Work gloves provide general protection against abrasions, cuts, and impacts, making them suitable for construction or handling rough materials. Chemical-resistant gloves are specifically designed to protect hands from hazardous substances like acids, solvents, and oils, with materials such as nitrile, neoprene, or butyl rubber enhancing durability. Choosing the right glove depends on the task's exposure risks, ensuring optimal safety and preventing skin injuries.
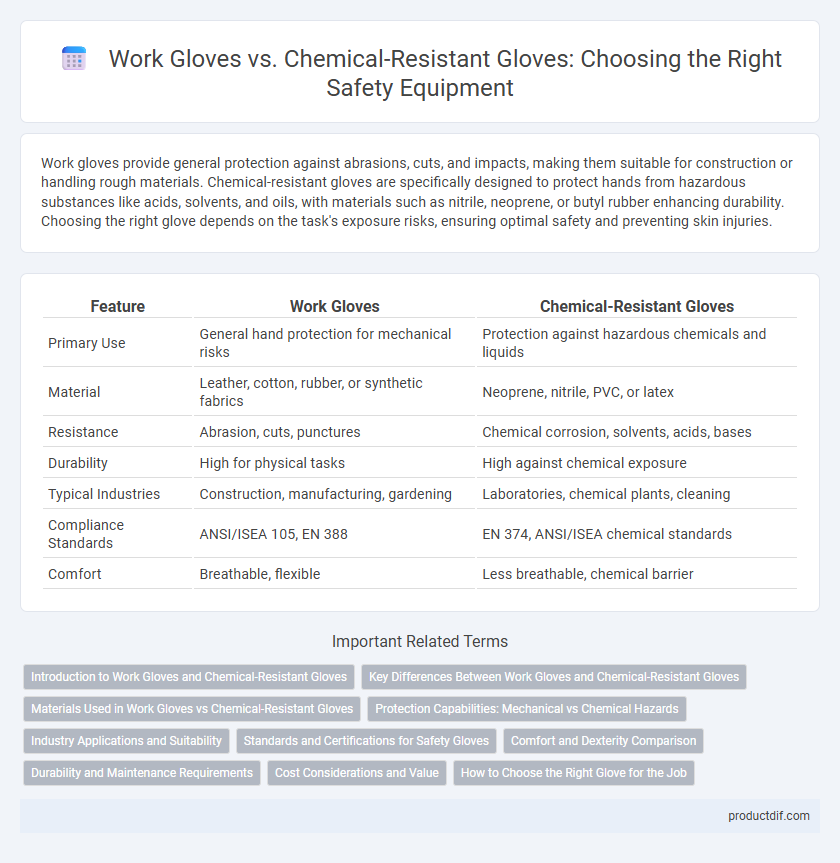
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Work Gloves | Chemical-Resistant Gloves |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General hand protection for mechanical risks | Protection against hazardous chemicals and liquids |
| Material | Leather, cotton, rubber, or synthetic fabrics | Neoprene, nitrile, PVC, or latex |
| Resistance | Abrasion, cuts, punctures | Chemical corrosion, solvents, acids, bases |
| Durability | High for physical tasks | High against chemical exposure |
| Typical Industries | Construction, manufacturing, gardening | Laboratories, chemical plants, cleaning |
| Compliance Standards | ANSI/ISEA 105, EN 388 | EN 374, ANSI/ISEA chemical standards |
| Comfort | Breathable, flexible | Less breathable, chemical barrier |
Introduction to Work Gloves and Chemical-Resistant Gloves
Work gloves provide general hand protection against cuts, abrasions, and impact hazards, commonly made from materials like leather, cotton, or synthetic fibers. Chemical-resistant gloves are specifically designed to shield hands from hazardous substances and corrosive chemicals, often constructed from nitrile, neoprene, or PVC. Choosing the appropriate glove depends on the nature of the task and exposure risks to ensure maximum hand safety.
