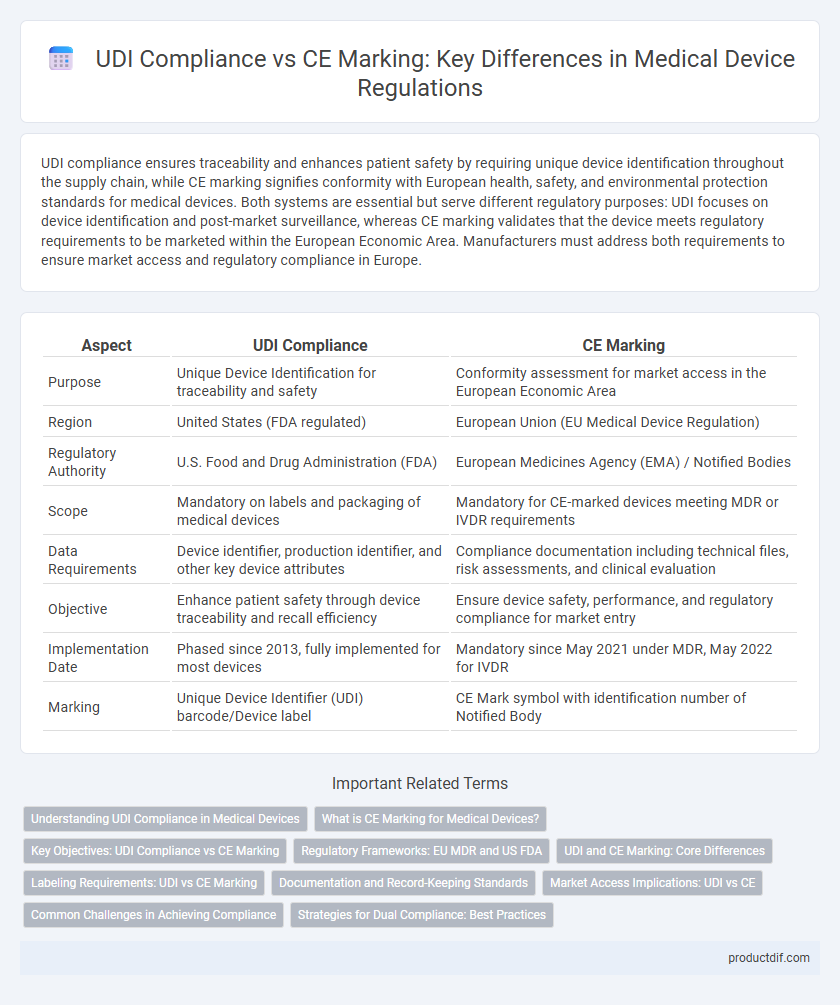
UDI compliance ensures traceability and enhances patient safety by requiring unique device identification throughout the supply chain, while CE marking signifies conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards for medical devices. Both systems are essential but serve different regulatory purposes: UDI focuses on device identification and post-market surveillance, whereas CE marking validates that the device meets regulatory requirements to be marketed within the European Economic Area. Manufacturers must address both requirements to ensure market access and regulatory compliance in Europe.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | UDI Compliance | CE Marking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Unique Device Identification for traceability and safety | Conformity assessment for market access in the European Economic Area |
| Region | United States (FDA regulated) | European Union (EU Medical Device Regulation) |
| Regulatory Authority | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | European Medicines Agency (EMA) / Notified Bodies |
| Scope | Mandatory on labels and packaging of medical devices | Mandatory for CE-marked devices meeting MDR or IVDR requirements |
| Data Requirements | Device identifier, production identifier, and other key device attributes | Compliance documentation including technical files, risk assessments, and clinical evaluation |
| Objective | Enhance patient safety through device traceability and recall efficiency | Ensure device safety, performance, and regulatory compliance for market entry |
| Implementation Date | Phased since 2013, fully implemented for most devices | Mandatory since May 2021 under MDR, May 2022 for IVDR |
| Marking | Unique Device Identifier (UDI) barcode/Device label | CE Mark symbol with identification number of Notified Body |
Understanding UDI Compliance in Medical Devices
UDI compliance in medical devices ensures traceability and enhances patient safety by providing a unique identifier for each product throughout its lifecycle. Unlike CE marking, which certifies conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, UDI focuses on standardized identification to improve post-market surveillance and recall efficiency. Manufacturers must integrate UDI requirements with existing regulatory frameworks to maintain market access and regulatory adherence globally.
