Bug fix addresses non-critical errors in software by updating the code to resolve issues found during regular maintenance, improving overall system stability. Hotfix targets urgent, high-impact problems requiring immediate correction, often deployed quickly to prevent service disruption and protect user experience. Understanding the distinction helps prioritize development resources and maintain efficient software lifecycle management.
Table of Comparison
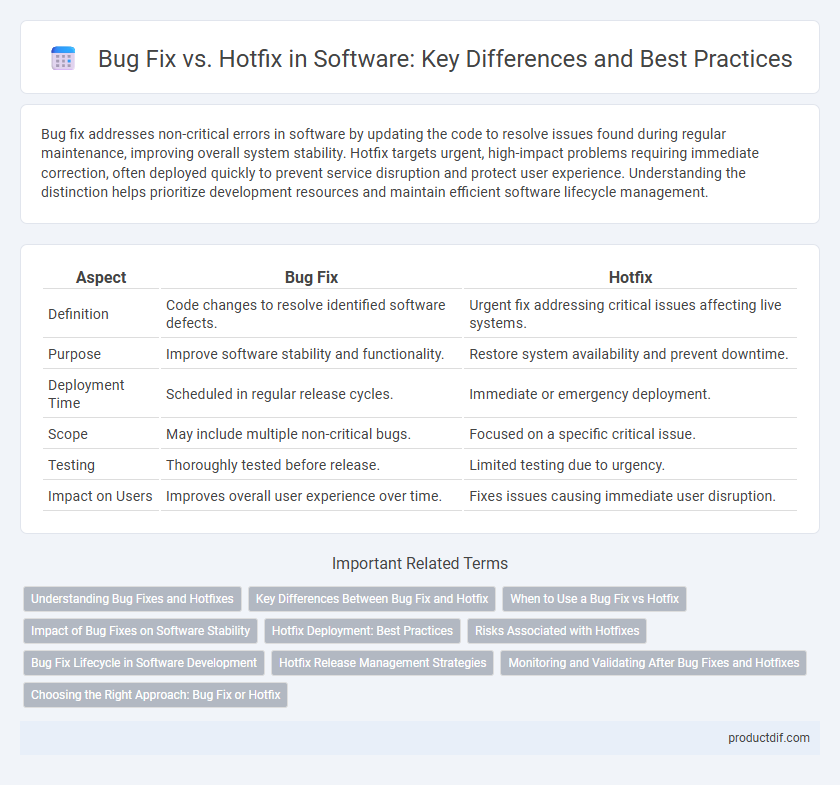
| Aspect | Bug Fix | Hotfix |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Code changes to resolve identified software defects. | Urgent fix addressing critical issues affecting live systems. |
| Purpose | Improve software stability and functionality. | Restore system availability and prevent downtime. |
| Deployment Time | Scheduled in regular release cycles. | Immediate or emergency deployment. |
| Scope | May include multiple non-critical bugs. | Focused on a specific critical issue. |
| Testing | Thoroughly tested before release. | Limited testing due to urgency. |
| Impact on Users | Improves overall user experience over time. | Fixes issues causing immediate user disruption. |
Understanding Bug Fixes and Hotfixes
Bug fixes resolve identified defects in software that impact functionality or user experience, typically distributed through regular update cycles. Hotfixes address critical issues requiring immediate resolution, often bypassing standard testing phases to minimize downtime or security risks. Understanding the distinction enables efficient prioritization in software maintenance and deployment strategies.
Key Differences Between Bug Fix and Hotfix
Bug fix addresses identified software defects usually within regular update cycles to improve overall system stability and functionality. Hotfix is an urgent, targeted patch deployed immediately to resolve critical issues causing major disruptions or security vulnerabilities. The main difference lies in timing and scope: bug fixes are planned improvements, while hotfixes are rapid responses to emergencies.
When to Use a Bug Fix vs Hotfix
A bug fix is typically used for addressing minor or non-critical software issues that can be scheduled within the regular release cycle, ensuring thorough testing before deployment. A hotfix is reserved for urgent, critical problems that negatively impact system functionality or security and require immediate application outside the standard release schedule. Developers choose a bug fix for planned maintenance and a hotfix for rapid problem resolution to minimize downtime and risk.
Impact of Bug Fixes on Software Stability
Bug fixes play a crucial role in enhancing software stability by resolving underlying issues that cause crashes, errors, or performance degradation. Unlike hotfixes, which are urgent patches addressing critical bugs rapidly, bug fixes undergo thorough testing to ensure long-term reliability and prevent regression. Effective bug management reduces downtime and improves user experience by maintaining consistent software operation.
Hotfix Deployment: Best Practices
Hotfix deployment requires immediate identification and resolution of critical bugs affecting software functionality or security, ensuring minimal downtime and preserving user experience. Best practices include thorough impact analysis, automated testing in isolated environments, and swift rollout using continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Maintaining detailed documentation and rollback plans is essential to mitigate risks and facilitate rapid recovery if issues arise post-deployment.
Risks Associated with Hotfixes
Hotfixes address critical software vulnerabilities rapidly but carry significant risks, including incomplete testing and potential introduction of new bugs that disrupt system stability. Unlike regular bug fixes, hotfixes are deployed under time pressure, which can lead to inadequate documentation and overlooked dependencies. These risks make a robust rollback plan and thorough post-deployment monitoring essential to maintain software reliability.
Bug Fix Lifecycle in Software Development
Bug fix lifecycle in software development begins with identifying and documenting the defect, followed by prioritizing the issue based on its severity and impact on functionality. Developers then analyze the root cause, implement the necessary code changes, and conduct thorough testing to verify the resolution. Once validated, the fix is integrated into the main codebase and deployed through scheduled releases or urgent patches like hotfixes to maintain software stability.
Hotfix Release Management Strategies
Hotfix release management strategies prioritize rapid identification, isolation, and deployment of critical patches to resolve urgent software defects disrupting production systems. Teams implement automated CI/CD pipelines and rollback mechanisms to ensure minimal downtime and risk during hotfix deployment. Monitoring tools and clear communication protocols are essential for validating hotfix effectiveness and maintaining system stability post-release.
Monitoring and Validating After Bug Fixes and Hotfixes
Monitoring and validating after bug fixes and hotfixes ensures software stability and performance by tracking error logs, user feedback, and system metrics in real-time. Automated testing frameworks and continuous integration tools validate that deployed fixes do not introduce regressions or new vulnerabilities. Effective post-deployment monitoring minimizes downtime and enhances the software's reliability and user experience.
Choosing the Right Approach: Bug Fix or Hotfix
Choosing the right approach between a bug fix and a hotfix depends on the severity and impact of the software issue. Bug fixes address identified defects during scheduled development cycles, ensuring thorough testing and integration, while hotfixes are urgent, immediate patches deployed to resolve critical problems affecting production environments. Evaluating the risk, urgency, and scope of the issue guides whether a controlled bug fix or rapid hotfix provides the best balance of stability and responsiveness.
Bug Fix vs Hotfix Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com