User-centered design prioritizes the needs, preferences, and behaviors of end-users, ensuring software interfaces are intuitive, accessible, and user-friendly to enhance overall satisfaction and usability. Developer-centered design focuses on the technical requirements and convenience for developers, often resulting in software optimized for ease of coding and maintenance but potentially overlooking user experience. Balancing both approaches leads to robust software that is both functional for developers and enjoyable for users.
Table of Comparison
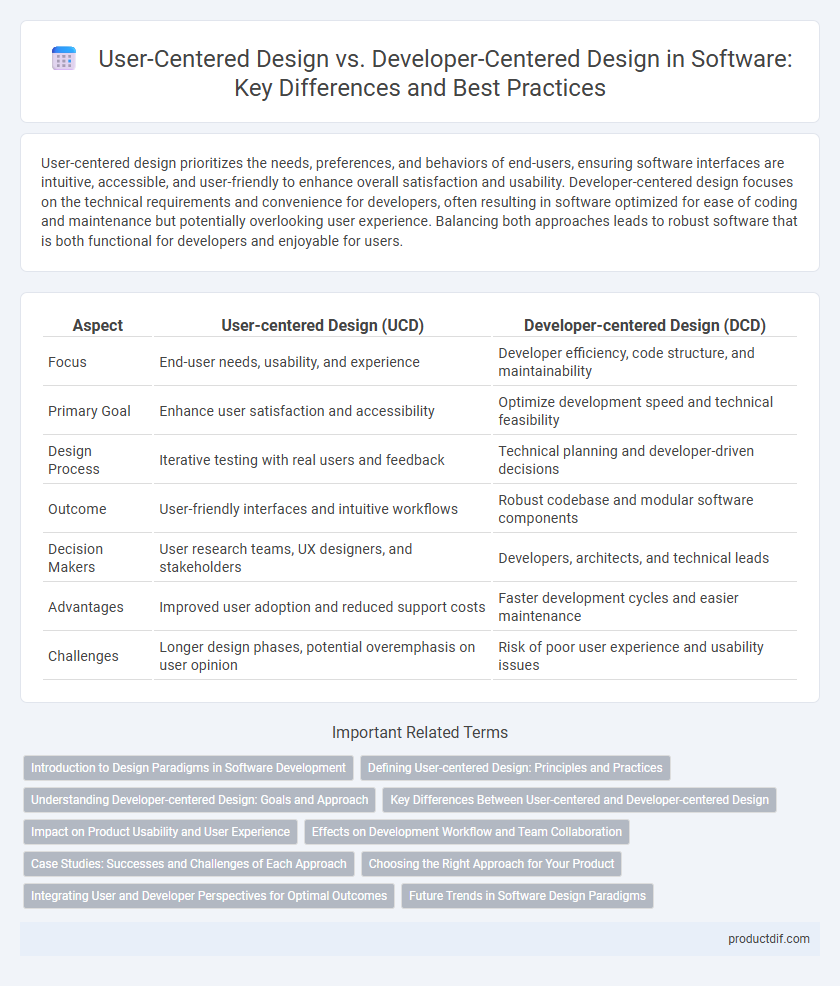
| Aspect | User-centered Design (UCD) | Developer-centered Design (DCD) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | End-user needs, usability, and experience | Developer efficiency, code structure, and maintainability |
| Primary Goal | Enhance user satisfaction and accessibility | Optimize development speed and technical feasibility |
| Design Process | Iterative testing with real users and feedback | Technical planning and developer-driven decisions |
| Outcome | User-friendly interfaces and intuitive workflows | Robust codebase and modular software components |
| Decision Makers | User research teams, UX designers, and stakeholders | Developers, architects, and technical leads |
| Advantages | Improved user adoption and reduced support costs | Faster development cycles and easier maintenance |
| Challenges | Longer design phases, potential overemphasis on user opinion | Risk of poor user experience and usability issues |
Introduction to Design Paradigms in Software Development
User-centered design prioritizes end-user needs and usability by involving users throughout the software development process, ensuring the product aligns with real-world tasks and enhances user experience. Developer-centered design focuses on technical feasibility and developer preferences, often emphasizing code efficiency and system architecture over user interaction. Understanding these paradigms helps balance functionality, usability, and maintainability in software projects.