Key Differences Between Work Gloves and Chemical-Resistant Gloves
Work gloves primarily offer protection against abrasions, cuts, and general workplace hazards, featuring materials such as leather, cotton, or synthetic fibers designed for durability and comfort. Chemical-resistant gloves are specifically engineered to prevent chemical penetration and skin exposure, constructed from materials like nitrile, neoprene, or PVC that provide resistance to acids, solvents, and toxic substances. The key differences lie in their material composition and specific protective capabilities, with work gloves suited for physical tasks and chemical-resistant gloves essential for handling hazardous chemicals safely.
Materials Used in Work Gloves vs Chemical-Resistant Gloves
Work gloves commonly feature materials such as leather, cotton, and synthetic fabrics designed for abrasion resistance and comfort during manual tasks. Chemical-resistant gloves utilize specialized materials like nitrile, neoprene, and PVC that provide robust protection against hazardous substances and corrosive chemicals. The choice of material directly impacts durability, flexibility, and the level of protection suitable for different industrial environments.
Protection Capabilities: Mechanical vs Chemical Hazards
Work gloves provide robust protection against mechanical hazards, including cuts, abrasions, and punctures, making them essential for general labor tasks. Chemical-resistant gloves are specifically designed to shield the skin from harmful substances such as acids, solvents, and oils, preventing chemical burns and contamination. Selecting the appropriate glove type depends on the nature of workplace hazards, ensuring optimal safety by addressing either mechanical impacts or chemical exposure.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Work gloves provide general protection against abrasion and impact, making them suitable for construction, manufacturing, and assembly line tasks where hand durability is essential. Chemical-resistant gloves are designed to shield hands from hazardous substances like acids, solvents, and oils, commonly used in chemical processing, laboratory work, and cleaning industries. Selecting the appropriate glove type depends on the specific hazards present, ensuring compliance with safety standards and preventing workplace injuries.
Standards and Certifications for Safety Gloves
Work gloves and chemical-resistant gloves must comply with specific standards and certifications to ensure adequate protection; ANSI/ISEA 105 evaluates cut, puncture, and abrasion resistance for general work gloves, while chemical-resistant gloves are certified under ASTM standards such as ASTM F739 for permeation resistance. EN 388 and EN 374 are critical European standards that certify mechanical protection and chemical resistance, respectively, providing a benchmark for glove performance in various industrial applications. Selecting gloves with the appropriate certifications guarantees compliance with safety regulations and enhances worker safety against mechanical hazards or chemical exposure.
Comfort and Dexterity Comparison
Work gloves typically offer greater comfort and dexterity due to softer materials like leather or fabric, which allow for better breathability and flexibility during general tasks. Chemical-resistant gloves, often made from nitrile, neoprene, or PVC, prioritize protection against hazardous substances but can be thicker and less flexible, potentially reducing tactile sensitivity. Choosing between these gloves involves balancing the need for chemical protection with maintaining hand comfort and fine motor skills for specific job requirements.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Work gloves typically offer moderate durability suitable for general tasks but require frequent replacement due to wear and tear. Chemical-resistant gloves provide enhanced durability against harsh substances and demand specific maintenance, such as thorough cleaning and proper storage to prevent material degradation. Selecting gloves with appropriate durability and maintenance needs ensures prolonged protection and cost efficiency in hazardous work environments.
Cost Considerations and Value
Work gloves generally offer lower upfront costs and are suitable for general tasks, providing moderate protection and durability. Chemical-resistant gloves, while more expensive, deliver superior safety against hazardous substances and reduce the risk of costly workplace injuries or contamination. Investing in chemical-resistant gloves often results in better long-term value due to enhanced protection and compliance with safety regulations.
How to Choose the Right Glove for the Job
Selecting the right glove for the job requires assessing the specific hazards present, such as abrasion, cuts, or chemical exposure. Work gloves offer general protection for mechanical risks, while chemical-resistant gloves provide specialized barriers against solvents, acids, and corrosive substances. Evaluating glove material compatibility, durability, and workplace conditions ensures optimal safety and performance.
Work gloves vs Chemical-resistant gloves Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com