Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects by improving development processes, ensuring that software is built correctly from the start. Quality Control (QC) involves systematically testing and inspecting the software to identify and fix defects after development. Both QA and QC are essential for delivering reliable, high-performing software products that meet user expectations.
Table of Comparison
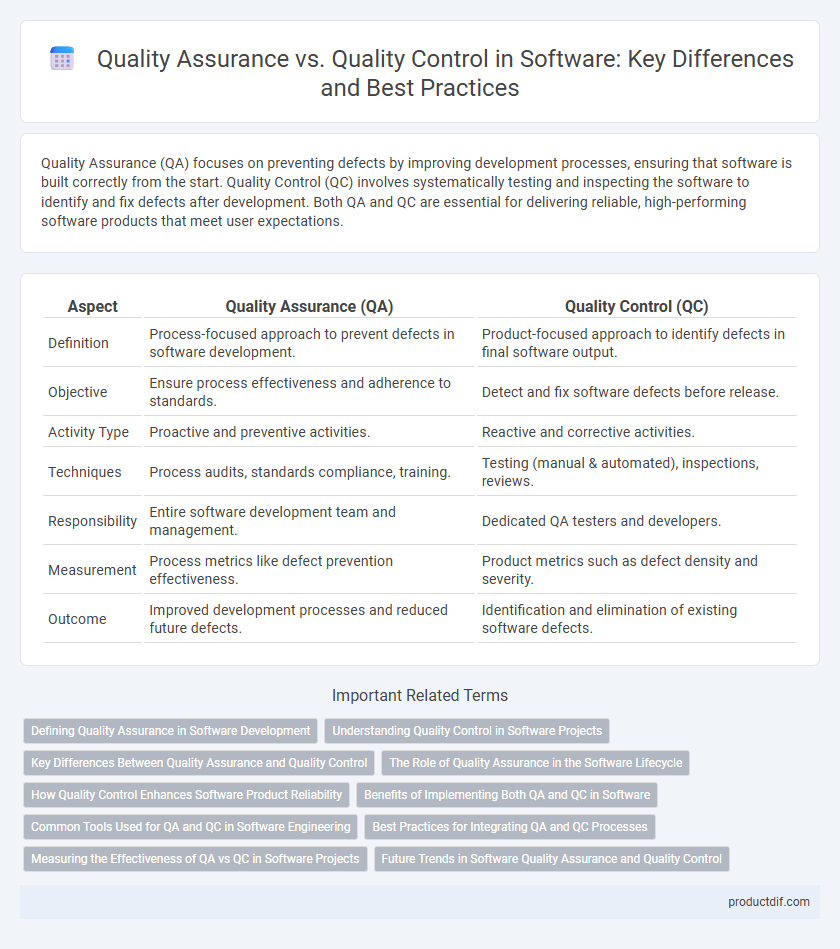
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process-focused approach to prevent defects in software development. | Product-focused approach to identify defects in final software output. |
| Objective | Ensure process effectiveness and adherence to standards. | Detect and fix software defects before release. |
| Activity Type | Proactive and preventive activities. | Reactive and corrective activities. |
| Techniques | Process audits, standards compliance, training. | Testing (manual & automated), inspections, reviews. |
| Responsibility | Entire software development team and management. | Dedicated QA testers and developers. |
| Measurement | Process metrics like defect prevention effectiveness. | Product metrics such as defect density and severity. |
| Outcome | Improved development processes and reduced future defects. | Identification and elimination of existing software defects. |
Defining Quality Assurance in Software Development
Quality Assurance in software development encompasses systematic activities and processes designed to ensure that software products meet specified requirements and standards throughout the development lifecycle. It involves process-oriented approaches such as code reviews, audits, and testing protocols to prevent defects and enhance product reliability. Effective Quality Assurance minimizes risk and improves overall software quality by embedding quality principles early in the development process.
Understanding Quality Control in Software Projects
Quality Control in software projects involves systematic testing and inspection to identify defects and ensure the product meets specified requirements. It emphasizes verification activities like code reviews, automated testing, and performance testing to detect issues early and maintain software reliability. Effective Quality Control mitigates risks, enhances user experience, and supports compliance with industry standards and client expectations.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality Assurance (QA) involves process-oriented activities aimed at preventing defects during software development, focusing on improving and optimizing development methodologies. Quality Control (QC) is product-oriented, centered on identifying and fixing defects in the final software through rigorous testing and inspection. Key differences include QA's proactive approach to ensure quality standards versus QC's reactive approach to detect and correct errors in the software output.
The Role of Quality Assurance in the Software Lifecycle
Quality Assurance (QA) in the software lifecycle ensures that defined processes and standards are followed to prevent defects and improve product quality from the initial design phase through deployment. QA involves systematic activities such as process audits, requirement reviews, and test planning to build a foundation for consistent software development and delivery. Integrating QA early reduces costly rework and enhances software reliability, user satisfaction, and compliance with industry standards.
How Quality Control Enhances Software Product Reliability
Quality Control (QC) enhances software product reliability by systematically identifying defects through rigorous testing and validation processes, ensuring that software meets predefined standards. Automated testing frameworks and continuous integration tools enable consistent defect detection, reducing the risk of failures in production environments. By implementing real-time monitoring and feedback loops, QC helps maintain high software performance and stability throughout development cycles.
Benefits of Implementing Both QA and QC in Software
Implementing both Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in software development enhances product reliability by combining process-oriented prevention with defect detection. QA establishes standardized methodologies and continuous improvement practices, while QC ensures code correctness through systematic testing and inspections. This integrated approach reduces software defects, accelerates time-to-market, and improves overall customer satisfaction by delivering high-quality software solutions.
Common Tools Used for QA and QC in Software Engineering
Common tools used for Quality Assurance (QA) in software engineering include Selenium for automated testing, Jenkins for continuous integration, and JIRA for defect tracking and project management. Quality Control (QC) tools primarily focus on identifying defects and include static code analyzers like SonarQube, load testing tools such as LoadRunner, and manual testing frameworks like TestRail. Both QA and QC leverage these tools to ensure software reliability, performance, and compliance with specified requirements.
Best Practices for Integrating QA and QC Processes
Implementing best practices for integrating Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) processes in software development enhances product reliability and user satisfaction. Establishing clear communication channels between QA teams and QC inspectors facilitates early defect detection and continuous improvement throughout the software lifecycle. Leveraging automated testing tools alongside manual reviews ensures comprehensive validation, promoting a seamless alignment of process adherence and product accuracy.
Measuring the Effectiveness of QA vs QC in Software Projects
Measuring the effectiveness of Quality Assurance (QA) in software projects involves evaluating process adherence, defect prevention rates, and continuous improvement metrics, while Quality Control (QC) effectiveness is assessed by defect detection rates, testing coverage, and the accuracy of identifying software bugs. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as defect density, mean time to detect (MTTD), and defect leakage provide quantifiable insights into both QA and QC contributions. Comparing these metrics enables project managers to balance preventive and detective quality activities, optimizing overall software quality outcomes.
Future Trends in Software Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Future trends in software quality assurance (QA) emphasize the integration of AI-driven testing tools and continuous quality monitoring to enhance defect detection and reduce time-to-market. Quality control (QC) is increasingly automated through real-time analytics and machine learning algorithms, enabling predictive quality insights and proactive issue resolution. The convergence of DevOps pipelines with advanced QA/QC frameworks accelerates deployment cycles while maintaining high software reliability and user satisfaction.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com