Defining User-centered Design: Principles and Practices
User-centered design (UCD) prioritizes the needs, preferences, and limitations of end users throughout the software development lifecycle, employing principles such as empathy, iterative testing, and usability evaluations to ensure intuitive interfaces. Core practices include user research, persona creation, scenario development, and continual feedback incorporation to align functionality with real-world user goals. By emphasizing accessibility, simplicity, and responsiveness, UCD enhances user satisfaction, engagement, and overall product success.
Understanding Developer-centered Design: Goals and Approach
Developer-centered design prioritizes system functionality and technical efficiency, emphasizing the needs and workflow of software developers. Its approach focuses on optimizing code maintainability, scalability, and integration with existing development tools to enhance productivity. Goals include minimizing development complexity and accelerating the implementation process while ensuring robust and flexible system architecture.
Key Differences Between User-centered and Developer-centered Design
User-centered design prioritizes user needs, behaviors, and feedback to create intuitive and accessible software interfaces, enhancing overall user experience and satisfaction. Developer-centered design focuses on technical feasibility, coding efficiency, and system architecture, often prioritizing developer convenience over user usability. Key differences include the decision-making process, with user-centered design driven by user research and usability testing, whereas developer-centered design is guided by technical constraints and developer expertise.
Impact on Product Usability and User Experience
User-centered design prioritizes understanding users' needs, behaviors, and feedback, resulting in enhanced product usability and a more intuitive user experience. In contrast, developer-centered design often emphasizes technical feasibility and developer preferences, which can lead to interfaces that are less accessible and harder to navigate. Studies show that products developed with user-centered approaches achieve higher satisfaction rates and reduced user errors, directly improving overall user engagement and retention.
Effects on Development Workflow and Team Collaboration
User-centered design enhances team collaboration by prioritizing end-user needs, leading to clearer communication and aligned goals throughout the development workflow. Developer-centered design often streamlines coding efficiency but may cause misalignment with user expectations, resulting in increased rework and fragmented teamwork. Integrating user feedback early fosters a more adaptive development process, improving product quality and cross-functional collaboration.
Case Studies: Successes and Challenges of Each Approach
User-centered design prioritizes end-user needs, resulting in higher user satisfaction and engagement as demonstrated in case studies from industry leaders like Apple and Google. Developer-centered design often accelerates development speed but risks usability issues, as seen in projects where technical constraints overshadowed user experience. Balancing these approaches through iterative feedback loops and cross-functional collaboration has proven effective in overcoming challenges and achieving successful software outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Product
User-centered design emphasizes usability and accessibility by involving real users throughout the development process, ensuring the product meets actual user needs and behavior patterns. Developer-centered design prioritizes technical feasibility and code efficiency, often leading to faster development cycles but potentially overlooking user experience nuances. Selecting the right approach depends on project goals, target audience complexity, and long-term maintenance priorities to balance functionality with user satisfaction.
Integrating User and Developer Perspectives for Optimal Outcomes
Integrating user-centered design and developer-centered design enhances software quality by aligning user needs with technical feasibility, resulting in more intuitive and robust applications. Collaborative workflows that incorporate continuous user feedback and developer insights streamline iteration cycles, reducing development costs and improving user satisfaction. Prioritizing transparent communication and empathy between users and developers fosters innovative solutions that address real-world problems effectively.
Future Trends in Software Design Paradigms
Future trends in software design paradigms emphasize a shift towards user-centered design, integrating AI-driven personalization and immersive experiences through augmented reality to enhance usability and engagement. Developer-centered design evolves with advanced tooling and automation, enabling faster iteration cycles and more efficient collaboration across distributed teams. The convergence of these approaches fosters adaptive systems that prioritize both seamless user experiences and streamlined development workflows.
User-centered Design vs Developer-centered Design Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com