DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery and improve system reliability. NoOps aims to automate infrastructure management entirely, reducing the need for manual operations and enabling developers to focus solely on coding. Both approaches seek to streamline software deployment but differ in the level of operational involvement and automation.
Table of Comparison
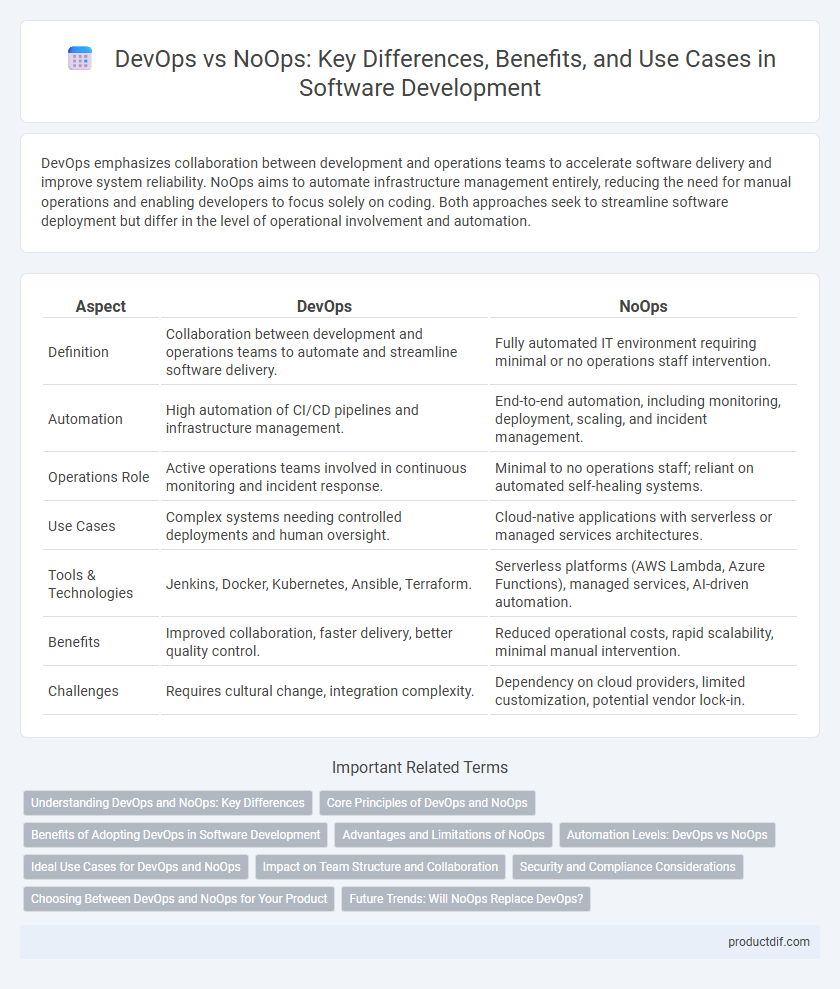
| Aspect | DevOps | NoOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaboration between development and operations teams to automate and streamline software delivery. | Fully automated IT environment requiring minimal or no operations staff intervention. |
| Automation | High automation of CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure management. | End-to-end automation, including monitoring, deployment, scaling, and incident management. |
| Operations Role | Active operations teams involved in continuous monitoring and incident response. | Minimal to no operations staff; reliant on automated self-healing systems. |
| Use Cases | Complex systems needing controlled deployments and human oversight. | Cloud-native applications with serverless or managed services architectures. |
| Tools & Technologies | Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, Terraform. | Serverless platforms (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions), managed services, AI-driven automation. |
| Benefits | Improved collaboration, faster delivery, better quality control. | Reduced operational costs, rapid scalability, minimal manual intervention. |
| Challenges | Requires cultural change, integration complexity. | Dependency on cloud providers, limited customization, potential vendor lock-in. |
Understanding DevOps and NoOps: Key Differences
DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to automate software delivery and infrastructure changes, enhancing deployment frequency and reliability. NoOps aims to eliminate the need for dedicated operations teams by leveraging fully automated environments and cloud-native technologies, focusing on developer-centric workflows. Understanding these paradigms highlights DevOps' focus on human collaboration versus NoOps' reliance on automation for operational tasks.