What is CE Marking for Medical Devices?
CE marking for medical devices signifies conformity with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and confirms that the device meets all safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. This certification is mandatory for marketing medical devices within the European Economic Area (EEA) and ensures product traceability, performance, and compliance with stringent standards. Unlike UDI compliance, which focuses on unique device identification for global traceability, CE marking primarily addresses regulatory approval and market access in Europe.
Key Objectives: UDI Compliance vs CE Marking
UDI compliance aims to enhance patient safety and traceability by providing a unique identifier for each medical device throughout its lifecycle. CE marking focuses on confirming that a medical device meets EU regulatory requirements for safety, health, and environmental protection before market entry. Both objectives ensure device accountability but target different aspects: UDI emphasizes post-market surveillance, while CE marking prioritizes pre-market conformity.
Regulatory Frameworks: EU MDR and US FDA
UDI compliance under the US FDA requires medical devices to have a unique device identifier for tracking and safety monitoring, aligning with Title 21 CFR Part 830. CE marking under the EU MDR mandates conformity with stringent safety and performance requirements specified in Regulation (EU) 2017/745. Both regulatory frameworks aim to enhance device traceability and patient safety but differ in scope, documentation, and enforcement mechanisms.
UDI and CE Marking: Core Differences
UDI compliance requires medical devices to have a unique device identifier for enhanced traceability and post-market surveillance, while CE marking confirms that a device meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. UDI focuses on device identification and data management across global supply chains, supporting regulatory transparency and patient safety. CE marking indicates conformity to EU directives but does not provide device-specific tracking as UDI does.
Labeling Requirements: UDI vs CE Marking
UDI compliance mandates the inclusion of a unique device identifier on medical device labels to ensure traceability throughout the product lifecycle, enhancing patient safety and regulatory oversight. CE marking requires conformity with European Union labeling standards, emphasizing compliance with the Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) and providing essential information such as device identification, manufacturer details, and safety instructions. While UDI focuses on standardized traceability, CE marking incorporates broader regulatory compliance, combining labeling with safety and performance documentation for market approval.
Documentation and Record-Keeping Standards
UDI compliance requires manufacturers to maintain detailed documentation and records of device identification, production, and distribution to ensure traceability throughout the supply chain. CE marking mandates comprehensive technical documentation demonstrating conformity with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), including risk management files, clinical evaluation reports, and quality system records. Both frameworks emphasize rigorous documentation standards, but UDI focuses on unique device identification for post-market surveillance, while CE marking integrates broader compliance evidence for market authorization.
Market Access Implications: UDI vs CE
UDI compliance enhances traceability and post-market surveillance, facilitating regulatory reporting and patient safety monitoring across global markets. CE marking demonstrates conformity with EU safety and performance requirements, enabling market access specifically within the European Economic Area. Both UDI and CE marking are essential, but UDI offers broader implications for global supply chain transparency, while CE marking is crucial for legal market entry in Europe.
Common Challenges in Achieving Compliance
Achieving UDI compliance and CE marking presents common challenges such as complex regulatory requirements, inconsistent global standards, and the need for precise data management to ensure traceability. Manufacturers often struggle with integrating UDI systems into existing quality management frameworks while meeting the stringent documentation and labeling rules mandated by the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Ensuring interoperability between UDI databases and CE marking documentation remains a critical hurdle for seamless market access and regulatory approval.
Strategies for Dual Compliance: Best Practices
Implementing a unified risk management system aligned with both UDI compliance and CE marking streamlines regulatory processes and enhances product safety documentation. Leveraging integrated software solutions facilitates accurate data submission to UDI databases while maintaining conformity with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) requirements for CE marking. Cross-functional collaboration between regulatory, quality, and IT teams ensures consistent labeling, traceability, and certification, optimizing market access in the US and European Union.
UDI compliance vs CE marking Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com