Native apps deliver superior performance and seamless user experiences by leveraging platform-specific features and hardware optimization on iOS or Android devices. Hybrid apps offer cross-platform compatibility and faster development cycles by combining web technologies within a single codebase but may face limitations in speed and responsiveness. Choosing between native and hybrid development depends on project requirements, budget, and desired user engagement.
Table of Comparison
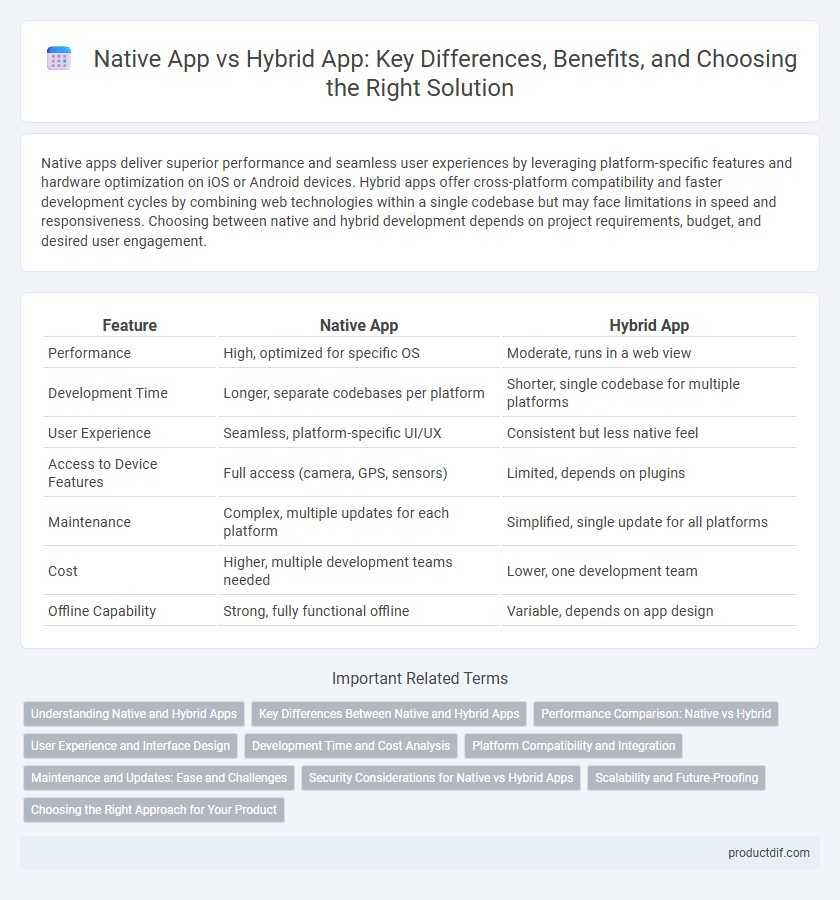
| Feature | Native App | Hybrid App |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | High, optimized for specific OS | Moderate, runs in a web view |
| Development Time | Longer, separate codebases per platform | Shorter, single codebase for multiple platforms |
| User Experience | Seamless, platform-specific UI/UX | Consistent but less native feel |
| Access to Device Features | Full access (camera, GPS, sensors) | Limited, depends on plugins |
| Maintenance | Complex, multiple updates for each platform | Simplified, single update for all platforms |
| Cost | Higher, multiple development teams needed | Lower, one development team |
| Offline Capability | Strong, fully functional offline | Variable, depends on app design |
Understanding Native and Hybrid Apps
Native apps are developed specifically for a particular operating system using platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android, ensuring high performance and seamless access to device features. Hybrid apps combine web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with a native container, allowing a single codebase to run across multiple platforms but potentially sacrificing some speed and responsiveness. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose between optimal performance and broader compatibility based on their target audience and development resources.
Key Differences Between Native and Hybrid Apps
Native apps are developed specifically for a single platform using platform-specific programming languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android, resulting in optimized performance and access to device features. Hybrid apps use web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript wrapped in a native container, enabling cross-platform compatibility but often with reduced performance and limited access to native device capabilities. Key differences include development cost, user experience, maintenance complexity, and the ability to leverage hardware features like GPS, camera, and push notifications.
Performance Comparison: Native vs Hybrid
Native apps deliver superior performance by leveraging platform-specific APIs and hardware acceleration, resulting in faster load times and smoother animations. Hybrid apps, built using web technologies wrapped in a native shell, often experience slower execution and limited access to device capabilities, causing potential lag and reduced responsiveness. Performance benchmarks consistently show native apps outperform hybrids in CPU-intensive tasks and real-time processing scenarios.
User Experience and Interface Design
Native apps deliver superior user experience through optimized performance and seamless integration with device-specific features, resulting in smoother animations and faster load times. Hybrid apps offer cross-platform compatibility using a single codebase but may suffer from inconsistent interface design and slower responsiveness due to reliance on web views. User interface design in native apps benefits from platform-specific guidelines, ensuring intuitive navigation and a polished look that enhances usability compared to the generic appearance often found in hybrid applications.
Development Time and Cost Analysis
Native app development typically requires more time and higher costs due to platform-specific coding for iOS and Android, demanding separate development teams and extensive testing. Hybrid apps leverage a single codebase using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, significantly reducing development time and cost by enabling simultaneous deployment across multiple platforms. Cost efficiency of hybrid apps often makes them ideal for startups or projects with limited budgets, while native apps deliver superior performance at a higher investment.
Platform Compatibility and Integration
Native apps offer superior platform compatibility and seamless integration with device-specific features, ensuring optimal performance on iOS or Android. Hybrid apps, built using web technologies within a native container, provide broader cross-platform compatibility but may face limitations in accessing advanced hardware functionalities. Businesses must weigh the trade-offs between native apps' deep integration and hybrid apps' cost-effective multi-platform support.
Maintenance and Updates: Ease and Challenges
Native apps offer streamlined maintenance and faster updates by leveraging platform-specific tools and APIs, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Hybrid apps face challenges in updates due to dependency on multiple frameworks and potential delays in cross-platform compatibility, often requiring more complex testing across devices. Efficient maintenance of native apps reduces downtime, while hybrid apps demand intricate coordination to manage codebases and platform-specific quirks.
Security Considerations for Native vs Hybrid Apps
Native apps offer enhanced security by leveraging platform-specific features such as biometric authentication and secure storage, reducing exposure to vulnerabilities common in web-based frameworks. Hybrid apps often rely on web technologies and embedded browsers, increasing risks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and data leakage if not properly sandboxed. Developers must implement rigorous security protocols and regular updates to mitigate these risks in both native and hybrid applications.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Native apps offer superior scalability and future-proofing by leveraging platform-specific features and updates directly from operating system providers, ensuring optimal performance and long-term support. Hybrid apps, while easier to develop across multiple platforms, may face limitations in scaling efficiently and adapting to rapid OS changes due to reliance on web technologies and third-party frameworks. Prioritizing scalability and future-proofing often means choosing native app development for robust, high-performance applications tailored to evolving device capabilities.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Product
Evaluating the choice between native and hybrid apps hinges on factors such as performance requirements, development cost, and target audience. Native apps offer superior speed, seamless integration with device features, and enhanced user experience but require separate codebases for each platform. Hybrid apps enable faster development and cross-platform compatibility using web technologies but may compromise on responsiveness and hardware interaction.
Native App vs Hybrid App Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com