The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) introduces stricter requirements for safety, clinical evaluation, and post-market surveillance compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD). MDR ensures greater transparency and traceability through the implementation of unique device identification (UDI) systems and enhanced documentation. Manufacturers must comply with MDR to maintain market access in the European Union, reflecting a shift towards more rigorous regulatory oversight for medical devices.
Table of Comparison
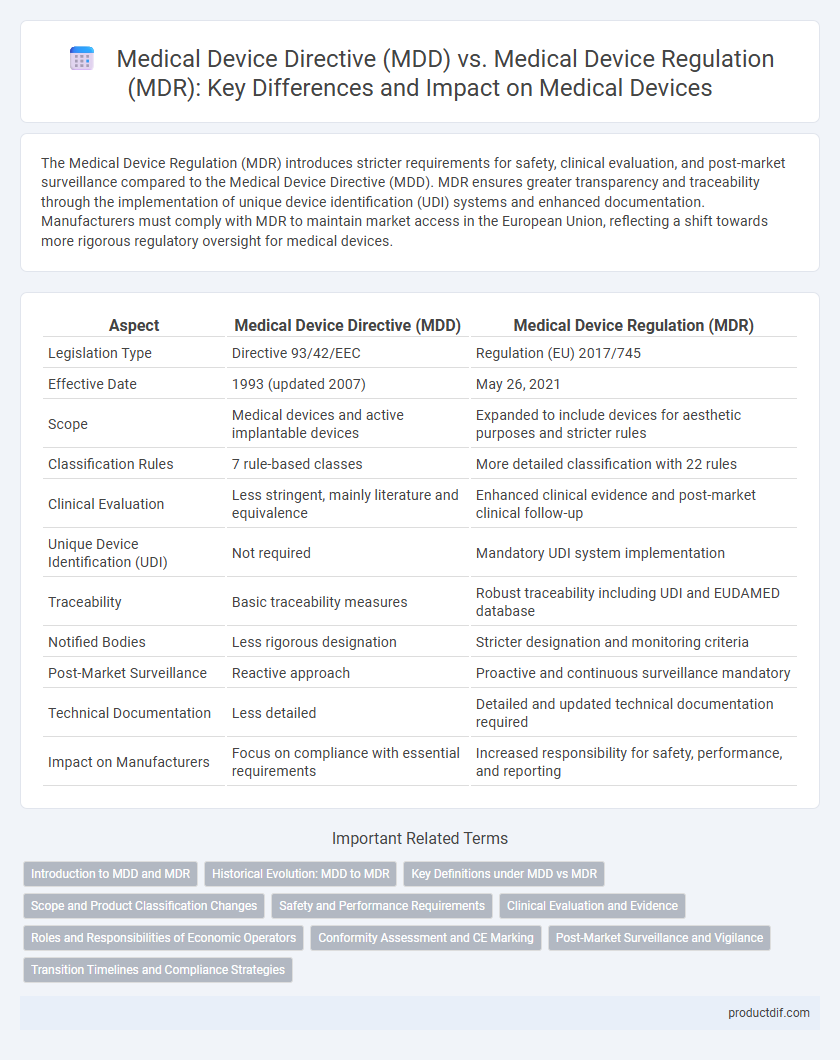
| Aspect | Medical Device Directive (MDD) | Medical Device Regulation (MDR) |
|---|---|---|
| Legislation Type | Directive 93/42/EEC | Regulation (EU) 2017/745 |
| Effective Date | 1993 (updated 2007) | May 26, 2021 |
| Scope | Medical devices and active implantable devices | Expanded to include devices for aesthetic purposes and stricter rules |
| Classification Rules | 7 rule-based classes | More detailed classification with 22 rules |
| Clinical Evaluation | Less stringent, mainly literature and equivalence | Enhanced clinical evidence and post-market clinical follow-up |
| Unique Device Identification (UDI) | Not required | Mandatory UDI system implementation |
| Traceability | Basic traceability measures | Robust traceability including UDI and EUDAMED database |
| Notified Bodies | Less rigorous designation | Stricter designation and monitoring criteria |
| Post-Market Surveillance | Reactive approach | Proactive and continuous surveillance mandatory |
| Technical Documentation | Less detailed | Detailed and updated technical documentation required |
| Impact on Manufacturers | Focus on compliance with essential requirements | Increased responsibility for safety, performance, and reporting |
Introduction to MDD and MDR
The Medical Device Directive (MDD) 93/42/EEC established the regulatory framework for medical devices in the European Union, focusing on ensuring safety and performance through conformity assessment procedures and CE marking. The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745 replaced the MDD to strengthen device traceability, clinical evaluation requirements, and post-market surveillance, enhancing patient safety and regulatory oversight. MDR introduces more rigorous classification rules and expanded scope to include devices without an intended medical purpose, improving overall compliance and transparency in the medical device industry.
