Thick-walled glassware offers enhanced durability and thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and everyday use where breakage risk is a concern. Thin-walled glassware, on the other hand, provides a more delicate and elegant appearance with better heat transfer properties, often preferred for tasting or presentation purposes. Choosing between thick-walled and thin-walled glassware depends on the balance of strength, insulation, and aesthetic appeal needed for specific glassware pet uses.
Table of Comparison
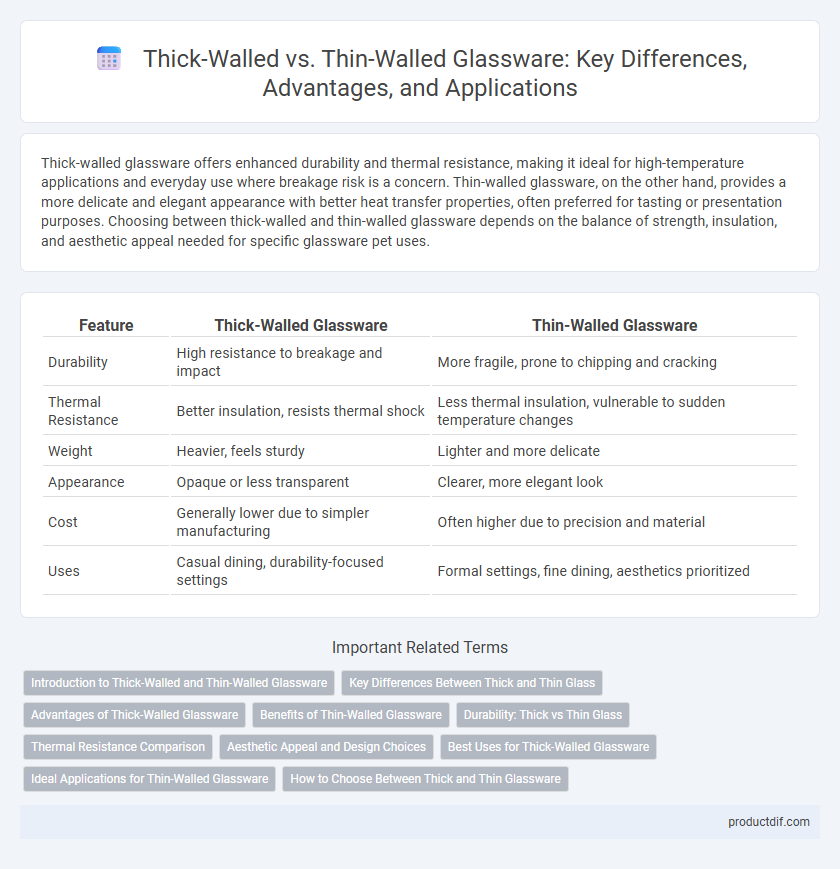
| Feature | Thick-Walled Glassware | Thin-Walled Glassware |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to breakage and impact | More fragile, prone to chipping and cracking |
| Thermal Resistance | Better insulation, resists thermal shock | Less thermal insulation, vulnerable to sudden temperature changes |
| Weight | Heavier, feels sturdy | Lighter and more delicate |
| Appearance | Opaque or less transparent | Clearer, more elegant look |
| Cost | Generally lower due to simpler manufacturing | Often higher due to precision and material |
| Uses | Casual dining, durability-focused settings | Formal settings, fine dining, aesthetics prioritized |
Introduction to Thick-Walled and Thin-Walled Glassware
Thick-walled glassware features robust construction that enhances durability and thermal resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty laboratory applications and high-temperature processes. Thin-walled glassware offers superior heat transfer efficiency and precision in measurements, preferred for delicate experiments requiring rapid temperature changes and minimal thermal inertia. Selecting between thick and thin walls depends on the specific requirements of chemical resistance, thermal shock tolerance, and mechanical strength needed in scientific or industrial settings.
Key Differences Between Thick and Thin Glass
Thick-walled glassware offers enhanced durability and thermal resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty use and temperature changes, while thin-walled glass provides a delicate appearance and superior clarity, enhancing the visual presentation of beverages. The thicker structure of thick-walled glass increases resistance to breakage but adds weight, whereas thin-walled glass is more fragile yet lightweight and elegant. Key differences also include manufacturing techniques, with thick glass typically molded for strength, and thin glass often blown for precision and finesse.
Advantages of Thick-Walled Glassware
Thick-walled glassware offers superior durability, reducing the risk of breakage in laboratory and industrial settings. Enhanced thermal resistance allows for better handling of temperature fluctuations without compromising structural integrity. The increased weight and robustness provide stability during precision measurements and chemical reactions.
Benefits of Thin-Walled Glassware
Thin-walled glassware offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced tactile experience, making it ideal for capturing the subtle aromas and flavors of fine beverages. Its lightweight construction improves ease of handling and reduces fatigue during prolonged use in professional and home settings. The delicate appearance of thin-walled glassware also elevates aesthetic appeal while maintaining adequate durability for everyday enjoyment.
Durability: Thick vs Thin Glass
Thick-walled glassware offers superior durability due to its increased resistance to impact and thermal stress, making it ideal for heavy use environments like restaurants and laboratories. Thin-walled glass, while aesthetically delicate and lightweight, is more prone to chipping and cracking under sudden temperature changes or physical shocks. Choosing thick glass enhances longevity and reduces replacement costs, especially in settings requiring frequent handling.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Thick-walled glassware offers superior thermal resistance due to its enhanced ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for high-heat applications. Thin-walled glassware, although less resistant to thermal shock, provides better heat transfer and quicker temperature equalization for delicate temperature-sensitive processes. Selecting between thick-walled and thin-walled glassware depends on the balance between durability under thermal stress and the need for efficient heat conduction.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Choices
Thick-walled glassware offers a robust, substantial feel that enhances the perception of quality and durability, making it a popular choice for modern and minimalist designs. Thin-walled glassware provides a delicate, refined appearance, highlighting transparency and elegance which suits upscale dining settings and intricate drink presentations. Design choices between thick and thin walls directly influence the tactile experience and visual impact, affecting both the aesthetic appeal and functional use of glassware.
Best Uses for Thick-Walled Glassware
Thick-walled glassware offers enhanced durability and thermal insulation, making it ideal for serving hot beverages like espresso or tea. Its robust construction reduces the risk of breakage and helps maintain temperature, providing a comfortable grip without heat transfer. This type of glassware is especially suited for frequent use in cafes and homes where longevity and heat retention are priorities.
Ideal Applications for Thin-Walled Glassware
Thin-walled glassware is ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control and rapid heat transfer, such as laboratory experiments and culinary uses like tasting glasses or fine wine glasses. Its delicate structure enhances the sensory experience by allowing wines and beverages to maintain their intended temperature and aroma. Thin-walled glass also suits environments needing minimal thermal insulation, promoting swift temperature equilibration and improved transparency for visual clarity.
How to Choose Between Thick and Thin Glassware
Choosing between thick-walled and thin-walled glassware depends on durability needs and aesthetic preferences. Thick-walled glassware offers enhanced strength and thermal insulation, making it ideal for casual use and hot beverages. Thin-walled glassware provides a delicate appearance and better tactile experience, preferred for formal settings and enhancing the flavor profile of drinks.
Thick-walled vs Thin-walled Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com