REST API follows a fixed endpoint structure, making it simple and predictable for basic CRUD operations, while GraphQL provides flexible queries that allow clients to request exactly the data they need, minimizing overfetching and underfetching. GraphQL excels in complex applications with diverse data requirements by enabling efficient data retrieval through a single API call, whereas REST APIs can require multiple requests to different endpoints. Choosing between REST and GraphQL depends on the specific project needs, including performance considerations, development complexity, and client-server interaction patterns.
Table of Comparison
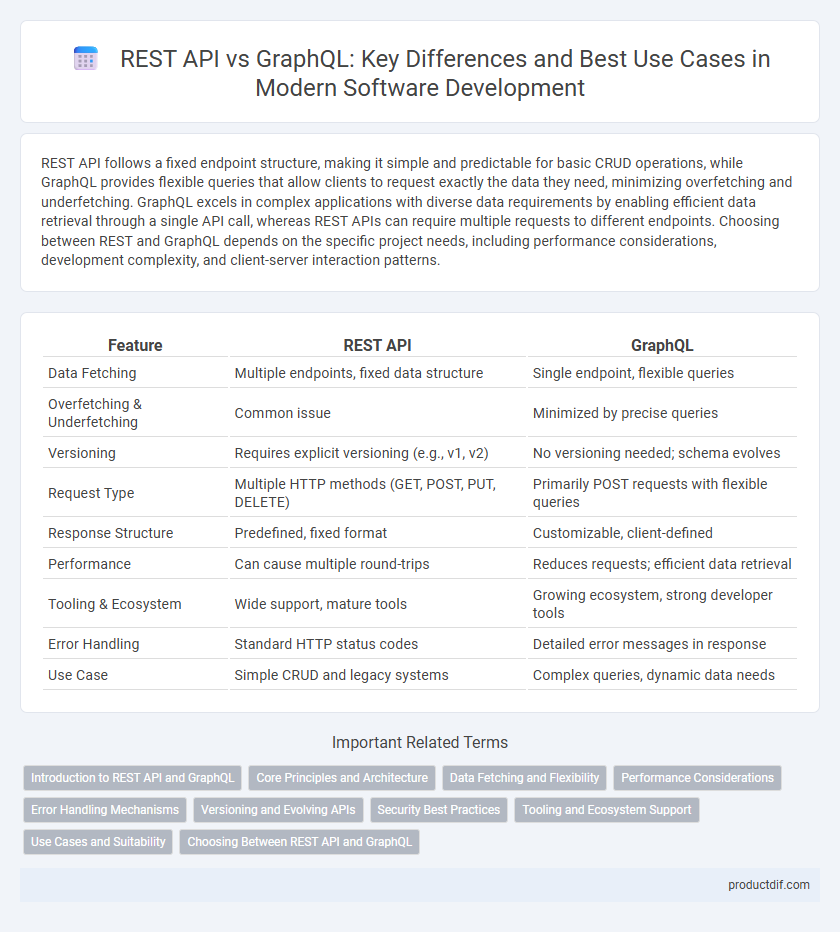
| Feature | REST API | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Multiple endpoints, fixed data structure | Single endpoint, flexible queries |
| Overfetching & Underfetching | Common issue | Minimized by precise queries |
| Versioning | Requires explicit versioning (e.g., v1, v2) | No versioning needed; schema evolves |
| Request Type | Multiple HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) | Primarily POST requests with flexible queries |
| Response Structure | Predefined, fixed format | Customizable, client-defined |
| Performance | Can cause multiple round-trips | Reduces requests; efficient data retrieval |
| Tooling & Ecosystem | Wide support, mature tools | Growing ecosystem, strong developer tools |
| Error Handling | Standard HTTP status codes | Detailed error messages in response |
| Use Case | Simple CRUD and legacy systems | Complex queries, dynamic data needs |
Introduction to REST API and GraphQL
REST API is an architectural style for designing networked applications, relying on stateless communication and standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to interact with resources represented as URLs. GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs that enables clients to request exactly the data they need, improving efficiency and reducing over-fetching compared to REST. Both REST API and GraphQL facilitate client-server communication but differ in data retrieval flexibility and response structure.
