A face shield provides full-face protection from flying debris and chemical splashes but lacks the specialized filtering and heat resistance of a welding mask. Welding masks are specifically designed with flame-resistant materials and auto-darkening lenses to shield the eyes and face from intense light and sparks during welding. Choosing the right safety equipment depends on the specific hazard, with welding masks offering targeted protection for high-heat environments while face shields suit general impact and splash protection.
Table of Comparison
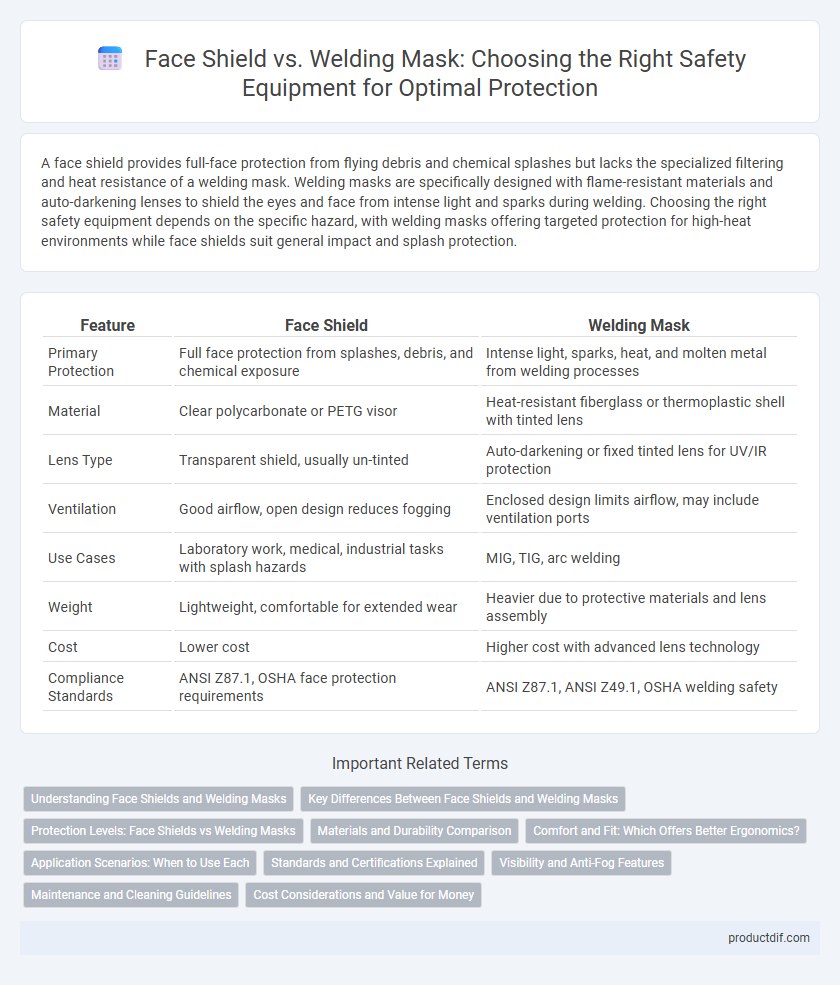
| Feature | Face Shield | Welding Mask |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Full face protection from splashes, debris, and chemical exposure | Intense light, sparks, heat, and molten metal from welding processes |
| Material | Clear polycarbonate or PETG visor | Heat-resistant fiberglass or thermoplastic shell with tinted lens |
| Lens Type | Transparent shield, usually un-tinted | Auto-darkening or fixed tinted lens for UV/IR protection |
| Ventilation | Good airflow, open design reduces fogging | Enclosed design limits airflow, may include ventilation ports |
| Use Cases | Laboratory work, medical, industrial tasks with splash hazards | MIG, TIG, arc welding |
| Weight | Lightweight, comfortable for extended wear | Heavier due to protective materials and lens assembly |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost with advanced lens technology |
| Compliance Standards | ANSI Z87.1, OSHA face protection requirements | ANSI Z87.1, ANSI Z49.1, OSHA welding safety |
Understanding Face Shields and Welding Masks
Face shields provide transparent, impact-resistant protection primarily against chemical splashes and debris, commonly used in laboratory and industrial settings. Welding masks are equipped with auto-darkening filters that shield the eyes and face from intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation produced during welding. Understanding the specific hazards and protection levels of each allows for proper equipment selection in various safety-critical environments.
