Vitrified glass pet dishes are highly durable and resistant to scratches, stains, and thermal shock, making them ideal for long-lasting use and safe daily cleaning. Non-vitrified glass tends to be more porous and fragile, which can absorb liquids and odors, leading to quicker wear and potential bacterial growth. Choosing vitrified glass ensures a hygienic, sturdy, and aesthetically pleasing option for pet owners seeking quality glassware.
Table of Comparison
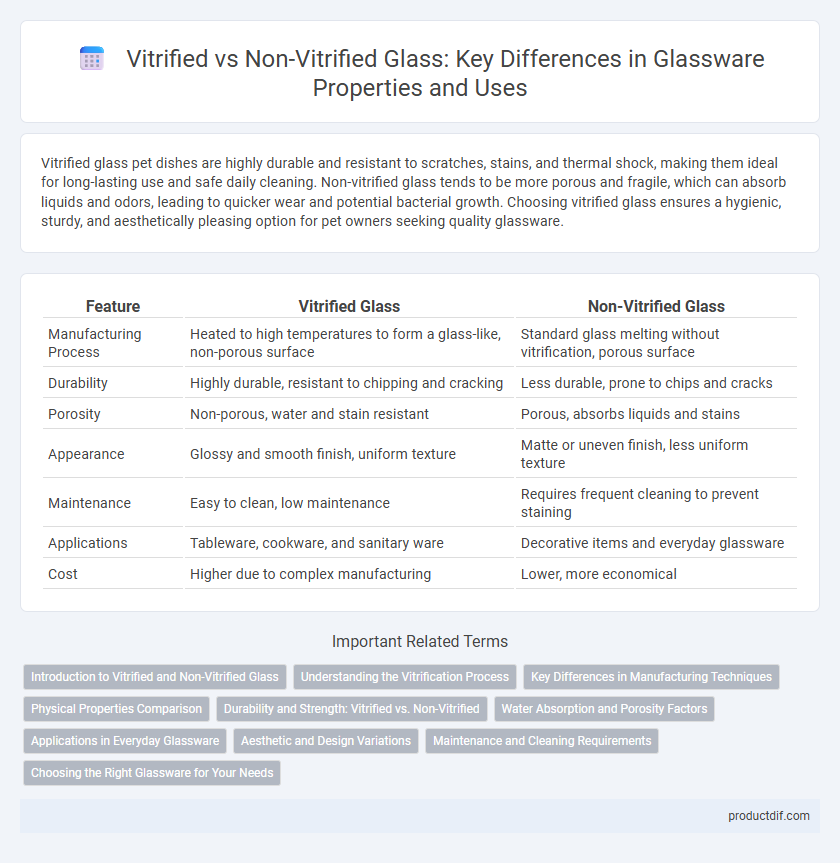
| Feature | Vitrified Glass | Non-Vitrified Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Heated to high temperatures to form a glass-like, non-porous surface | Standard glass melting without vitrification, porous surface |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chipping and cracking | Less durable, prone to chips and cracks |
| Porosity | Non-porous, water and stain resistant | Porous, absorbs liquids and stains |
| Appearance | Glossy and smooth finish, uniform texture | Matte or uneven finish, less uniform texture |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, low maintenance | Requires frequent cleaning to prevent staining |
| Applications | Tableware, cookware, and sanitary ware | Decorative items and everyday glassware |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing | Lower, more economical |
Introduction to Vitrified and Non-Vitrified Glass
Vitrified glass is created through a high-temperature firing process that fuses silica and other materials into a dense, non-porous surface, making it highly durable and resistant to moisture and staining. Non-vitrified glass lacks this ceramic fusion, resulting in a more porous and less durable material prone to water absorption and surface wear. Understanding the differences in composition and firing methods is essential for selecting appropriate glassware for specific durability and usage needs.
Understanding the Vitrification Process
Vitrified glass undergoes a high-temperature firing process that transforms its composition into a dense, non-porous, and highly durable surface, enhancing resistance to chipping and moisture absorption. In contrast, non-vitrified glass retains a more porous and less durable structure due to the absence of this intense heat treatment. Understanding the vitrification process highlights its role in producing stronger, longer-lasting glassware suitable for both domestic and industrial applications.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Techniques
Vitrified glass undergoes a high-temperature firing process that fuses the glass particles into a dense, non-porous material, enhancing durability and resistance to water and chemicals. Non-vitrified glass is produced at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less durable structure prone to water absorption and staining. The key difference lies in the vitrification process, which significantly improves the strength and longevity of vitrified glass compared to non-vitrified glass.
Physical Properties Comparison
Vitrified glass exhibits superior durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to non-vitrified glass, making it less prone to chipping and cracking under high temperatures. Its dense, non-porous structure enables higher mechanical strength and improved chemical resistance, ideal for applications requiring enhanced longevity. Non-vitrified glass, with a more porous and fragile composition, tends to absorb liquids and deteriorate faster, limiting its use in heavy-duty or high-stress environments.
Durability and Strength: Vitrified vs. Non-Vitrified
Vitrified glass exhibits superior durability and strength due to its low porosity and fused composition, making it highly resistant to scratches, cracks, and chemical damage. Non-vitrified glass is comparatively porous, which results in lower resistance to wear and increased susceptibility to chipping and staining. The vitrification process enhances mechanical properties, ensuring longer-lasting glassware for heavy-use environments.
Water Absorption and Porosity Factors
Vitrified glass exhibits significantly lower water absorption and porosity levels compared to non-vitrified glass, enhancing its durability and resistance to staining. The vitrification process fuses glass particles at high temperatures, creating a dense, non-porous surface that inhibits moisture penetration. In contrast, non-vitrified glass has a more porous structure, allowing higher water absorption that can lead to structural weakening and increased susceptibility to damage over time.
Applications in Everyday Glassware
Vitrified glass is highly durable and resistant to thermal shock, making it ideal for everyday glassware such as mugs, plates, and bowls used in households and restaurants where frequent heating and cooling occur. Non-vitrified glass, being more porous and less resistant to chemical wear, is often found in decorative items or low-cost glassware with limited exposure to temperature changes. The choice between vitrified and non-vitrified glass significantly impacts the longevity and suitability of glassware in daily use environments.
Aesthetic and Design Variations
Vitrified glass offers a sleek, high-gloss finish with enhanced clarity, making it ideal for modern, minimalist designs that emphasize light and transparency. Non-vitrified glass typically exhibits a more opaque and textured surface, lending itself well to rustic or vintage-inspired aesthetics with a matte, handcrafted appeal. Design variations in vitrified glass include uniform surfaces and vibrant color consistency, while non-vitrified options provide unique patterns and organic imperfections valued in artisanal or decorative glassware.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Vitrified glass requires minimal maintenance due to its non-porous surface, resisting stains, scratches, and bacterial growth, which simplifies cleaning with just mild detergents. Non-vitrified glass is more porous and susceptible to absorbing dirt and stains, necessitating more frequent cleaning with specialized products and cautious handling to avoid damage. The durability and low upkeep of vitrified glass make it ideal for environments demanding hygiene and ease of maintenance.
Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Needs
Vitrified glass offers enhanced durability, resistance to thermal shock, and a smooth, non-porous surface ideal for frequent use and hot beverages. Non-vitrified glass, while often more affordable and visually appealing, tends to be more porous and less resistant to chipping, making it better suited for decorative or occasional use. Selecting the right glassware depends on balancing factors like longevity, purpose, and budget, with vitrified glass preferred for everyday practicality and non-vitrified for aesthetic versatility.
Vitrified Glass vs Non-Vitrified Glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com