Historical Evolution: MDD to MDR
The transition from the Medical Device Directive (MDD 93/42/EEC) to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745) marks a significant update in European medical device legislation, introduced to enhance patient safety and device efficacy. The MDR, enforced since May 2021, incorporates stricter clinical evaluation requirements, increased post-market surveillance, and more rigorous device classification rules compared to the MDD framework established in 1993. This evolution addresses gaps identified under the MDD, reflecting advances in technology and ensuring better alignment with current healthcare standards and innovation.
Key Definitions under MDD vs MDR
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) introduces stricter and more comprehensive definitions for key terms such as "medical device," "accessory," and "implantable device" compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD), enhancing clarity and scope. MDR expands the definition of medical devices to include software and explicitly categorizes accessories as devices in their own right, whereas MDD had a more limited and ambiguous approach. This evolution in definitions under MDR ensures improved regulatory oversight and better alignment with technological advancements in medical devices.
Scope and Product Classification Changes
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) expands the scope to include a broader range of products, such as implantable devices and software intended for medical purposes, compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD). MDR introduces more stringent classification rules based on risk, duration of use, and invasiveness, resulting in reclassification of many devices to higher risk classes. These changes demand manufacturers to reassess product classification and comply with enhanced conformity assessment procedures under MDR.
Safety and Performance Requirements
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) enforces stricter safety and performance requirements compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD), mandating comprehensive clinical evaluations and post-market surveillance. MDR emphasizes enhanced traceability through Unique Device Identification (UDI) and requires robust risk management to address device-related hazards throughout the product lifecycle. These regulations aim to improve patient safety and device effectiveness by mandating higher transparency, stricter documentation, and ongoing compliance monitoring.
Clinical Evaluation and Evidence
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) enforces more stringent requirements for clinical evaluation and evidence compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD), emphasizing continuous post-market clinical follow-up and comprehensive data collection. MDR mandates robust clinical investigations and updated scientific literature to demonstrate safety and performance, whereas MDD allowed more reliance on equivalence data. Enhanced scrutiny under MDR ensures higher transparency, traceability, and patient safety through detailed clinical evaluation reports and persistent evidence generation.
Roles and Responsibilities of Economic Operators
Under the Medical Device Directive (MDD), roles and responsibilities of economic operators such as manufacturers, authorized representatives, and distributors were less explicitly defined, leading to ambiguities in product compliance and market surveillance. The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) establishes clearer, more stringent obligations, requiring manufacturers to ensure device safety and performance, authorized representatives to act as legal entities within the EU, and distributors to verify product conformity and proper documentation before market placement. MDR enhances accountability by mandating specific post-market surveillance activities and traceability responsibilities among all economic operators, reducing risks associated with non-compliant devices.
Conformity Assessment and CE Marking
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) introduces more stringent Conformity Assessment requirements compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD), emphasizing enhanced clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance. Under MDR, manufacturers must provide comprehensive technical documentation and involve notified bodies more rigorously to obtain CE marking. This transition aims to improve device safety, performance, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle in the European market.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) enforces more rigorous post-market surveillance (PMS) and vigilance requirements compared to the Medical Device Directive (MDD), emphasizing continuous safety monitoring and proactive risk management. Under MDR, manufacturers must implement comprehensive PMS plans, including periodic safety update reports (PSURs) and trend reporting, to promptly identify and mitigate potential device-related risks. Vigilance reporting deadlines are shortened, and the scope of reportable incidents is expanded to enhance patient safety and regulatory compliance across the European Union.
Transition Timelines and Compliance Strategies
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) replaced the Medical Device Directive (MDD) with a transition period ending on May 26, 2021, requiring manufacturers to update technical documentation and ensure compliance with stricter safety and performance requirements. Compliance strategies emphasize early gap analysis, risk management updates, and alignment with the MDR's unique device identification (UDI) system to maintain market access. Manufacturers must also prioritize clinical evaluation reports and post-market surveillance enhancements to meet the MDR's rigorous regulatory framework.
Medical Device Directive (MDD) vs Medical Device Regulation (MDR) Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com