Core Principles of DevOps and NoOps
DevOps centers on collaboration, continuous integration, and automation to optimize software development and IT operations for faster delivery and improved reliability. NoOps aims to minimize or eliminate the need for dedicated operations teams by leveraging advanced automation, cloud-native infrastructure, and self-healing systems. Both approaches emphasize automation, but DevOps prioritizes cultural collaboration, whereas NoOps focuses on fully automated, autonomous IT environments.
Benefits of Adopting DevOps in Software Development
Adopting DevOps in software development accelerates deployment cycles by integrating continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, which enhance collaboration between development and operations teams. This approach improves software quality through automated testing and monitoring, reducing errors and downtime. Organizations leveraging DevOps report increased productivity, faster time-to-market, and higher customer satisfaction due to rapid feedback loops and iterative improvements.
Advantages and Limitations of NoOps
NoOps offers the advantage of fully automated deployment and maintenance processes, significantly reducing the need for human intervention and enabling faster delivery cycles. This approach minimizes operational overhead and allows development teams to focus solely on coding and innovation. However, the limitations include reliance on robust automation tools and potential challenges in handling complex or custom infrastructure issues without dedicated operations support.
Automation Levels: DevOps vs NoOps
DevOps emphasizes partial automation by integrating continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and infrastructure as code (IaC) to streamline development and operations collaboration. NoOps targets full automation, using advanced AI-driven tools and autonomous cloud platforms to eliminate manual intervention in deployment, monitoring, and maintenance tasks. This results in higher automation levels with NoOps, reducing human dependency while DevOps balances automation with human oversight.
Ideal Use Cases for DevOps and NoOps
DevOps is ideal for complex software projects requiring continuous integration, frequent updates, and collaborative development among cross-functional teams. NoOps suits organizations aiming for full automation of infrastructure management, minimizing manual intervention and enabling developers to focus solely on coding and deployment. Enterprises with hybrid cloud environments benefit from a combined approach, using DevOps for customization and NoOps for streamlined operational tasks.
Impact on Team Structure and Collaboration
DevOps fosters cross-functional teams by integrating development and operations roles, enhancing collaboration and accelerating delivery cycles through shared responsibilities and continuous feedback loops. NoOps aims to minimize operational involvement by leveraging automation and cloud-native services, shifting focus toward development teams with reduced need for dedicated operations staff. This shift transforms team structures, promoting streamlined workflows but potentially reducing direct operational insights within the team.
Security and Compliance Considerations
DevOps integrates security and compliance early through continuous monitoring, automated testing, and collaboration between development and operations teams, enhancing risk management and regulatory adherence. NoOps shifts the responsibility for security and compliance largely to cloud service providers, which can simplify internal processes but may reduce direct control over data protection and auditability. Evaluating security frameworks, shared responsibility models, and compliance certifications is crucial when deciding between DevOps and NoOps for safeguarding software infrastructure.
Choosing Between DevOps and NoOps for Your Product
Choosing between DevOps and NoOps depends on your product's complexity and deployment needs. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to enhance continuous integration and delivery, ideal for products requiring frequent updates and robust infrastructure management. NoOps leverages automation to minimize operational overhead, best suited for simpler applications or cloud-native products needing minimal manual intervention.
Future Trends: Will NoOps Replace DevOps?
Emerging trends in software development suggest NoOps aims to minimize manual intervention by leveraging AI-driven automation and continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, potentially transforming traditional DevOps workflows. However, while NoOps streamlines operational tasks, DevOps' emphasis on cross-functional collaboration and cultural integration remains vital for complex enterprise environments. The future likely involves a hybrid approach, where AI-powered NoOps tools augment rather than fully replace DevOps teams to enhance agility and efficiency.
DevOps vs NoOps Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com