Open source software offers transparency, flexibility, and community-driven innovation, allowing developers to customize and improve the code freely. Proprietary software provides dedicated support, streamlined user experiences, and often stronger security measures due to controlled access. Businesses must weigh the cost benefits and customization potential of open source against the reliability and comprehensive services of proprietary solutions.
Table of Comparison
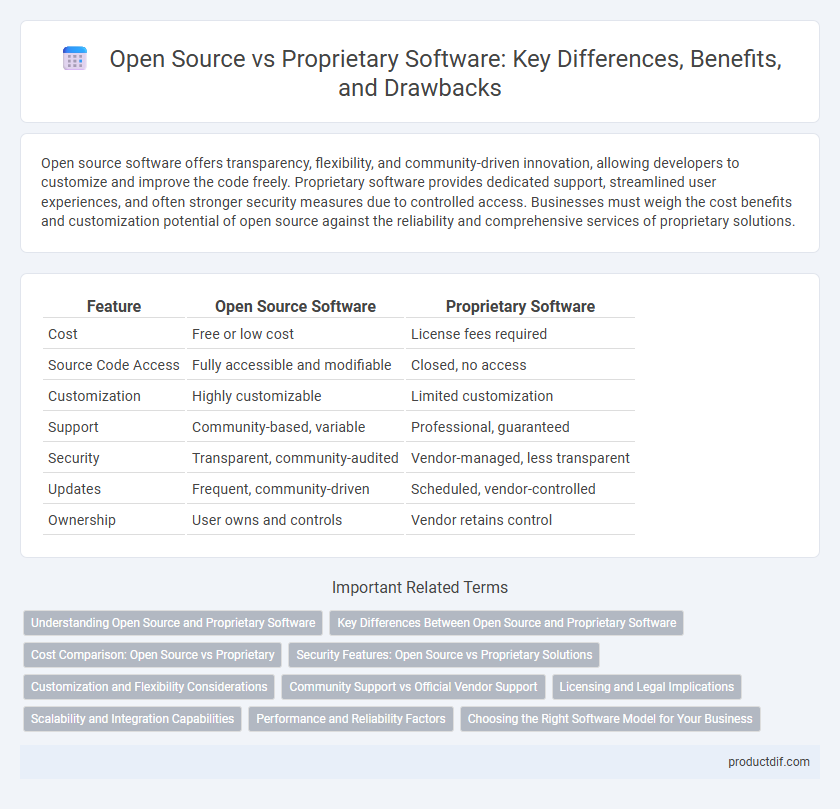
| Feature | Open Source Software | Proprietary Software |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or low cost | License fees required |
| Source Code Access | Fully accessible and modifiable | Closed, no access |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Support | Community-based, variable | Professional, guaranteed |
| Security | Transparent, community-audited | Vendor-managed, less transparent |
| Updates | Frequent, community-driven | Scheduled, vendor-controlled |
| Ownership | User owns and controls | Vendor retains control |
Understanding Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open source software is characterized by publicly accessible source code that users can modify, distribute, and enhance, fostering community collaboration and transparency. Proprietary software restricts access to its source code, granting users limited rights under licensing agreements while maintaining control over distribution and development. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions regarding software flexibility, security, and cost.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open source software offers users access to its source code, enabling customization and community-driven development, while proprietary software restricts source code access and emphasizes vendor-controlled distribution. Open source solutions typically provide greater transparency, flexibility, and often lower costs, whereas proprietary software usually includes dedicated support, warranties, and may offer specialized features with licensing fees. Security models also differ, with open source relying on community scrutiny and proprietary software depending on vendor-managed updates and protections.
Cost Comparison: Open Source vs Proprietary
Open source software typically offers significant cost advantages over proprietary solutions due to its zero licensing fees and community-driven development. Proprietary software often involves high upfront costs, ongoing subscription fees, and additional expenses for updates and support. Organizations choosing open source can reduce total cost of ownership while maintaining flexibility for customization and integration.
Security Features: Open Source vs Proprietary Solutions
Open source software security features benefit from transparent code review by a global community, enabling rapid identification and patching of vulnerabilities. Proprietary solutions rely on internal teams for security updates and may offer more controlled access but lack the broad scrutiny that open source projects enjoy. Both models implement encryption and authentication mechanisms; however, open source's transparency often leads to faster response times in addressing emergent threats.
Customization and Flexibility Considerations
Open source software offers extensive customization options and flexibility by allowing users to modify and adapt the source code to meet specific needs. Proprietary software typically restricts access to source code, limiting customization and making users reliant on vendor updates and support. Organizations seeking tailored solutions and adaptability often prefer open source for its ability to align with evolving business requirements.
Community Support vs Official Vendor Support
Open source software thrives on robust community support, offering extensive collaboration, rapid issue resolution, and diverse customization options driven by a global user base. Proprietary software relies primarily on official vendor support, providing dedicated technical assistance, structured updates, and guaranteed service-level agreements tailored to enterprise needs. Choosing between these options depends on prioritizing flexible innovation through community involvement or stability and accountability through vendor-managed services.
Licensing and Legal Implications
Open source software licenses, such as GPL and MIT, grant users the freedom to modify, distribute, and access source code, fostering transparency and collaboration but often requiring derivative works to adopt the same license. Proprietary software licenses impose restrictions on usage, copying, and modification, typically protecting intellectual property through closed-source agreements and limiting user rights to ensure vendor control. Understanding the legal implications is essential for compliance, as violations can lead to contract breaches, loss of access, or costly litigation.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
Open source software offers superior scalability through customizable codebases and a vast ecosystem of reusable components, enabling seamless integration with diverse systems. Proprietary software often provides specialized integration tools and dedicated support but may limit scalability due to closed architectures and licensing restrictions. Evaluating scalability and integration capabilities is critical for selecting software solutions that align with evolving business demands and complex IT environments.
Performance and Reliability Factors
Open source software often delivers high performance by enabling community-driven optimizations and rapid bug fixes, benefiting from transparent code inspection. Proprietary software may offer enhanced reliability through dedicated support teams and rigorous quality assurance processes, ensuring consistent performance under controlled environments. Evaluating performance and reliability depends on specific use cases, as open source can provide flexibility and innovation, while proprietary solutions emphasize stability and vendor accountability.
Choosing the Right Software Model for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate software model for your business hinges on factors like budget, customization needs, and support requirements. Open source software offers flexibility, community-driven innovation, and cost efficiency, making it ideal for businesses seeking control and scalability. Proprietary software provides dedicated vendor support, robust security features, and comprehensive updates, suited for organizations prioritizing reliability and ease of use.
Open Source vs Proprietary Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com