consequences of Feature Creep
Feature creep introduces uncontrolled changes and additions, leading to extended development timelines and increased project costs in software development. This risk often results in reduced product quality, as resources become stretched and testing phases are compromised. Over time, feature creep can cause user confusion, decreased satisfaction, and ultimately, project failure due to misaligned objectives and bloated functionality.
Advantages of Implementing Scope Freeze
Implementing scope freeze minimizes project delays and budget overruns by locking requirements early in the development process. This approach enhances team focus and efficiency, reducing the risk of feature creep that can complicate project goals. Clear boundaries ensure consistent stakeholder expectations and improve overall product quality by concentrating efforts on core functionalities.
Feature Creep vs Scope Freeze: Key Differences
Feature creep occurs when new features continuously get added during the software development process, leading to project delays and budget overruns. Scope freeze, in contrast, involves locking the project requirements at a specific point to prevent changes, ensuring timely delivery and controlled costs. Managing feature creep effectively while enforcing scope freeze policies helps balance flexibility with project discipline in software development.
Strategies to Prevent Feature Creep
Implementing strict change control processes is essential to prevent feature creep in software development, ensuring all new features undergo rigorous evaluation for impact and relevance. Prioritizing a well-defined project scope with clear requirements helps maintain focus and limits deviations that lead to scope expansion. Regular stakeholder communication and employing agile methodologies like iterative development allow teams to adapt while adhering to agreed-upon objectives, effectively controlling feature addition.
Best Practices for Enforcing Scope Freeze
Enforcing scope freeze requires establishing clear project requirements and obtaining stakeholder agreement to prevent feature creep effectively. Implementing rigorous change control processes and using project management tools ensures that any modifications are systematically reviewed and approved. Regular communication and documentation maintain alignment among team members, reinforcing adherence to the defined scope.
Real-world Examples: Feature Creep and Scope Freeze
Feature creep frequently occurs in projects like the development of Microsoft Windows, where continuous addition of features extended timelines and inflated budgets. Conversely, scope freeze is exemplified by the initial version of the iPhone, which limited features to ensure timely release and maintain project focus. Real-world software development demonstrates that balancing feature creep and scope freeze influences product success and delivery efficiency.
Balancing Flexibility and Discipline in Product Roadmaps
Balancing flexibility and discipline in product roadmaps requires managing feature creep and scope freeze effectively to ensure on-time, high-quality software delivery. Excessive feature creep can dilute focus and extend timelines, while rigid scope freeze may ignore evolving user needs and market trends. Implementing iterative development cycles and clear prioritization frameworks enables teams to adapt product scope dynamically without compromising core objectives.
Feature Creep vs Scope Freeze Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com