Core Principles and Architecture
REST API relies on a client-server architecture with stateless communication and predefined endpoints representing resources, promoting scalability and simplicity through standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, and DELETE. GraphQL uses a single endpoint that allows clients to request precisely the data they need via flexible queries, enabling more efficient data retrieval and reducing over-fetching or under-fetching. The core principle of REST is resource-based design with fixed data structures, while GraphQL centers on query-based data fetching with a strong schema that defines types and relationships dynamically.
Data Fetching and Flexibility
REST API typically requires multiple endpoints for different data resources, leading to over-fetching or under-fetching of data. GraphQL enables clients to request exactly the data they need in a single query, optimizing data fetching and reducing network overhead. This flexibility empowers developers to tailor responses dynamically, enhancing performance and improving user experience in complex applications.
Performance Considerations
REST API often involves multiple endpoints and over-fetching or under-fetching data, which can lead to increased latency and inefficient network usage. GraphQL optimizes performance by allowing clients to request exactly the data needed in a single query, reducing payload size and minimizing the number of requests. However, GraphQL's performance depends on the complexity of query resolution and server-side resolvers, requiring careful schema design and caching strategies to maintain optimal response times.
Error Handling Mechanisms
REST API typically uses standard HTTP status codes to indicate errors, such as 404 for not found or 500 for server errors, with error details included in the response body. GraphQL employs a unified error response structure where errors are returned within the "errors" array of the JSON response, allowing multiple errors to be reported in a single query. This approach provides more granular error information linked to specific parts of the query, improving client-side error handling and debugging.
Versioning and Evolving APIs
REST APIs often require versioning through URI changes like /v1/ or /v2/ to manage evolving endpoints, which can lead to multiple maintained versions. GraphQL evolves APIs more fluidly by enabling clients to request only needed fields, allowing schema extensions without breaking existing queries. This flexibility reduces the need for explicit versioning and supports seamless API iteration.
Security Best Practices
REST API security best practices emphasize strict authentication methods such as OAuth 2.0 and API keys, enforcing HTTPS to protect data in transit, and implementing rate limiting to prevent abuse. GraphQL security focuses on query complexity analysis, depth limiting to avoid denial-of-service attacks, and thorough validation of incoming queries to ensure only authorized data access. Both require robust logging and monitoring to detect anomalies and safeguard against common threats like injection and insecure direct object references (IDOR).
Tooling and Ecosystem Support
REST API benefits from mature tooling and widespread ecosystem support, including numerous libraries, debugging tools, and API gateways that simplify development and integration. GraphQL's ecosystem is rapidly growing, offering advanced developer tools like GraphiQL, Apollo Studio, and strong integrations with modern frontend frameworks for efficient querying and real-time updates. Both APIs have rich ecosystems, but REST's longer presence provides a broader range of stable, well-documented tools compared to GraphQL's innovative but less mature options.
Use Cases and Suitability
REST API is well-suited for applications requiring standardized CRUD operations with fixed endpoints, making it ideal for simple, resource-based architectures like public APIs and microservices. GraphQL excels in complex data-fetching scenarios where clients need precise queries and reduced over-fetching, making it perfect for dynamic, real-time applications such as mobile apps and dashboards. Choosing between REST and GraphQL depends on factors like data complexity, client requirements, and performance optimization needs.
Choosing Between REST API and GraphQL
Choosing between REST API and GraphQL depends on the specific data requirements and application architecture; REST API offers straightforward resource-based endpoints and caching advantages, while GraphQL provides flexible queries that reduce over-fetching and under-fetching by allowing clients to request exactly the data they need. For applications with complex relationships and varying client data needs, GraphQL enhances efficiency and reduces network overhead. Conversely, REST APIs remain ideal for simpler, scalable services with well-defined resources and robust HTTP caching.
REST API vs GraphQL Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com