Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation and validated learning to quickly build and iterate products based on customer feedback. Design Thinking focuses on empathizing with users to deeply understand their needs and creatively solve problems through iterative prototyping. Both methodologies prioritize iteration but differ in approach: Lean Startup drives market-fit validation, while Design Thinking centers on user-centric innovation.
Table of Comparison
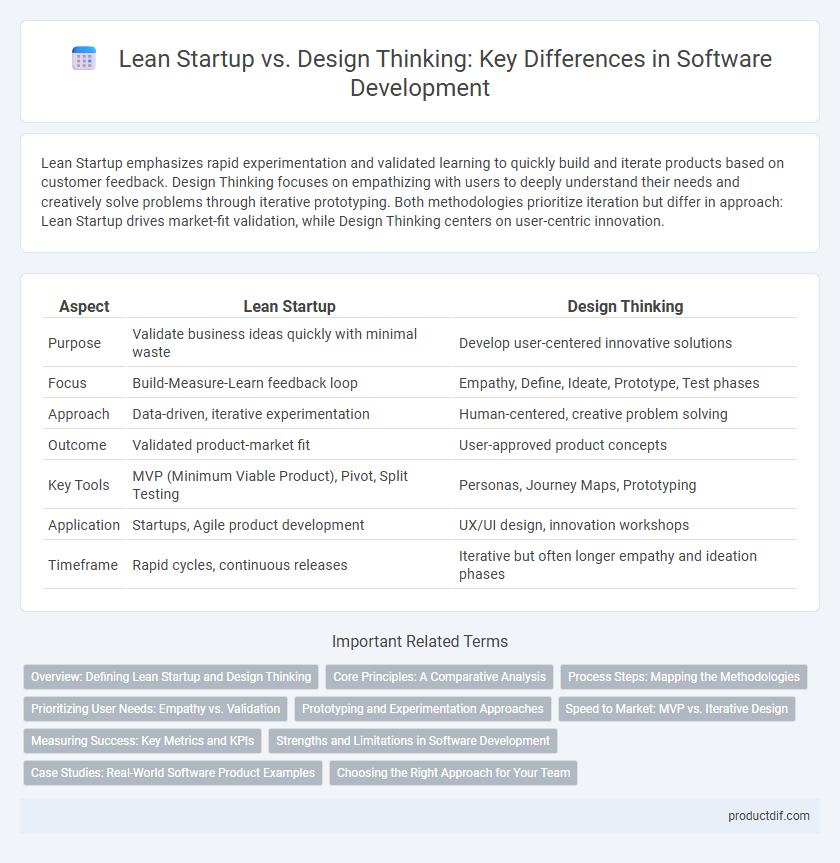
| Aspect | Lean Startup | Design Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validate business ideas quickly with minimal waste | Develop user-centered innovative solutions |
| Focus | Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop | Empathy, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test phases |
| Approach | Data-driven, iterative experimentation | Human-centered, creative problem solving |
| Outcome | Validated product-market fit | User-approved product concepts |
| Key Tools | MVP (Minimum Viable Product), Pivot, Split Testing | Personas, Journey Maps, Prototyping |
| Application | Startups, Agile product development | UX/UI design, innovation workshops |
| Timeframe | Rapid cycles, continuous releases | Iterative but often longer empathy and ideation phases |
Overview: Defining Lean Startup and Design Thinking
Lean Startup is a methodology emphasizing rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to quickly adapt to market needs. Design Thinking focuses on human-centered innovation through empathizing with users, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing. Both approaches aim to reduce risk in software development by fostering creativity and responsiveness but differ in their primary processes and mindset.
Core Principles: A Comparative Analysis
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to minimize market risks and optimize resource allocation. Design Thinking centers on empathizing with users, defining problems, and ideating innovative solutions through a human-centered, collaborative approach. Both methodologies prioritize user feedback but differ in application focus: Lean Startup targets business model validation while Design Thinking drives creative problem-solving and user experience enhancement.
Process Steps: Mapping the Methodologies
The Lean Startup process emphasizes a Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop to quickly validate assumptions through minimum viable products (MVPs) and iterative testing. Design Thinking follows a human-centered approach with steps including Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test, focusing on user needs and creative problem-solving. Mapping these methodologies reveals Lean Startup prioritizes rapid experimentation and metrics-driven learning, while Design Thinking centers on empathy and iterative solution refinement.
Prioritizing User Needs: Empathy vs. Validation
Lean Startup emphasizes validation through rapid experimentation and metrics to prioritize user needs, ensuring product-market fit via data-driven feedback loops. Design Thinking focuses on empathy by deeply understanding users' emotions, motivations, and pain points to create human-centered solutions. Both approaches prioritize user needs but differ in methodology: Lean Startup validates assumptions with real user feedback, while Design Thinking uncovers latent needs through empathetic research.
Prototyping and Experimentation Approaches
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid prototyping and iterative experimentation through minimum viable products (MVPs) to quickly test hypotheses and gather user feedback for data-driven improvements. Design Thinking focuses on empathizing with users and creating low-fidelity prototypes to explore multiple solutions, encouraging creative iteration based on human-centered insights. Both methodologies prioritize learning through experimentation but differ in scope; Lean Startup seeks validated learning to accelerate market fit, while Design Thinking fosters innovation through deep user understanding and divergent ideation.
Speed to Market: MVP vs. Iterative Design
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid speed to market by developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that validates core assumptions quickly through real user feedback. Design Thinking employs iterative design cycles that refine solutions based on user empathy and testing, which may extend the timeline but enhance product relevance. MVP prioritizes launching early with basic features, while Design Thinking focuses on evolving concepts through continuous iteration for deeper user alignment.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics and KPIs
Measuring success in Lean Startup relies heavily on actionable metrics such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and churn rate to validate hypotheses through rapid experimentation and iterative feedback. Design Thinking emphasizes qualitative KPIs like user satisfaction scores, empathy mapping results, and prototype testing outcomes to gauge user-centered innovation effectiveness. Both methodologies prioritize data-driven decision-making but differ in their focus on quantitative metrics versus qualitative insights for continuous improvement.
Strengths and Limitations in Software Development
Lean Startup accelerates software development by emphasizing rapid prototyping, validated learning, and iterative releases, reducing market risks through continuous user feedback. Design Thinking excels in fostering user-centric innovation by deeply understanding user needs and encouraging creative problem-solving, leading to highly intuitive and effective software solutions. Lean Startup may struggle with complex problem exploration, while Design Thinking can be time-intensive, making their combined application vital for balanced agile development.
Case Studies: Real-World Software Product Examples
Lean Startup methodology is exemplified by Dropbox, which utilized rapid MVP iterations and user feedback to refine its cloud storage solution efficiently. Design Thinking is prominently demonstrated by IDEO's work on software interfaces, emphasizing empathic user research and creative problem-solving to enhance user experience. Both approaches have proven effective in real-world software product development by fostering innovation and aligning products closely with user needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation and validated learning to reduce market risks for software teams aiming to launch minimal viable products quickly. Design Thinking prioritizes user-centric problem-solving by deeply understanding pain points through empathy and iterative prototyping, ideal for teams focusing on innovation and user experience. Selecting the right approach depends on your team's goals: use Lean Startup for fast market entry and scalability, and Design Thinking for creative solutions to complex user challenges.
Lean Startup vs Design Thinking Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com