Toughened glass offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance by undergoing a rapid cooling process, making it ideal for pet water bowls and feeding dishes that require durability. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing superior safety by holding fragments together if broken, reducing injury risk for pets. Both types improve the safety and longevity of glassware pet products, but toughened glass prioritizes impact resistance while laminated glass emphasizes shatter containment.
Table of Comparison
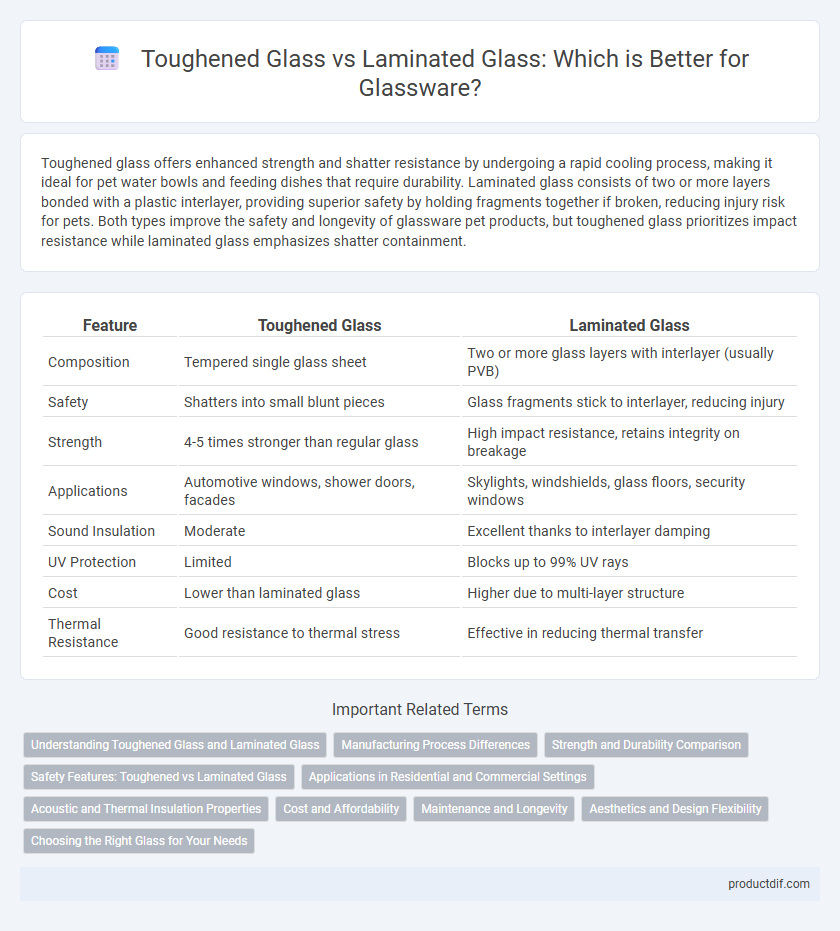
| Feature | Toughened Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Tempered single glass sheet | Two or more glass layers with interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Safety | Shatters into small blunt pieces | Glass fragments stick to interlayer, reducing injury |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass | High impact resistance, retains integrity on breakage |
| Applications | Automotive windows, shower doors, facades | Skylights, windshields, glass floors, security windows |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Excellent thanks to interlayer damping |
| UV Protection | Limited | Blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Cost | Lower than laminated glass | Higher due to multi-layer structure |
| Thermal Resistance | Good resistance to thermal stress | Effective in reducing thermal transfer |
Understanding Toughened Glass and Laminated Glass
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is heat-treated to increase its strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing injury risk. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds shards together when broken for enhanced safety and sound insulation. Both types are widely used in construction and automotive industries for their durability and protective properties.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Toughened glass is manufactured through a rapid heating and cooling process called thermal tempering, which induces compressive stresses on the surface, enhancing its strength and resistance to impact. Laminated glass is produced by bonding two or more glass layers together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), under heat and pressure, creating a composite that holds together when shattered. The thermal tempering of toughened glass improves durability, whereas the lamination process provides enhanced safety and sound insulation by preventing glass shards from dispersing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Toughened glass offers high strength due to its thermal tempering process, making it resistant to impact and sudden temperature changes, ideal for safety applications. Laminated glass combines multiple glass layers with an interlayer, enhancing durability by holding shards together upon breakage, providing superior resistance against penetration and long-term wear. Both types excel in strength, but toughened glass prioritizes impact resistance while laminated glass emphasizes shatter retention and multi-layer protection.
Safety Features: Toughened vs Laminated Glass
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, enhances safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, preventing shattering as the glass fragments adhere to the plastic layer, maintaining integrity and reducing penetration hazards. Both toughened and laminated glass offer distinct safety benefits, with laminated glass providing superior resistance against forced entry and impact retention.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Settings
Toughened glass is widely used in residential settings for windows, doors, and shower enclosures due to its high strength and safety features, shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact to reduce injury risk. Laminated glass finds extensive application in commercial settings, offering enhanced security and sound insulation by holding together when shattered, making it ideal for storefronts, skylights, and facades. Both types provide safety but are chosen based on specific needs such as impact resistance for toughened glass and structural integrity plus noise reduction for laminated glass.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Properties
Toughened glass offers enhanced thermal insulation due to its increased strength and resistance to temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for environments requiring durability and heat resistance. Laminated glass excels in acoustic insulation by incorporating a PVB interlayer that effectively dampens sound vibrations, significantly reducing noise transmission. Combining these glasses can optimize both thermal and acoustic performance, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency in architectural applications.
Cost and Affordability
Toughened glass generally costs less than laminated glass due to its simpler manufacturing process, making it a more affordable option for projects with tight budgets. Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and noise reduction but comes at a higher price point because of the added interlayer and lamination process. Selecting between the two depends on balancing cost constraints with desired safety and performance features in glassware applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Toughened glass offers superior resistance to impact and scratches, requiring minimal maintenance and ensuring a longer lifespan in high-traffic areas. Laminated glass, enhanced by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides excellent durability against shattering and UV damage, preserving clarity and structural integrity over time. Both types benefit from regular cleaning with non-abrasive materials to optimize performance and extend their service life.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Toughened glass offers a sleek, modern appearance with a uniform surface ideal for minimalist designs and large, uninterrupted panes. Laminated glass provides enhanced design flexibility by allowing incorporation of colors, textures, and printed interlayers, enabling customized aesthetic effects. Both types support diverse architectural styles, but laminated glass stands out for creative expression in decorative applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Toughened glass offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance, making it ideal for safety-critical applications like doors and windows in high-traffic areas. Laminated glass features a plastic interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, providing superior security and sound insulation for environments requiring both safety and noise reduction. Selecting the right glass depends on factors such as impact resistance, safety requirements, and acoustic performance tailored to your specific project.
Toughened Glass vs Laminated Glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com