SQL databases use structured query language and predefined schemas to manage relational data with ACID compliance, making them ideal for complex queries and transactional systems. NoSQL databases offer flexible schemas and horizontal scalability, efficiently handling unstructured or semi-structured data, which suits big data and real-time web applications. Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on data consistency requirements, scalability needs, and the nature of the workload.
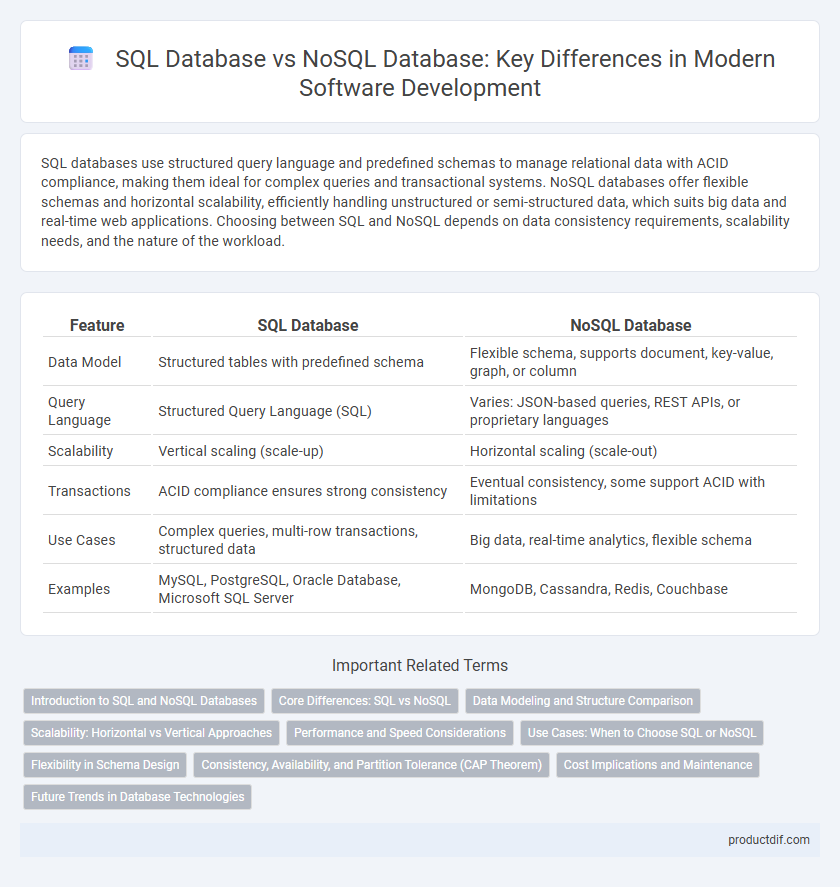
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SQL Database | NoSQL Database |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Structured tables with predefined schema | Flexible schema, supports document, key-value, graph, or column |
| Query Language | Structured Query Language (SQL) | Varies: JSON-based queries, REST APIs, or proprietary languages |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling (scale-up) | Horizontal scaling (scale-out) |
| Transactions | ACID compliance ensures strong consistency | Eventual consistency, some support ACID with limitations |
| Use Cases | Complex queries, multi-row transactions, structured data | Big data, real-time analytics, flexible schema |
| Examples | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server | MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Couchbase |
Introduction to SQL and NoSQL Databases
SQL databases use structured query language to manage relational data with predefined schemas, ensuring data integrity and supporting complex queries. NoSQL databases offer flexible schema designs ideal for handling unstructured or semi-structured data, enabling scalability and high performance in distributed environments. Selecting between SQL and NoSQL depends on specific application requirements like consistency, scalability, and data complexity.
Core Differences: SQL vs NoSQL
SQL databases use structured query language and predefined schemas to store data in tables with rows and columns, ensuring strong ACID compliance for transactional consistency. NoSQL databases provide flexible schema designs, supporting various data models like document, key-value, graph, or column-family stores, optimized for horizontal scaling and handling unstructured or semi-structured data. The core difference lies in scalability and data structure: SQL prioritizes relational integrity and complex queries, while NoSQL emphasizes distributed architecture and high-volume, variable data handling.
Data Modeling and Structure Comparison
SQL databases rely on structured data models using predefined schemas with tables, rows, and columns, enabling complex queries and relational integrity through joins and foreign keys. NoSQL databases offer flexible, schema-less designs supporting various data structures like documents, key-value pairs, graphs, or wide-column stores, optimizing scalability and horizontal distribution. Data modeling in SQL suits transactional applications requiring consistency, while NoSQL excels in handling unstructured or rapidly evolving data formats.
Scalability: Horizontal vs Vertical Approaches
SQL databases typically utilize vertical scaling by enhancing the hardware capacity of a single server to manage increased loads, which can be limited by physical constraints. NoSQL databases prioritize horizontal scaling by distributing data across multiple servers or nodes, enabling seamless expansion and improved performance for large datasets and high-traffic applications. This horizontal architecture supports rapid scaling and fault tolerance, making NoSQL a preferred choice for dynamic, big data environments.
Performance and Speed Considerations
SQL databases offer strong consistency and complex query capabilities, making them ideal for transactional applications where data integrity is critical; their structured schema can optimize performance for well-defined relational data. NoSQL databases provide high scalability and faster write/read speeds for unstructured or semi-structured data, excelling in distributed environments with large volumes of variable data. Performance depends on use case, with SQL suited for complex joins and ACID compliance, while NoSQL optimizes horizontal scaling and low-latency operations.
Use Cases: When to Choose SQL or NoSQL
SQL databases are ideal for applications requiring complex queries, structured data, and ACID compliance such as financial systems, inventory management, and customer relationship management. NoSQL databases excel in scenarios demanding high scalability, flexible schema, and rapid development like real-time analytics, content management, and Internet of Things (IoT) data storage. Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on data structure, consistency requirements, and scalability needs specific to the project's use case.
Flexibility in Schema Design
SQL databases enforce a rigid, predefined schema, requiring schema changes through migrations and structured table designs that ensure data consistency but limit adaptability. NoSQL databases offer dynamic schema capabilities, allowing developers to store unstructured or semi-structured data without predefined schemas, which enhances flexibility in handling evolving data models. This schema flexibility makes NoSQL databases ideal for applications with rapidly changing requirements or diverse data formats.
Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance (CAP Theorem)
SQL databases prioritize consistency and availability, ensuring ACID-compliant transactions and structured schemas ideal for complex queries and critical applications. NoSQL databases emphasize availability and partition tolerance, offering eventual consistency models that scale horizontally across distributed systems. The CAP theorem highlights the trade-offs between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance, guiding database selection based on application requirements.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
SQL databases generally incur higher upfront costs due to licensing fees and require specialized DBAs for maintenance, increasing ongoing expenses. NoSQL databases often offer lower initial costs with open-source options and scale horizontally on commodity hardware, reducing infrastructure expenses but potentially increasing complexity in maintenance. Evaluating total cost of ownership depends on data structure needs, read/write workload, and operational expertise available.
Future Trends in Database Technologies
SQL databases maintain strong consistency and structured schemas favorable for transactional applications, while NoSQL databases excel in scalability and flexibility for unstructured data. Future trends emphasize hybrid database architectures combining SQL and NoSQL features to support diverse data types and real-time analytics. Cloud-native database services and advancements in AI-driven query optimization are driving next-generation databases toward enhanced performance and automation.
SQL Database vs NoSQL Database Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com