Hotfix releases address critical bugs or security vulnerabilities that require immediate attention without waiting for the next scheduled update, ensuring system stability and security. Patch releases typically bundle minor bug fixes, performance improvements, and minor feature updates, following a regular release cycle. Prioritizing hotfixes minimizes downtime, while patches maintain overall software quality and user experience.
Table of Comparison
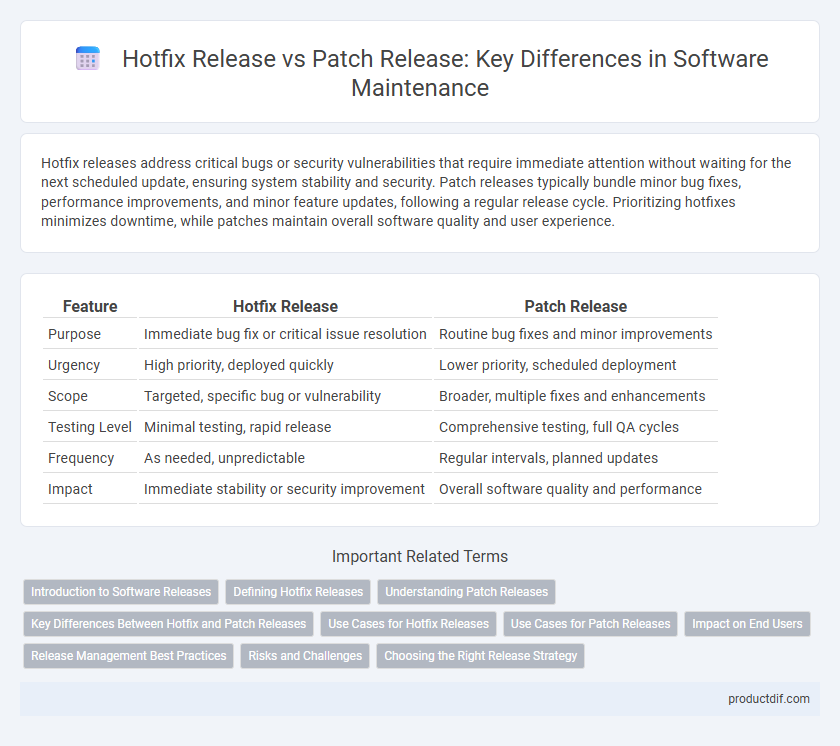
| Feature | Hotfix Release | Patch Release |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Immediate bug fix or critical issue resolution | Routine bug fixes and minor improvements |
| Urgency | High priority, deployed quickly | Lower priority, scheduled deployment |
| Scope | Targeted, specific bug or vulnerability | Broader, multiple fixes and enhancements |
| Testing Level | Minimal testing, rapid release | Comprehensive testing, full QA cycles |
| Frequency | As needed, unpredictable | Regular intervals, planned updates |
| Impact | Immediate stability or security improvement | Overall software quality and performance |
Introduction to Software Releases
A hotfix release addresses critical bugs or security vulnerabilities requiring immediate resolution without waiting for the next scheduled update, ensuring minimal disruption to users. Patch releases, on the other hand, bundle multiple fixes and improvements into a planned update cycle, enhancing overall software stability and performance. Understanding the distinction between hotfix and patch releases helps optimize software maintenance strategies and reduce downtime.
Defining Hotfix Releases
A hotfix release addresses critical bugs or security vulnerabilities in software, typically deployed urgently to resolve issues affecting system stability or user functionality. Unlike regular patch releases, hotfixes are small, targeted updates designed for immediate application without waiting for the next scheduled maintenance cycle. These releases often bypass extensive testing protocols to minimize downtime and prevent widespread disruption.
Understanding Patch Releases
Patch releases provide targeted updates to software, focusing on fixing specific bugs, improving security, and enhancing stability without introducing new features. These releases are typically smaller and less disruptive than hotfixes, allowing for thorough testing and scheduled deployment. Patch releases play a crucial role in maintaining software reliability by addressing vulnerabilities and performance issues identified after the major release.
Key Differences Between Hotfix and Patch Releases
Hotfix releases address critical bugs or vulnerabilities that require immediate resolution without waiting for the next scheduled update, often targeting specific issues in production environments. Patch releases encompass a broader set of updates, including bug fixes, security enhancements, and minor improvements, usually bundled into regular maintenance cycles. Hotfixes are typically smaller, urgent, and isolated, while patches provide comprehensive, planned updates improving overall software stability and performance.
Use Cases for Hotfix Releases
Hotfix releases address critical issues that disrupt software functionality or security, requiring immediate resolution without waiting for the next scheduled update. Use cases include fixing severe bugs, security vulnerabilities, or performance bottlenecks in production environments that impact end-users or business operations. Hotfixes ensure minimal downtime and rapid deployment to maintain system stability and user trust.
Use Cases for Patch Releases
Patch releases are primarily used to address minor bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues without introducing major changes to the software's core functionality. They enable rapid deployment of fixes that maintain system stability and security, especially in production environments where downtime must be minimized. Common use cases include resolving critical security flaws, fixing compatibility issues, and updating localized content or UI elements.
Impact on End Users
Hotfix releases address critical bugs or security vulnerabilities immediately, minimizing downtime and preventing significant disruptions for end users. Patch releases provide scheduled updates that improve software stability and performance but may require planned downtime, causing less urgent yet noticeable user interruptions. Both strategies ensure continuous software reliability, with hotfixes prioritizing urgent fixes and patches focusing on comprehensive improvements.
Release Management Best Practices
Hotfix releases address critical bugs or security vulnerabilities that require immediate deployment, often bypassing standard release cycles to minimize downtime. Patch releases bundle multiple non-urgent bug fixes and minor improvements, following scheduled maintenance windows to ensure stability and thorough testing. Effective release management balances the urgency of hotfix deployment with the structured validation of patch releases, maintaining system reliability and minimizing disruption.
Risks and Challenges
Hotfix releases address critical issues quickly but carry risks such as insufficient testing and potential system instability, which can disrupt production environments. Patch releases, although more thoroughly tested, may introduce compatibility challenges and require downtime, impacting user productivity. Both approaches demand careful change management to minimize deployment failures and ensure system reliability.
Choosing the Right Release Strategy
Selecting the right release strategy depends on the urgency and scope of the software issue: hotfix releases address critical bugs or security vulnerabilities requiring immediate resolution, minimizing downtime and user impact. Patch releases involve scheduled updates targeting multiple non-critical defects or minor improvements, ensuring system stability without disrupting operations. Evaluating the severity of the problem and deployment windows optimizes the choice between hotfix and patch releases for effective software maintenance.
Hotfix Release vs Patch Release Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com