Key Differences Between Face Shields and Welding Masks
Face shields provide full-face protection mainly against splashes, flying debris, and chemical hazards, while welding masks are specifically designed to protect against intense light, sparks, and heat generated during welding. Welding masks incorporate specialized lenses with varying shade levels to filter harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation, a feature absent in standard face shields. The choice depends on the nature of the task, with welding masks indispensable for welding applications and face shields suited for general industrial safety needs.
Protection Levels: Face Shields vs Welding Masks
Face shields offer limited protection primarily against splashes and debris, making them suitable for light industrial tasks but insufficient for high-heat environments. Welding masks provide advanced protection with heat-resistant materials and filtering lenses that shield against intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation during welding processes. Choosing the appropriate gear depends on the required level of impact resistance, heat exposure, and optical protection for specific safety needs.
Materials and Durability Comparison
Face shields typically use polycarbonate or acetate lenses known for impact resistance and clarity, providing lightweight protection against debris and splashes but limited heat resistance. Welding masks employ heat-resistant materials such as fiberglass or thermoplastic shells combined with specialized tinted lenses that withstand extreme temperatures and intense light during welding. In terms of durability, welding masks offer superior longevity under harsh conditions, while face shields are more suitable for general safety with moderate durability.
Comfort and Fit: Which Offers Better Ergonomics?
Face shields provide lightweight comfort with adjustable straps and clear visibility, making them suitable for longer wear and less strenuous tasks. Welding masks, especially those with padded headbands and adjustable fittings, offer superior protection but can be heavier and may cause more discomfort during extended use. Ergonomically, face shields tend to be better for comfort and fit in low-intensity environments, while welding masks prioritize safety with a trade-off in wearability.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each
Face shields are ideal for protection against splashes, flying debris, and chemical exposure in environments like laboratories, healthcare, and light manufacturing. Welding masks provide specialized protection from intense heat, sparks, and harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation during welding, cutting, and grinding tasks. Selecting the appropriate gear depends on the specific hazards present, with welding masks required in high-heat metalwork and face shields suitable for general impact and splash resistance.
Standards and Certifications Explained
Face shields and welding masks are governed by distinct safety standards to ensure adequate protection; face shields typically comply with ANSI Z87.1 standards for impact resistance and face protection in general industrial applications, while welding masks must meet the stringent ANSI Z87.1 and ANSI Z89.1 standards for eye and face protection against intense light, sparks, and heat. Certification by organizations like OSHA and CSA validates that these protective devices reliably shield users in their respective environments, with welding masks often requiring additional auto-darkening filter certification such as the EN 379 standard in Europe.
Visibility and Anti-Fog Features
Welding masks often feature auto-darkening lenses that adjust visibility instantly when welding, enhancing precision, while face shields provide a clear, unobstructed view suitable for tasks requiring broad visibility but may lack advanced anti-fog capabilities. High-quality face shields incorporate anti-fog coatings or ventilation to reduce condensation, critical for maintaining clear vision during prolonged use. Welding masks prioritize protective functionality and may include limited anti-fog solutions, making face shields more advantageous for operators needing consistent visibility without lens darkening.
Maintenance and Cleaning Guidelines
Face shields require regular cleaning with mild soap and water to maintain clear visibility and prevent scratches, while welding masks demand careful inspection and replacement of protective lenses to avoid damage from sparks and intense heat. Both types of equipment should be stored in a clean, dry place to prevent contamination and degradation of materials. Proper maintenance ensures maximum protection and extends the lifespan of the safety gear in industrial environments.
Cost Considerations and Value for Money
Face shields generally cost less than welding masks, making them a budget-friendly option for light-duty protection, but they lack the specialized features required for welding tasks. Welding masks, though more expensive upfront, offer superior value for money by providing essential glare protection, heat resistance, and impact durability that enhance safety during welding operations. Investing in a quality welding mask reduces long-term costs associated with eye injuries and equipment replacement, delivering greater overall value for professional welders.
Face shield vs Welding mask Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com