Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for pets includes items like protective boots, safety goggles, and harnesses designed to safeguard animals from environmental hazards. In contrast, MPE (Mechanical Protective Equipment) refers to physical barriers or structures such as pet carriers, crates, and gates that prevent injury by restricting movement or exposure to dangerous areas. Choosing the right type depends on the specific risks pets face, with PPE providing direct protection and MPE offering containment and physical safety.
Table of Comparison
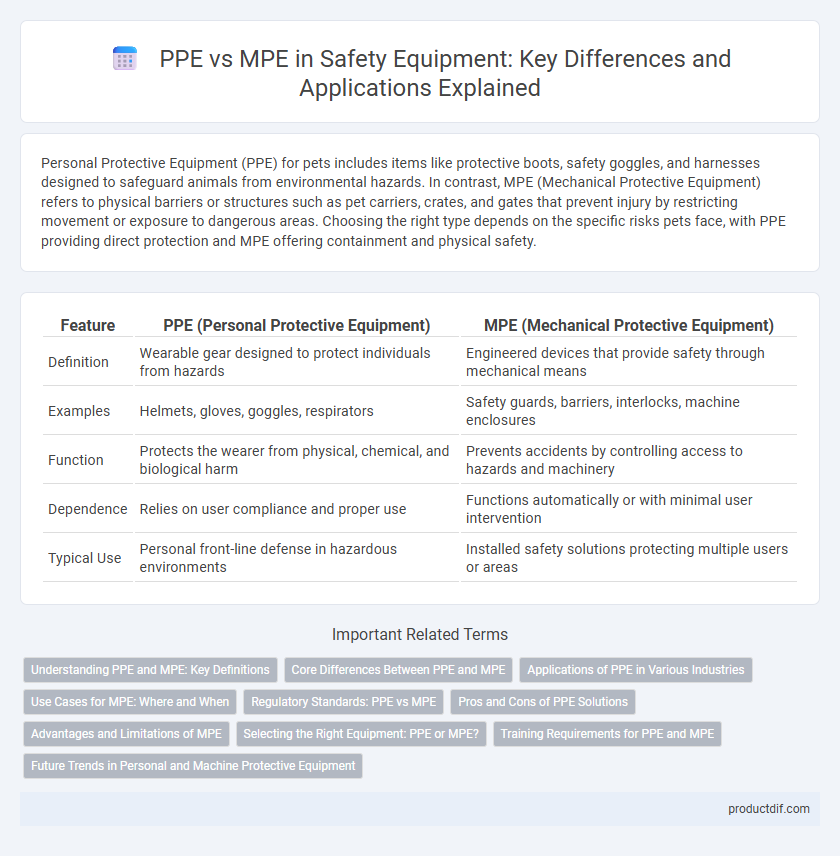
| Feature | PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) | MPE (Mechanical Protective Equipment) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wearable gear designed to protect individuals from hazards | Engineered devices that provide safety through mechanical means |
| Examples | Helmets, gloves, goggles, respirators | Safety guards, barriers, interlocks, machine enclosures |
| Function | Protects the wearer from physical, chemical, and biological harm | Prevents accidents by controlling access to hazards and machinery |
| Dependence | Relies on user compliance and proper use | Functions automatically or with minimal user intervention |
| Typical Use | Personal front-line defense in hazardous environments | Installed safety solutions protecting multiple users or areas |
Understanding PPE and MPE: Key Definitions
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to specialized clothing or equipment worn by workers to minimize exposure to hazards that cause serious workplace injuries and illnesses. Medium Protective Equipment (MPE) offers a balanced level of defense, typically used in environments where risks are moderate and do not require full PPE deployment. Understanding the distinctions between PPE and MPE enables organizations to implement appropriate safety measures tailored to specific hazard levels, ensuring optimal worker protection without unnecessary burden.
Core Differences Between PPE and MPE
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to gear designed to shield individuals from physical, chemical, or biological hazards, including gloves, helmets, and masks. Mechanical Protective Equipment (MPE) specifically focuses on safeguarding against mechanical risks such as cuts, impacts, or abrasions, often involving reinforced gloves, guards, and helmets with enhanced structural components. The core difference lies in PPE's broad protective scope versus MPE's targeted protection against mechanical threats within hazardous work environments.
Applications of PPE in Various Industries
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential across industries such as construction, healthcare, manufacturing, and chemical processing to protect workers from physical, chemical, and biological hazards. PPE applications include helmets, gloves, goggles, respiratory masks, and protective clothing designed to minimize exposure to dangerous environments and reduce injury risks. The versatility of PPE ensures compliance with safety regulations while enhancing employee safety in high-risk workplace conditions.
Use Cases for MPE: Where and When
Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) guidelines are crucial in environments with high levels of electromagnetic radiation, such as telecommunications towers, medical imaging facilities, and industrial microwave ovens. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is essential when direct physical barriers or protective gear, like gloves or helmets, cannot fully mitigate exposure risks, whereas MPE sets numerical limits ensuring workplace safety by defining safe exposure durations and intensities. Use cases for MPE include monitoring RF radiation in broadcasting stations and maintaining safe distances during MRI procedures to prevent tissue damage and thermal effects.
Regulatory Standards: PPE vs MPE
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) must comply with regulatory standards such as OSHA, ANSI, and ISO to ensure worker safety against hazardous exposures. Machinery Protection Equipment (MPE) adheres to standards like ISO 13849 and IEC 62061, focusing on safeguarding machinery operation and minimizing risk of mechanical injury. Understanding the distinct regulatory frameworks governing PPE and MPE is critical for maintaining compliance and ensuring effective safety management.
Pros and Cons of PPE Solutions
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) offers direct physical barriers against hazards, including gloves, helmets, and respirators, ensuring immediate worker protection. However, PPE relies heavily on correct usage and maintenance, posing risks if improperly handled or neglected. While PPE is essential for individual safety, it does not eliminate hazards at the source, potentially leading to greater long-term exposure risks.
Advantages and Limitations of MPE
Minimal Protective Equipment (MPE) offers increased comfort and mobility compared to traditional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), reducing user fatigue during extended use. MPE is designed with advanced materials that provide targeted protection without the bulk, enhancing agility in high-risk environments. However, its limitations include reduced coverage and potential vulnerability to certain hazards that PPE's comprehensive designs typically mitigate.
Selecting the Right Equipment: PPE or MPE?
Choosing between Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Mechanical Protective Equipment (MPE) depends on the specific hazards and risk levels present in the workplace. PPE is designed to protect workers from direct exposure to hazards through wearable items like gloves, helmets, and respirators, while MPE involves engineering controls such as machine guards and barriers that reduce or eliminate exposure to risks. Selecting the right equipment requires a thorough hazard assessment to determine whether individual protection or mechanical safeguards offer the most effective defense.
Training Requirements for PPE and MPE
Training requirements for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) include proper selection, correct usage, maintenance, and limitations to ensure user safety and regulatory compliance. Machine Protective Equipment (MPE) training emphasizes hazard recognition, equipment installation, operation, and routine inspection to prevent mechanical failures and workplace injuries. Compliance with OSHA standards mandates documented training programs for both PPE and MPE, tailored to specific workplace hazards and equipment types.
Future Trends in Personal and Machine Protective Equipment
Emerging advances in PPE and MPE emphasize integrated sensory technology and artificial intelligence, enhancing real-time hazard detection and worker-machine interaction. Innovations prioritize ergonomic design and lightweight materials to improve user comfort and compliance on industrial sites. The convergence of wearable technology with machine learning algorithms signals a future where adaptive, predictive protection systems minimize workplace injuries and operational downtime.
PPE vs MPE Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com