The freemium model offers a basic version of software indefinitely at no cost, allowing users to experience essential features while encouraging upgrades to premium plans for advanced capabilities. In contrast, a free trial provides full access to all features for a limited time, creating urgency for users to evaluate the software before committing to a purchase. Choosing between the two depends on target audience behavior and the software's complexity, as freemium fosters long-term engagement while free trials drive quicker conversion.
Table of Comparison
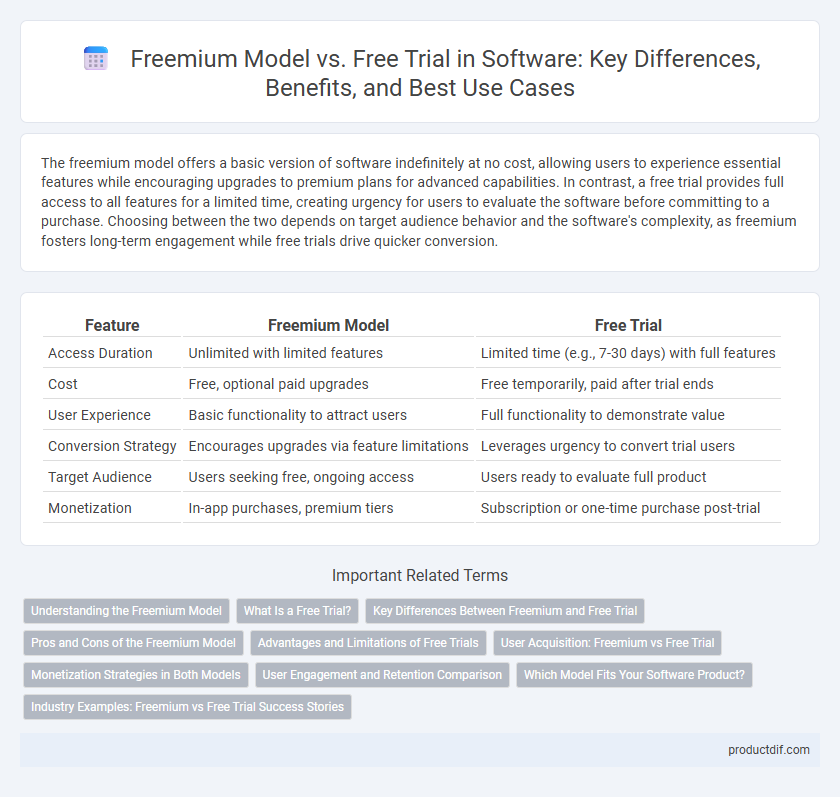
| Feature | Freemium Model | Free Trial |
|---|---|---|
| Access Duration | Unlimited with limited features | Limited time (e.g., 7-30 days) with full features |
| Cost | Free, optional paid upgrades | Free temporarily, paid after trial ends |
| User Experience | Basic functionality to attract users | Full functionality to demonstrate value |
| Conversion Strategy | Encourages upgrades via feature limitations | Leverages urgency to convert trial users |
| Target Audience | Users seeking free, ongoing access | Users ready to evaluate full product |
| Monetization | In-app purchases, premium tiers | Subscription or one-time purchase post-trial |
Understanding the Freemium Model
The freemium model offers users core software features at no cost while generating revenue through premium upgrades, creating long-term engagement and scalable user bases. This approach contrasts with free trials, which limit access to full features for a short period, prompting users to decide quickly on purchase. Understanding the freemium model is crucial for software companies aiming to maximize user retention and incremental revenue without upfront barriers.
What Is a Free Trial?
A free trial is a promotional offer that allows users to access the full or limited features of software for a specific period without payment, enabling potential customers to evaluate the product's value and functionality firsthand. Unlike the freemium model, which provides indefinite access to basic features for free, free trials give temporary access to premium capabilities, encouraging users to convert to paid subscriptions once the trial expires. Free trials are commonly used in SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms to reduce customer acquisition friction and demonstrate product benefits before purchase.
Key Differences Between Freemium and Free Trial
The freemium model offers users continuous access to a basic version of software with restrictions on features or usage, encouraging upgrades for premium capabilities. In contrast, a free trial provides full access to all features for a limited time, after which users must purchase a subscription to continue usage. Key differences include the duration of access--unlimited for freemium versus time-limited for free trials--and feature availability, where freemium restricts features, while free trials offer complete feature sets temporarily.
Pros and Cons of the Freemium Model
The freemium model allows indefinite access to basic software features at no cost, driving user acquisition and fostering product familiarity while potentially converting a percentage of users into paying customers. However, it can lead to slower revenue growth due to reliance on premium upgrades and may attract users who never convert, increasing support costs and straining resources. Balancing feature limitations and value in the free tier is critical to maintaining user engagement without undermining the premium subscription appeal.
Advantages and Limitations of Free Trials
Free trials provide users with full access to software features for a limited time, enabling firsthand evaluation without financial commitment, which often leads to higher conversion rates. The primary limitation of free trials includes their time constraint, which may pressure users into premature decisions and fail to showcase long-term software value. Unlike freemium models, free trials do not offer ongoing free usage, potentially reducing user retention after the trial period ends.
User Acquisition: Freemium vs Free Trial
Freemium models drive user acquisition by offering continuous access to basic features, encouraging widespread adoption and long-term engagement, which helps build a large user base over time. Free trials create urgency by granting temporary access to premium features, attracting users motivated to evaluate the full product before committing to a purchase. Both strategies optimize user acquisition, but freemium models often generate higher volume by reducing barriers to entry, while free trials aim for higher conversion rates through immediate value demonstration.
Monetization Strategies in Both Models
The freemium model offers basic software features for free while monetizing through premium upgrades and in-app purchases, optimizing user retention and revenue growth. In contrast, the free trial provides full access for a limited time, driving urgency and incentivizing users to convert to paid subscriptions. Effective monetization strategies depend on balancing value provided during the free phase with compelling reasons to upgrade or subscribe post-trial.
User Engagement and Retention Comparison
The freemium model drives sustained user engagement by offering essential features for free while enticing upgrades through premium functionalities, enhancing long-term retention rates. In contrast, free trials provide full access for a limited period, creating urgency but often leading to sharp drop-offs once the trial ends. Data shows freemium users exhibit higher lifetime value and consistent activity, whereas free trial users tend to spike in engagement initially but decline post-trial expiration.
Which Model Fits Your Software Product?
Choosing between the freemium model and a free trial depends heavily on your software's complexity and target audience engagement. The freemium model suits products with ongoing value and diverse features, encouraging users to upgrade over time, while free trials are ideal for demonstrating premium functionality quickly to more decision-oriented buyers. Analyze user behavior data and revenue goals to determine which option aligns best with your product's growth strategy.
Industry Examples: Freemium vs Free Trial Success Stories
Dropbox exemplifies the freemium model by offering core storage features for free while monetizing premium plans, driving rapid user growth and sustained revenue. In contrast, Adobe Creative Cloud employs a free trial strategy, providing full access to its suite for a limited period, successfully converting trial users into long-term subscribers. Slack combines both approaches by offering a free tier alongside trial periods for advanced features, maximizing user acquisition and retention in the collaboration software industry.
Freemium Model vs Free Trial Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com